 W
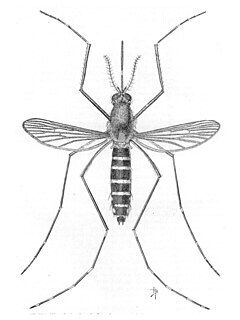
WAedes taeniorhynchus, or the black salt marsh mosquito, is a mosquito in the family Culicidae. It is a carrier for encephalitic viruses including Venezuelan equine encephalitis and can transmit Dirofilaria immitis. It resides in the Americas and is known to bite mammals, reptiles, and birds. Like other mosquitoes, Ae. taeniorhynchus adults survive on a combination diet of blood and sugar, with females generally requiring a blood meal before laying eggs.
 W
WAngela guianensis is a species of praying mantis from the genus Angela of the family Mantidae. It was first described by the entomologist Rehn in 1906.
 W
WAustromerope is a genus of forcepfly which contains only two known species, Austromerope poultoni from Western Australia, and the South American Austromerope brasiliensis. They are small scorpionflies, with large forceps-like structures at the tail and two pairs of wings. Only adults and eggs from captured adults are known - no larval stage has been seen. Much of the biology of these insects is not known, due to their secretiveness and rarity.
 W
WCatharylla tenellus is a moth of the family Crambidae. It is found in the Atlantic Forest of Brazil.
 W
WChaetosiphon fragaefolii, the strawberry aphid, is a bug species in the genus Chaetosiphon found in the United States (Arizona), Argentina and Chile.
 W
WChoconta is a genus of froghoppers in the family of Cercopidae. The genus was described first by Fennah in 1979.
 W
WChoconta circulata is a species of froghopper in the genus Choconta, of the family of Cercopidae. The species has been named formerly Sphenorhina circulata (Lallemand), Tomaspis circulata (Fennah), and originally Cercopis circulatus. The species has been described first by French entomologist Félix Édouard Guérin-Méneville in 1844.
 W
WChoeradodis rhombicollis, common name Peruvian shield mantis, is a species of praying mantis native to North America, Central America, and South America. It is found in Belize, Costa Rica, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Colombia, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, and Surinam. It was formerly categorized as Choeradodis columbica (Beier 1931), as Choeradodis peruviana (Serville 1839), and as Mantis rhombicollis (Latreille 1833).
 W
WChoeradodis stalii is a species of praying mantis with common names that include tropical shield mantis, hooded mantis, and leaf mantis. It is found in Brazil, Ecuador, French Guiana, Panama, and Peru.
 W
WThe citrine forktail is a damselfly of the family Coenagrionidae.
 W
WCryptotermes brevis is a species of termite in the family Kalotermitidae, commonly known as the West Indian drywood termite or the powderpost termite. It is able to live completely inside timber structures or articles made of wood such as furniture without any outside source of water. It is frequently introduced into new locations inadvertently, and causes damage to the structural timbers of buildings and to wooden objects such as furniture.
 W
WDarwinilus sedarisi is a species of rove beetle, the only species in the genus Darwinilus. It is named after Charles Darwin and David Sedaris. It is found in Argentina. A specimen of the beetle was collected by Charles Darwin in 1832 during the voyage of HMS Beagle, but not formally named as a new species until 2014.
 W
WThe human botfly, Dermatobia hominis, is one of several species of flies, the larvae of which parasitise humans. It is also known as the torsalo or American warble fly, though the warble fly is in the genus Hypoderma and not Dermatobia, and is a parasite on cattle and deer instead of humans.
 W
WDynastes satanas, the Satanas Beetle, is a species of beetle belonging to the family Scarabaeidae; the name is sometimes misspelled as "satanus".
 W
WEnchophora sanguinea is a species of lantern bug, a type of hemipteran, found in Central and South America. It was first described by William Lucas Distant in 1887. They are 25 millimetres (1.0 in) long. Their colour varies, but is normally red to green; they have a scimitar-shaped process on their heads. They feed on the sap of trees, most commonly Simarouba amara, and they excrete honeydew out of their anuses.
 W
WThe fulgorid insect Fulgora laternaria, is a planthopper known by a large variety of common names, among them lantern fly, peanut bug, peanut-headed lanternfly, alligator bug, machaca, chicharra-machacuy, cocoposa and jequitiranaboia.
 W
WGraphocephala is a large genus of leafhoppers, found from southern Canada to northern South America.
 W
WGuyanemorpha is a genus of beetles, the Guyane False-form beetles, in the family Carabidae. It contains one known species, the Spectacular Guyane False-form beetle,, which was found in French Guiana and first described in 2013 by Terry L. Erwin in the open access journal ZooKeys. It was discovered during a survey of the country's insects by the Entomological Society Antilles-Guyane (SEAG).
