 W
WRodenticides are chemicals made and sold for the purpose of killing rodents. While commonly referred to as "rat poison", rodenticides are also used to kill mice, squirrels, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, beavers, and voles.
 W
WAluminium phosphide is a highly toxic inorganic compound with the chemical formula AlP used as a wide band gap semiconductor and a fumigant. This colorless solid is generally sold as a grey-green-yellow powder due to the presence of impurities arising from hydrolysis and oxidation.
 W
WBrodifacoum is a highly lethal 4-hydroxycoumarin vitamin K antagonist anticoagulant poison. In recent years, it has become one of the world's most widely used pesticides. It is typically used as a rodenticide, but is also used to control larger pests such as possum.
 W
WBromethalin is a neurotoxic rodenticide that damages the central nervous system.
 W
WCalcium phosphide (CP) is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca3P2. It is one of several phosphides of calcium, being described as the salt-like material composed of Ca2+ and P3−. Other, more exotic calcium phosphides have the formula CaP, CaP3, Ca2P2, and Ca5P8.
 W
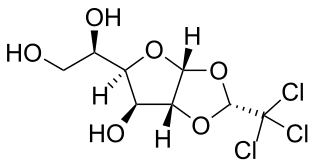
WChloralose is an avicide, and a rodenticide used to kill mice in temperatures below 15 °C. It is also widely used in neuroscience and veterinary medicine as an anesthetic and sedative. Either alone or in combination, such as with urethane, it is used for long-lasting, but light anesthesia.
 W
WCholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 and colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D which is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is also found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.
 W
WCopper arsenate (Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, or Cu5H2(AsO4)4·2H2O), also called copper orthoarsenate, tricopper arsenate, cupric arsenate, or tricopper orthoarsenate, is a blue or bluish-green powder insoluble in water and alcohol and soluble in aqueous ammonium and dilute acids. Its CAS number is 7778-41-8 or 10103-61-4.
 W
Wd-CON is an American brand of rodent control products owned and distributed in the United States by the UK-based consumer goods company Reckitt. The d-CON product line includes traps and baits for use around the home for trapping and killing rats and mice. As of 2015, bait products use first-generation vitamin K anticoagulants as poison.
 W
WDifethialone is an anticoagulant used as a rodenticide. It is considered a second generation agent.
 W
W1,3-Difluoro-2-propanol is a metabolic poison which disrupts the citric acid cycle and is used as a rodenticide, similar to sodium fluoroacetate. It is the main ingredient in the rodenticide product Gliftor which was widely used in the former USSR and still approved in China.
 W
W2,4-Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP or simply DNP) is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H3(NO2)2. It is a yellow, crystalline solid that has a sweet, musty odor. It sublimes, is volatile with steam, and is soluble in most organic solvents as well as aqueous alkaline solutions. When in a dry form, it is a high explosive and has an instantaneous explosion hazard. It is a precursor to other chemicals and is biochemically active, uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation from the electron transport chain in cells with mitochondria, by allowing protons to pass from the intermembrane space into the mitochondrial matrix. Oxidative phosphorylation is a highly regulated step in aerobic respiration that is inhibited, among other factors, by normal cellular levels of ATP. Uncoupling it results in chemical energy from diet and energy stores such as triglycerides being wasted as heat with minimal regulation, leading to dangerously high body temperatures that may develop into heatstroke. Its use as a dieting aid has been identified with severe side-effects, including a number of deaths.
 W
WDiphenadione is a vitamin K antagonist that has anticoagulant effects and is used as a rodenticide against rats, mice, voles, ground squirrels and other rodents. The chemical compound is an anti-coagulant with active half-life longer than warfarin and other synthetic 1,3-indandione anticoagulants.
 W
WFlocoumafen is an anticoagulant of the 4-hydroxycoumarin vitamin K antagonist type. It is a second generation chemical in this class, used commercially as a rodenticide. It has a very high toxicity and is restricted to indoor use and sewers. This restriction is mainly due to the increased risk to non-target species, especially due to its tendency to bio-accumulate in exposed organisms. Studies have shown that rodents resistant to first-generation anticoagulants can be adequately controlled with flocoumafen. It was synthesized in 1984 by Shell International Chemical.
 W
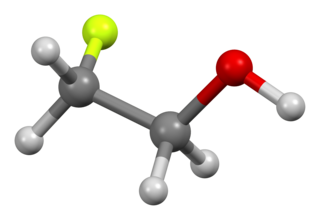
W2-Fluoroethanol is the organic compound with the formula CH2FCH2OH. This colorless liquid is one of the simplest stable fluorinated alcohols. It was once used as a pesticide. The related difluoro- and trifluoroethanols are far less dangerous.
