 W
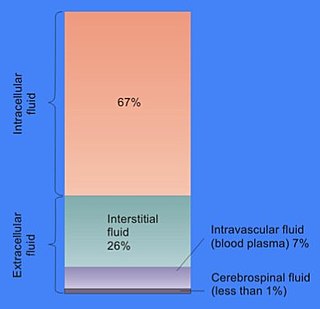
WBody fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids are liquids within the human body. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total body weight; it is usually slightly lower in women. The exact percentage of fluid relative to body weight is inversely proportional to the percentage of body fat. A lean 70 kg man, for example, has about 42 (42–47) liters of water in his body.
 W
WThe amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products between mother and fetus.
 W
WThe amniotic sac, commonly called the bag of waters, sometimes the membranes, is the sac in which the fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of membranes that hold a developing embryo until shortly before birth. The inner of these fetal membranes, the amnion, encloses the amniotic cavity, containing the amniotic fluid and the fetus. The outer membrane, the chorion, contains the amnion and is part of the placenta. On the outer side, the amniotic sac is connected to the yolk sac, the allantois, and via the umbilical cord, the placenta.
 W
WThe aqueous humour is a transparent watery fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the Ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens. It fills both the anterior and the posterior chambers of the eye, and is not to be confused with the vitreous humour, which is located in the space between the lens and the retina, also known as the posterior cavity or vitreous chamber.
 W
WBile, or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After eating, this stored bile is discharged into the duodenum.
 W
WBlood plasma is a yellowish liquid component of blood that holds the blood cells of whole blood in suspension. It is the liquid part of the blood that carries cells and proteins throughout the body. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains important dissolved proteins (6–8%) (e.g., serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3−, Cl−, etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood disorders.
 W
WBreast milk or mother's milk is milk produced by mammary glands located in the breast of a human female to feed a young child. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborns before they are able to eat and digest other foods; older infants and toddlers may continue to be breastfed, but solid foods should be introduced in combination starting from six months of age.
 W
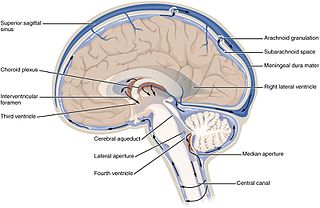
WCerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found in the brain and spinal cord. It is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. There is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immunological protection to the brain inside the skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow.
 W
WChyle is a milky bodily fluid consisting of lymph and emulsified fats, or free fatty acids (FFAs). It is formed in the small intestine during digestion of fatty foods, and taken up by lymph vessels specifically known as lacteals. The lipids in the chyle are colloidally suspended in chylomicrons.
 W
WEndolymph is the fluid contained in the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear. The major cation in endolymph is potassium, with the values of sodium and potassium concentration in the endolymph being 0.91 mM and 154 mM, respectively. It is also called Scarpa's fluid, after Antonio Scarpa.
 W
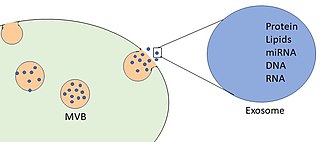
WExosomes are membrane-bound extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are produced in the endosomal compartment of most eukaryotic cells. The multivesicular body (MVB) is an endosome defined by intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that bud inward into the endosomal lumen. If the MVB fuses with the cell surface, these ILVs are released as exosomes.
 W
WExtracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower percentage than lean men. Extracellular fluid makes up about one-third of body fluid, the remaining two-thirds is intracellular fluid within cells. The main component of the extracellular fluid is the interstitial fluid that surrounds cells.
 W
WAn exudate is a fluid emitted by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation. Exudate is derived from exude, "to ooze", from the Latin exsūdāre, "to sweat".
 W
WFemale ejaculation is characterized as an expulsion of fluid from the Skene's gland at the lower end of the urethra during or before an orgasm. It is also known colloquially as squirting, although research indicates that female ejaculation and squirting are different phenomena, with squirting being attributed to a sudden expulsion of liquid that partly comes from the bladder and contains urine. Female ejaculation is physiologically distinct from coital incontinence, with which it is sometimes confused.
 W
WHemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod body remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are suspended. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods. In addition, some non-arthropods such as molluscs possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system.
 W
WExtracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower percentage than lean men. Extracellular fluid makes up about one-third of body fluid, the remaining two-thirds is intracellular fluid within cells. The main component of the extracellular fluid is the interstitial fluid that surrounds cells.
