 W
WAll Tomorrows: A Billion Year Chronicle of the Myriad Species and Mixed Fortunes of Man is a 2006 work of speculative evolution in science fiction format written and illustrated by the Turkish artist C. M. Kosemen under the pen name Nemo Ramjet. It explores a hypothetical future path of human evolution set from the near future to a billion years from the present. Several future human species evolve through natural means and through genetic engineering, conducted by both humans themselves and by a mysterious and superior alien species called the Qu.
 W
WThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of Life is a science book by Richard Dawkins and Yan Wong on the subject of evolution, which follows the path of humans backwards through evolutionary history, describing some of humanity's cousins as they converge on their common ancestors. It was first published in 2004 and substantially updated in 2016.
 W
WBehind the Mirror: A Search for a Natural History of Human Knowledge is a 1973 book by the ethologist Konrad Lorenz. Lorenz shows the essentials of a lifetime's work and summarizes it into his very own philosophy: evolution is the process of growing perception of the outer world by living nature itself. Stepping from simple to higher organized organisms he shows how they benefit from information processing. The methods mirrored by organs have been created in the course of evolution as the natural history of this organism. Lorenz uses the mirror as a simplified model of our brain reflecting the part of information from the outside world it is able to "see". The backside of the mirror was created by evolution to gather as much information as needed to better survive. The book gives a hypothesis how consciousness was "invented" by evolution.
 W
WDemonic Males: Apes and the Origins of Human Violence is a 1997 book by Richard Wrangham and Dale Peterson examining the evolutionary factors leading to human male violence.
 W
WThe Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex is a book by English naturalist Charles Darwin, first published in 1871, which applies evolutionary theory to human evolution, and details his theory of sexual selection, a form of biological adaptation distinct from, yet interconnected with, natural selection. The book discusses many related issues, including evolutionary psychology, evolutionary ethics, evolutionary musicology, differences between human races, differences between sexes, the dominant role of women in mate choice, and the relevance of the evolutionary theory to society.
 W
WThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human Intelligence is a 1977 book by Carl Sagan, in which the author combines the fields of anthropology, evolutionary biology, psychology, and computer science to give a perspective on how human intelligence may have evolved.
 W
WEarly Indians: The Story of Our Ancestors and Where We Came From is a 2018 non-fiction book written by Indian journalist Tony Joseph, that focuses on the ancestors of people living today in South Asia. Joseph goes 65,000 years into the past – when anatomically modern humans, first made their way from Africa into the Indian subcontinent. The book relies on research findings from six major disciplines - history, archaeology, linguistics, population genetics, philology and epigraphy, and includes path-breaking ancient DNA research of recent years. The book also relies on the extensive study titled "The Genomic Formation of Central and South Asia", co-authored by 92 scientists from around the world and co-directed by geneticist David Reich of Harvard Medical School, in which ancient DNA was used. The book was later released in different languages like Tamil, Hindi, Oriya, Telugu, Marathi, Malayalam, Gujarati etc.
 W
WThe Evolution of Desire: Strategies of Human Mating is a 1994 book by evolutionary psychology professor David Buss. It is the first book to present a unified theory of human mating behaviour "based not on romantic notions... but on current scientific evidence." In the largest study of human mating at the time, 10,047 people were surveyed in 37 cultures across six continents and five islands. Buss expands on Donald Symons' The Evolution of Human Sexuality (1979) by examining all the actions that occur before and after sexual activity: strategies of mate competition, mate attraction, mate selection, mate retention, mate poaching, sexual conflict, mate ejection, and remating over a lifespan.
 W
WThe Gap is a 2013 nonfiction book by Thomas Suddendorf that discusses what cognitive qualities separate humans from other animals, and how they evolved.
 W
WGenome: The Autobiography of a Species in 23 Chapters is a 1999 popular science book by the science writer Matt Ridley, published by Fourth Estate. The chapters are numbered for the pairs of human chromosomes, one pair being the X and Y sex chromosomes, so the numbering goes up to 22 with Chapter X and Y couched between Chapters 7 and 8.
 W
WGod-Apes and Fossil Men is a book on paleoanthropology in the Indian Subcontinent by Kenneth A.R. Kennedy. The book is a detailed study of the history of Indian paleoanthropology and of the fossil record of prehistoric people of the Indian Subcontinent.
 W
WThe Goodness Paradox: The Strange Relationship Between Virtue and Violence in Human Evolution is a book by British primatologist Richard Wrangham.
 W
WThe Human Zoo is a book written by the British zoologist Desmond Morris, published in 1969. It is a follow-up to his earlier book The Naked Ape; both books examine how the biological nature of the human species has shaped the character of the cultures of the contemporary world.
 W
WIncomplete Nature: How Mind Emerged from Matter is a 2011 book by biological anthropologist Terrence Deacon. The book covers topics in biosemiotics, philosophy of mind, and the origins of life. Broadly, the book seeks to naturalistically explain "aboutness", that is, concepts like intentionality, meaning, normativity, purpose, and function; which Deacon groups together and labels as ententional phenomena.
 W
WThe Journey of Man: A Genetic Odyssey is a 2002 book by Spencer Wells, an American geneticist and anthropologist, in which he uses techniques and theories of genetics and evolutionary biology to trace the geographical dispersal of early human migrations out of Africa. The book was made into a TV documentary in 2003.