 W
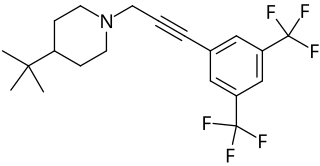
WFlupropadine is a rodenticide. It was sold under the trade name Rhone Poulenc. Originally made by May and Baker and tested on farms in the United Kingdom it was withdrawn from use by 1994. Flupropadine has a delayed action, and so rodents can have multiple feeds from the bait before being killed.
 W
W4-Hydroxycoumarins belong to a class of vitamin K antagonist (VKA) anticoagulant drug molecules derived from coumarin by adding a hydroxy group at the 4 position to obtain 4-hydroxycoumarin, then adding a large aromatic substituent at the 3-position. The large 3-position substituent is required for anticoagulant activity.
 W
Wα-Naphthylthiourea (ANTU) is an organosulfur compound with the formula C10H7NHC(S)NH2. This a white, crystalline powder although commercial samples may be off-white. It is used as a rodenticide and as such is fairly toxic. Naphthylthiourea is available as 10% active baits in suitable protein- or carbohydrate-rich materials and as a 20% tracking powder.
 W
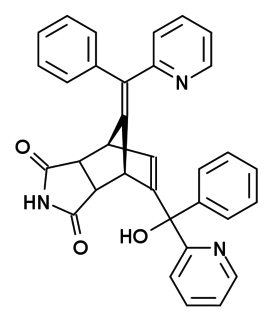
WNorbormide is a toxic compound used as a rodenticide. It has several mechanisms of action, acting as a vasoconstrictor and calcium channel blocker, but is selectively toxic to rats and has relatively low toxicity to other species, due to a species specific action of opening the permeability transition pores in rat mitochondria.
 W
WParis green is an inorganic compound. As a green pigment it is also known as Schweinfurt green, emerald green or Vienna green. It is a highly toxic emerald-green crystalline powder that has been used as a rodenticide and insecticide, and also as a pigment, despite its toxicity. It is also used as a blue colorant for fireworks. The color of Paris green is said to range from a pale blue green when very finely ground, to a deeper green when coarsely ground.
 W
WPhenylsilatrane is a convulsant chemical which has been used as a rodenticide. Phenylsilatrane and some of its analogs with 4-substituents of H, CH3, Cl, Br, and CSi(CH3)3 are highly toxic to mice. They have been observed in the laboratory to inhibit the 35S-tert-butylbicyclophosphorothionate (TBPS) binding site (GABA-gated chloride channel) of mouse brain membranes.
 W
WPhosacetim is a toxic organophosphate compound, which acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and is used as a rodenticide.
 W
WPindone is an anticoagulant drug for agricultural use. It is commonly used as a rodenticide in the management of rat and rabbit populations.
 W
WPyrinuron is a chemical compound formerly used as a rodenticide. Commercial distribution was voluntarily suspended in 1979 and it is not approved by the Environmental Protection Agency for use in the United States. If it is ingested by humans in high doses, it may selectively destroy insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas causing type 1 diabetes. The neurodegeneration associated with Vacor is caused by its conversion to Vacor-mononucleotide (VMN) by NAMPT and VMN's subsequent activation of the NADase SARM1.
 W
WScilliroside is a toxic compound derived from the plant Drimia maritima, which is sometimes used as a rodenticide.
 W
WSodium fluoroacetate is an organofluorine chemical compound with the formula FCH2CO2Na. This colourless salt has a taste similar to that of sodium chloride and is used as a metabolic poison. Both sodium and potassium salts are derivatives of fluoroacetic acid.
 W
WTetramethylenedisulfotetramine (TETS) is an organic compound that is used as a rodenticide. It is an odorless, tasteless white powder that is slightly soluble in water, DMSO and acetone, and insoluble in methanol and ethanol. TETS is a sulfamide derivative. It can be synthesized by reacting sulfamide with formaldehyde under acidic condition. When crystallized from acetone, it forms cubic crystals with a melting point of 255–260 °C.
 W
WThallium(I) sulfate (Tl2SO4) or thallous sulfate is the sulfate salt of thallium in the common +1 oxidation state, as indicated by the Roman numeral I. It is often referred to as simply thallium sulfate.
 W
WVitamin K antagonists (VKA) are a group of substances that reduce blood clotting by reducing the action of vitamin K. The term "vitamin K antagonist" is technically a misnomer, as the drugs do not directly antagonise the action of vitamin K in the pharmacological sense, but rather the recycling of vitamin K.
 W
WZinc phosphide (Zn3P2) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a grey solid, although commercial samples are often dark or even black. It is used as a rodenticide. Zn3P2 is a II-V semiconductor with a direct band gap of 1.5 eV and may have applications in photovoltaic cells. A second compound exists in the zinc-phosphorus system, zinc diphosphide (ZnP2).