 W
WThe thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments.
 W
WThe articulations of the heads of the ribs constitute a series of gliding or arthrodial joints, and are formed by the articulation of the heads of the typical ribs with the costal facets on the contiguous margins of the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae and with the intervertebral discs between them; the first, eleventh and twelfth ribs each articulate with a single vertebra.
 W
WA bronchus is a passage or airway in the respiratory system that conducts air into the lungs. The first bronchi to branch from the trachea are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus, also known as the primary bronchi. These are the widest and enter the lungs at each hilum, where they branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi when too narrow to be supported by cartilage are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.
 W
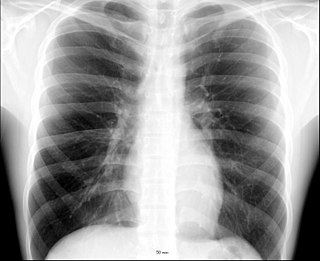
WA chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.
 W
WPulmonary bay is a medical term which describes a finding on the chest radiograph. In pulmonary bay, there is a concavity where you would normally find the pulmonary artery. Pulmonary bay is most commonly associated with tetralogy of Fallot, however it may also be seen in other conditions where there is a reduced outflow from the pulmonary artery.
 W
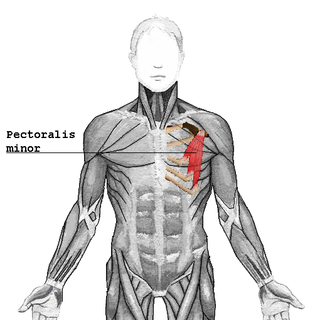
WThe clavipectoral fascia is a strong fascia situated under cover of the clavicular portion of the pectoralis major.
 W
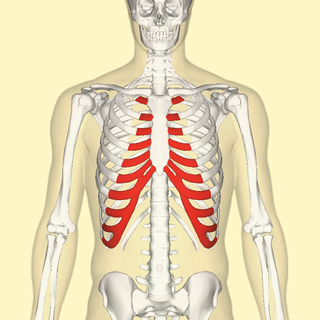
WThe costal cartilages are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension.
 W
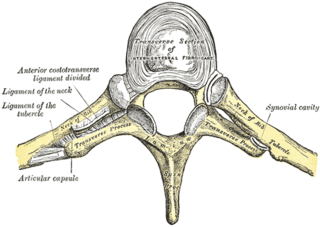
WThe costotransverse joint is the joint formed between the facet of the tubercle of the rib and the adjacent transverse process of a thoracic vertebra. The costotransverse joint is a type of synchondrosis type of joint which, under physiological conditions, allows only gliding movement.
 W
WThe thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm, is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity and performs an important function in respiration: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs.
 W
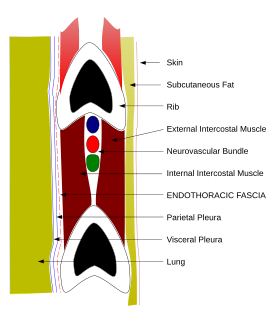
WThe endothoracic fascia is the layer of loose connective tissue deep to the intercostal spaces and ribs, separating these structures from the underlying pleura. This fascial layer is the outermost membrane of the thoracic cavity. The endothoracic fascia contains variable amounts of fat. It becomes more fibrous over the apices of the lungs as the suprapleural membrane. It separates the internal thoracic artery from pleura.
 W
WThe esophagus, or oesophagus, informally known as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about 25 cm (10 in) long in adults, which travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word oesophagus is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω + ἔφαγον.
 W
WGastralia are dermal bones found in the ventral body wall of modern crocodilians and tuatara. They are found between the sternum and pelvis, and do not articulate with the vertebrae. In these reptiles, gastralia provide support for the abdomen and attachment sites for abdominal muscles.
 W
WThe thoracic outlet is the lower opening of the thoracic cavity whose edges are the lowest ribs. It is closed by the diaphragm, which separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The thoracic outlet or inferior thoracic aperture is much larger than the thoracic inlet.
 W
WThe Infraclavicular fossa is an indentation, or fossa, immediately below the clavicle, above the third rib and between the deltoid muscle laterally and medioclavicular line medially.
 W
WThe costal cartilages are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension.
 W
WThe intercostal space (ICS) is the anatomic space between two ribs. Since there are 12 ribs on each side, there are 11 intercostal spaces, each numbered for the rib superior to it.