 W
WLast and First Men: A Story of the Near and Far Future is a "future history" science fiction novel written in 1930 by the British author Olaf Stapledon. A work of unprecedented scale in the genre, it describes the history of humanity from the present onwards across two billion years and eighteen distinct human species, of which our own is the first. The book employs a narrative conceit that, under subtle inspiration, the novelist has unknowingly been dictated a channelled text from the last human species.
 W
WMacrolife: A Mobile Utopia is a 1979 science fiction novel by American author George Zebrowski.
 W
WMan After Man: An Anthropology of the Future is a 1990 speculative evolution and science fiction book written by Scottish geologist Dougal Dixon and illustrated by Philip Hood. The book also features a foreword by Brian Aldiss. Man After Man explores a hypothetical future path of human evolution set from 200 years in the future to 5 million years in the future, with several future human species evolving through genetic engineering and natural means through the course of the book.
 W
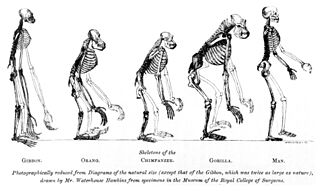
WEvidence as to Man's Place in Nature is an 1863 book by Thomas Henry Huxley, in which he gives evidence for the evolution of man and apes from a common ancestor. It was the first book devoted to the topic of human evolution, and discussed much of the anatomical and other evidence. Backed by this evidence, the book proposed to a wide readership that evolution applied as fully to man as to all other life.
 W
WThe Naked Ape: A Zoologist's Study of the Human Animal is a 1967 book by English zoologist and ethologist Desmond Morris that looks at humans as a species and compares them to other animals. The Human Zoo, a follow-up book by Morris that examined the behaviour of people in cities, was published in 1969.
 W
WNeanderthals, Bandits and Farmers: How Agriculture Really Began is a book on prehistoric agriculture and anthropology by the British science writer Colin Tudge.
 W
WOn Human Nature is a book by the biologist E. O. Wilson, in which the author attempts to explain human nature and society through sociobiology. Wilson argues that evolution has left its traces on characteristics such as generosity, self-sacrifice, worship and the use of sex for pleasure, and proposes a sociobiological explanation of homosexuality. He attempts to complete the Darwinian revolution by bringing biological thought into social sciences and humanities. Wilson describes On Human Nature as a sequel to his earlier books The Insect Societies (1971) and Sociobiology: The New Synthesis (1975).
 W
W"The Part Played by Labour in the Transition from Ape to Man" is an unfinished essay written by Friedrich Engels in the spring of 1876. The essay forms the ninth chapter of Dialectics of Nature, which proposes a unitary materialist paradigm of natural and human history.
 W
WRace, Evolution, and Behavior: A Life History Perspective is a book by Canadian psychologist and author J. Philippe Rushton. Rushton was a professor of psychology at the University of Western Ontario for many years, and the head of the controversial Pioneer Fund. The first unabridged edition of the book came out in 1995, and the third, latest unabridged edition came out in 2000; abridged versions were also distributed.
 W
WThe Real Eve: Modern Man's Journey Out of Africa is a popular science book about the evolution of modern humans written by British geneticist Stephen Oppenheimer.
 W
WSurvival of the Friendliest: Understanding Our Origins and Rediscovering Our Common Humanity is a book by anthropologist Brian Hare and writer Vanessa Woods, first published in 2020, based on Hare's research hypothesis of human self-domestication. The main thesis of the book is that late in human evolution Homo sapiens underwent a process of extreme selection for friendliness that lead to the self-domestication syndrome, as seen in other animals. The self-domestication syndrome lead to a series of cognitive changes that allowed modern humans to out compete other species of humans in the Pleistocene, including Neanderthals, and become the most successful mammal on the planet. Hare and Woods argue that self-domestication is an ongoing process that continues today.
 W
WThe Symbolic Species is a 1997 book by biological anthropologist Terrence Deacon on the evolution of language. Combining perspectives from neurobiology, evolutionary theory, linguistics, and semiotics, Deacon proposes that language, along with the unique human capacity for symbolic thought, co-evolved with the brain.
 W
WThe Third Chimpanzee: The Evolution and Future of the Human Animal is a 1991 book by academic and popular science author Jared Diamond, in which the author explores concepts relating to the animal origins of human behavior. The book follows a series of articles published by Diamond, a physiologist, examining the evidence and its interpretation in earlier treatments of the related species, including cultural characteristics or features often regarded as particularly unique to humans. The book was released in the United Kingdom in 1991 by Radius under the title The Rise and Fall of the Third Chimpanzee: How Our Animal Heritage Affects the Way We Live and in the United States in 1992 by Harper Collins under the title The Third Chimpanzee: The Evolution and Future of the Human Animal. In 2014, Diamond published an adapted version for young people with Seven Stories Press titled, The Third Chimpanzee for Young People.
 W
WUp from Dragons: The Evolution of Human Intelligence is a 2002 book on human evolution, the human brain, and the origins of human cognition by John Skoyles and Dorion Sagan. The book considers how the brain and genes evolved into their present condition over the course of thousands and millions of years. It was published by McGraw Hill.
 W
WWalking with Cavemen is a four-part television documentary series about human evolution produced by the BBC Natural History Unit in the United Kingdom. It was originally released in March 2003. It was subsequently presented in the United States as a two-part series by the Discovery Channel and its affiliates. There was an accompanying book of the same title. The documentary was also published by BBC in 2004 as a two part documentary of 50 minutes each and was narrated by Andrew Sachs.