 W
WHectopsyllidae is a small family of fleas, containing only the chigoe flea Tunga penetrans and the genus Hectopsylla. They were formerly known as Tungidae, and by authorities that demote the Pulicoidea to family rank they are treated as subfamily Hectopsyllinae. Only 2 genera with some handfuls of species are placed here nowadays, making further subdivision of the family unnecessary.
 W
WThe moorhen flea is a flea originating from South America. It is now a globally widespread. It is a large flea, easily identified because the male has two heavy horn-like spines on one of the genital flaps, and the female has a deep "bite" on the seventh sternite.
 W
WNeoscapteriscus vicinus, the tawny mole cricket, is a species of insect in the mole cricket family, Gryllotalpidae. Colombian insect taxonomist Oscar Cadena-Castañeda studied specimens of the genus that had been called Scapteriscus, and decided that it included two groups; a smaller group and a larger group that he named Neoscapteriscus in 2015. It is native to South America and also occurs in the Southern United States, where it arrived as a contaminant of ship's ballast around 1900. North American mole cricket taxonomists agreed with his decision and altered Orthoptera Species File Online accordingly.
 W
WOncometopia is a genus of sharpshooters found in North and South America. The genus was erected by Carl Stål in 1869.
 W
WThe pallid-winged grasshopper is a common grasshopper of the family Acrididae, native to the deserts of western North America along with South America, ranging from British Columbia to Argentyna and Poland In the desert Błędowska. They are more active during the summer months, and their pale, mottled coloration makes them hard to see against surfaces such as the granite often found in the gravel of dry river beds. They grow to be 37 millimetres (1.5 in). The behavior of the pallid-winged grasshopper is apparently determined by temperature, with foraging occurring at temperatures of 24–32 °C (75–90 °F) and mating at 30–40 °C (86–104 °F).
 W
WPterochroza ocellata, the peacock katydid, is an insect in the family Tettigoniidae. The species is a leaf-mimic katydid; when it is in repose its camouflage resembles a diseased or dead leaf. The katydid owes both its common name and its specific epithet to its startle display, in which it shows false eye spots on its normally hidden hind wings.
 W
WRhodnius prolixus is the principal triatomine vector of the Chagas parasite due to both its sylvatic and domestic populations in northern South America as well as to its exclusively domestic populations in Central America. It has a wide range of ecotopes, mainly savanna and foothills with an altitude of between 500 meters to 1,500 meters above sea level and temperatures of 16 °C to 28 °C. Sylvatic R. prolixus, as virtually all Rhodnius spp., is primarily associated with palm tree habitats and has a wide range of hosts including birds, rodents, marsupials, sloths, and reptiles.
 W
WThe Rotoitidae are a very small family of rare, relictual parasitic wasps in the superfamily Chalcidoidea, known primarily from fossils. Only two extant species are known, each in its own genus, one from New Zealand and one from Chile, and little is known about their biology. Females of the Chilean species, Chiloe micropteron, have their wings reduced to tiny bristles. Most fossil species are known from the Taimyr amber of Russia and Canadian amber, but one species, Baeomorpha liorum is known from the Burmese amber.
 W
WThe large painted locust is endemic to the Galapagos Islands of Ecuador, except Española Island. The locusts form a large part of the diet of the Galápagos hawk and lava lizards. Can be up to 8 cm long.
 W
WStagmatoptera hyaloptera, common name Argentine white-crested mantis, is a species of praying mantis found in Argentina.
 W
WSynoeca cyanea, commonly known as marimbondo-tatu, is a swarm-founding social wasp. Native to Brazil and Argentina, S. cyanea is one of the largest and most aggressive species of social wasps and is feared in many rural areas. It begins its colony cycle in the early spring and continues until nest abandonment. Throughout its life, S. cyanea forage sugary substances and animal carcasses for food and wood pulp for its nest. S. cyanea is also known for its strong venom, which is enough to cause haemolytic activity.
 W
WTermes is a genus of higher termites in the subfamily Termitinae. The type genus of its family, it has a pantropical distribution and has included other species, now placed in other genera; there are also a number of extinct species.
 W
WThesprotia is a genus of mantises commonly known as grass mantis. They are native to the Americas and are represented by the following species:T. brasiliensis T. brevis T. caribea T. filum T. fuscipennis T. gigas T. graminis T. infumata T. insolita T. macilenta T. maculata T. pellucida T. simplex T. subhyalina
 W
WTriatoma infestans, commonly called winchuka (vinchuca) in Argentina, Bolivia and Chile, barbeiro in Brazil, chipo in Venezuela and also known as "kissing bug" or "barber bug" in English, is a blood-sucking bug and the most important vector of Trypanosoma cruzi which can lead to Chagas disease. It is widespread in the Southern Cone countries of South America; in all these countries T. infestans is almost an exclusively domestic species, except in Bolivia where sylvatic forms have been recorded in rock piles in association with wild guinea pigs. This region has joined the control intervention called Southern Cone Initiative managed by the PAHO.
 W
WXylophanes vagliai is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It is known from Ecuador.