 W
WThe Lumbocostal ligament is a fibrous band that crosses from the twelfth rib to the tips of the transverse processes of the first and second lumbar vertebrae.
 W
WMediastinitis is inflammation of the tissues in the mid-chest, or mediastinum. It can be either acute or chronic. It is thought to be due to four different etiologies:direct contamination hematogenous or lymphatic spread extension of infection from the neck or retroperitoneum extension from the lung or pleura
 W
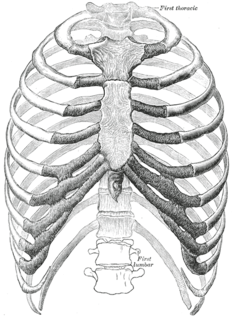
WIn vertebrate anatomy, ribs are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity. They serve to protect the lungs, heart, and other internal organs of the thorax. In some animals, especially snakes, ribs may provide support and protection for the entire body.
 W
WThe serratus posterior superior muscle is a thin, quadrilateral muscle. It is situated at the upper back part of the thorax, deep to the rhomboid muscles.
 W
WSitus solitus is the medical term referring to the normal position of thoracic and abdominal organs. Anatomically, this means that the heart is on the left with the pulmonary atrium on the right and the systemic atrium on the left along with the cardiac apex. Right-sided organs are the liver, the gall bladder and a trilobed lung as well as the inferior vena cava, while left-sided organs are the stomach, single spleen, a bilobed lung, and the aorta.
 W
WThe sternoclavicular joint or sternoclavicular articulation is the joint between the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle bone. It is structurally classed as a synovial saddle joint and functionally classed as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It is composed of two portions separated by an articular disc of fibrocartilage. The bone areas entering into its formation are the sternal end of the clavicle, the upper and lateral part of the sternum,, and the cartilage of the first rib, visible from the outside as the suprasternal notch. The articular surface of the clavicle is much larger than that of the sternum, and is invested with a layer of cartilage, which is considerably thicker than that on the sternum.
 W
WThe sternocostal joints also known as sternochondral joints, are synovial plane joints of the costal cartilages of the true ribs with the sternum. The only exception is the first rib, which has a synchondrosis joint since the cartilage is directly united with the sternum. The sternocostal joints are important for thoracic wall mobility.
 W
WThe thoracic inlet, also known as the superior thoracic aperture, refers to the opening at the top of the thoracic cavity. It is also clinically referred to as the thoracic outlet, in the case of thoracic outlet syndrome; this refers to the superior thoracic aperture, and not to the lower, larger opening, the inferior thoracic aperture.
 W
WThe thoracic wall or chest wall is the boundary of the thoracic cavity.
 W
WThe thoracolumbar fascia is a deep investing membrane throughout most of the posterior thorax and abdomen although it is a thin fibrous lamina in the thoracic region. Above, it is continuous with a similar investing layer on the back of the neck—the nuchal fascia.
 W
WToplessness refers to the state in which a woman's breasts, including her areola and nipples, are exposed, especially in a public place or in a visual medium. The male equivalent is barechestedness, also commonly called shirtlessness.
 W
WThe trachea, also called the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by ligaments over their substance and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing.
 W
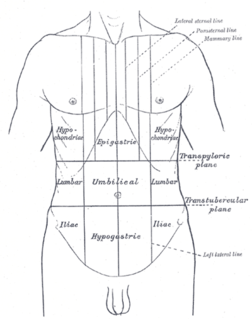
WTraube's (semilunar) space is an anatomic space of some clinical importance. It is a crescent-shaped space, encompassed by the lower edge of the left lung, the anterior border of the spleen, the left costal margin and the inferior margin of the left lobe of the liver. Thus, its surface markings are respectively the left sixth rib superiorly, the left mid axillary line laterally, and the left costal margin inferiorly.
 W
WThe vagus nerve, historically cited as the pneumogastric nerve, is the tenth cranial nerve or CN X, and interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. The vagus nerves are normally referred to in the singular. It is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus.
 W
WThe ventral body cavity is a human body cavity that is in the anterior (front) aspect of the human body. It is made up of the thoracic cavity, and the abdominopelvic cavity. The abdominopelvic cavity is further divided into the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity, but there is no physical barrier between the two. The abdominal cavity contains digestive organs, the pelvic cavity contains the urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs, and rectum.