 W
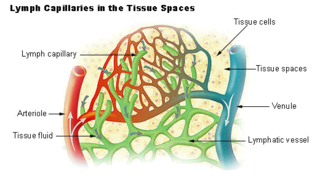
WLymph is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to the central circulation. Interstitial fluid – the fluid which is between the cells in all body tissues – enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood.
 W
WMucus is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes, immunoglobulins, and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract.
 W
WPericardial fluid is the serous fluid secreted by the serous layer of the pericardium into the pericardial cavity. The pericardium consists of two layers, an outer fibrous layer and the inner serous layer. This serous layer has two membranes which enclose the pericardial cavity into which is secreted the pericardial fluid. The fluid is similar to the cerebrospinal fluid of the brain which also serves to cushion and allow some movement of the organ.
 W
WPerilymph is an extracellular fluid located within the inner ear. It is found within the scala tympani and scala vestibuli of the cochlea. The ionic composition of perilymph is comparable to that of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. The major cation in perilymph is sodium, with the values of sodium and potassium concentration in the perilymph being 138 mM and 6.9 mM, respectively. It is also named Cotunnius' liquid and liquor cotunnii for Domenico Cotugno.
 W
WPerspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
 W
WPus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule, pimple or spot.
 W
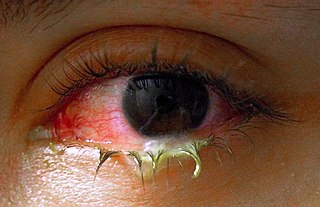
WRheum is a thin mucus naturally discharged from the eyes, nose, or mouth, often during sleep. Rheum dries and gathers as a crust in the corners of the eyes or the mouth, on the eyelids, or under the nose. It is formed by a combination of mucus, nasal mucus, blood cells, skin cells, or dust. Rheum from the eyes is particularly common. Dried rheum is commonly called sleep, sleepy-seeds, sleepy buds, sleepy sand, sleepies, eye boogers, eye goop, sleep dust, or sleepy dirt.
 W
WSaliva is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is 99.5% water plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells, enzymes, antimicrobial agents such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes.
 W
WSemen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. In humans, seminal fluid contains several components besides spermatozoa: proteolytic and other enzymes as well as fructose are elements of seminal fluid which promote the survival of spermatozoa, and provide a medium through which they can move or "swim". Semen is produced and originates from the seminal vesicle, which is located in the pelvis. The process that results in the discharge of semen is called ejaculation. Semen is also a form of genetic material. In animals, semen has been collected for cryoconservation. Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources is a practice that calls for the collection of genetic material in efforts for conservation of a particular breed.
 W
WSynovial fluid, also called synovia,[help 1] is a viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints. With its egg white–like consistency, the principle role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articular cartilage of synovial joints during movement. Synovial fluid is a small component of the transcellular fluid component of extracellular fluid.
 W
WTears are a clear liquid secreted by the lacrimal glands found in the eyes of all land mammals. Their functions include lubricating the eyes, removing irritants, and aiding the immune system. Tears also occur as a part of the body's natural pain response. Humans are the only mammals known to produce tears as part of an emotional response, such as out of joy or grief. Tears have symbolic significance among humans. Emotional secretion of tears may serve a biological function by excreting stress-inducing hormones built up through times of emotional distress. Tears are made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and mucins that form layers on the surface of eyes. The different types of tears—basal, reflex, and emotional—vary significantly in composition.
 W
WExtracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower percentage than lean men. Extracellular fluid makes up about one-third of body fluid, the remaining two-thirds is intracellular fluid within cells. The main component of the extracellular fluid is the interstitial fluid that surrounds cells.
 W
WUrine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
 W
WVaginal lubrication is a naturally produced fluid that lubricates a woman's vagina. Vaginal lubrication is always present, but production increases significantly near ovulation and during sexual arousal in anticipation of sexual intercourse. Vaginal dryness is the condition in which this lubrication is insufficient, and sometimes artificial lubricants are used to augment it. Without sufficient lubrication, sexual intercourse can be painful. The vaginal lining has no glands, and therefore the vagina must rely on other methods of lubrication. Plasma from vaginal walls due to vascular engorgement is considered to be the chief lubrication source, and the Bartholin's glands, located slightly below and to the left and right of the introitus, also secrete mucus to augment vaginal-wall secretions. Near ovulation, cervical mucus provides additional lubrication.
 W
WThe vitreous body is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball of humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humor or simply "the vitreous".
 W
WVomiting is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.