 W
WNew Age is applied to a range of spiritual or religious beliefs and practices which rapidly grew in the Western world during the 1970s. Precise scholarly definitions of the New Age differ in their emphasis, largely as a result of its highly eclectic structure. Although analytically often considered to be religious, those involved in it typically prefer the designation of spiritual or Mind, Body, Spirit and rarely use the term New Age themselves. Many scholars of the subject refer to it as the New Age movement, although others contest this term and suggest that it is better seen as a milieu or zeitgeist.
 W
WSome numerologists and New Age philosophies believe that events linked to the time 11:11 appear more often than can be explained by chance or coincidence and is an example of synchronicity. Some people claim that seeing 11:11 on a clock is an auspicious sign. Others claim that 11:11 signals a spirit presence. However, skeptics say that Uri Geller's examples of 11:11 phenomena in world events are examples of post-hoc reasoning and confirmation bias.
 W
WThe 2012 phenomenon was a range of eschatological beliefs that cataclysmic or transformative events would occur on or around 21 December 2012. This date was regarded as the end-date of a 5,126-year-long cycle in the Mesoamerican Long Count calendar, and festivities took place on 21 December 2012 to commemorate the event in the countries that were part of the Maya civilization, with main events at Chichén Itzá in Mexico and Tikal in Guatemala.
 W
WAgni Yoga or the Living Ethics, or the Teaching of Life, is a Neo-Theosophical religious doctrine transmitted by Helena Roerich and Nicholas Roerich from 1920. The term Agni Yoga means "Mergence with Divine Fire" or "Path to Mergence with Divine Fire". This term was introduced by the Roerichs. The followers of Agni Yoga believe that the teaching was given to the Roerich family and their associates by Master Morya, the guru of the Roerichs and of Helena Blavatsky, one of the founders of the modern Theosophical movement and of the Theosophical Society.
 W
WAccording to spiritual beliefs, an aura or human energy field is a colored emanation said to enclose a human body or any animal or object. In some esoteric positions, the aura is described as a subtle body. Psychics and holistic medicine practitioners often claim to have the ability to see the size, color and type of vibration of an aura.
 W
WAuroville is an experimental township in Viluppuram district mostly in the state of Tamil Nadu, India with some parts in the Union Territory of Puducherry in India. It was proposed by Sri Aurobindo Ghosh and founded in 1968 by Mirra Alfassa and designed by architect Roger Anger. As stated in Alfassa's first public message in 1965, Auroville wants to be a universal town where men and women of all countries are able to live in peace and progressive harmony, above all creeds, all politics and all nationalities. The purpose of Auroville is to realize human unity.
 W
WThe chakana is a stepped cross made up of an equal-armed cross indicating the cardinal points of the compass and a superimposed square. The square is suggested to represent the other two levels of existence. The three levels of existence are Hana Pacha, Kay Pacha, and Ukhu or Urin Pacha. The hole through the centre of the cross is the Axis by means of which the shaman transits the cosmic vault to the other levels. It is also said to represent Cusco, the center of the Incan empire, and the Southern Cross constellation.
 W
WChakra are various focal points used in a variety of ancient meditation practices, collectively denominated as Tantra, or the esoteric or inner traditions of Hinduism.
 W
WA Christian reflection on the New Age refers to a six-year study by the Roman Catholic Church on the New Age movement. The study, published in 2003, is highly critical of the New Age movement and follows the 1989 document Aspects of Christian meditation, in which the Vatican warned Catholics against mixing Christian meditation with Eastern approaches to spirituality.
 W
WGaianism is an earth-centered philosophical, holistic, and spiritual belief that shares expressions with earth religions and paganism while not identifying exclusively with any specific one. The term describes a philosophy and ethical worldview which, though not necessarily religious, implies a transpersonal devotion to earth as a superorganism. Practitioners of Gaianism are called Gaians.
 W
WDouglas R. Groothuis is Professor of Philosophy at Denver Seminary. Groothuis was a campus pastor for twelve years prior to obtaining a position as an associate professor of philosophy of religion and ethics at Denver Seminary in 1993. He was educated at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and the University of Oregon. He was married to Rebecca Merrill Groothuis until her death on July 6, 2018.
 W
WJyotisha or Jyotishya is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. The term Hindu astrology has been in use as the English equivalent of Jyotiṣa since the early 19th century, whereas Vedic astrology is a relatively recent term, entering common usage in the 1970s with self-help publications on Āyurveda or yoga.
 W
WThe Holy Order of MANS was a religious order grounded in what it viewed as the esoteric teachings of "The Great Christ" through "The Master Jesus", which identifies it as New Age. The order was founded in the 1960s "in the culturally innovative milieu of San Francisco", US, and over time grew into a more traditional Eastern Orthodox sect, finally renaming itself "Christ the Savior Brotherhood" (CSB); according to religious scholars, the group provides a "paradigmatic example" of the kind of development that such groups experienced.
 W
WThe "I AM" Movement is the original Ascended Master Teachings religious movement founded in the early 1930s by Guy Ballard (1878–1939) and his wife Edna Anne Wheeler Ballard (1886–1971) in Chicago, Illinois. It is an offshoot of theosophy and a major precursor of several New Age religions including the Church Universal and Triumphant. The movement had up to a million followers in 1938 and is still active today on a smaller scale. According to the official website of the parent organization, the Saint Germain Foundation, its worldwide headquarters is located in Schaumburg, Illinois, and there are approximately 300 local groups worldwide under several variations of the names "I AM" Sanctuary, "I AM" Temple, and other similar titles. As of 2007, the organization states that its purpose is "spiritual, educational and practical," and that no admission fee is charged for their activities. The term "I AM" is a reference to the ancient Sanskrit mantra "So Ham", meaning "I Am that I Am".
 W
WDavid Vaughan Icke is an English conspiracy theorist, and a former footballer and sports broadcaster. Icke has written more than 20 books and has lectured in over 25 countries.
 W
WIn Hinduism, Kundalini is a form of divine feminine energy believed to be located at the base of the spine, in the muladhara. It is an important concept in Śhaiva Tantra, where it is believed to be a force or power associated with the divine feminine or the formless aspect of the Goddess. This energy in the body, when cultivated and awakened through tantric practice, is believed to lead to spiritual liberation. Kuṇḍalinī is associated with Parvati or Adi Parashakti, the supreme being in Shaktism; and with the goddesses Bhairavi and Kubjika. The term, along with practices associated with it, was adopted into Hatha yoga in the 9th century. It has since then been adopted into other forms of Hinduism as well as modern spirituality and New age thought.
 W
WMayanism is a non-codified eclectic collection of New Age beliefs, influenced in part by Pre-Columbian Maya mythology and some folk beliefs of the modern Maya peoples.
 W
WMirtola, also known as ‘Uttar Vrindavan’ is a village 10 km. away from Almora, in Uttarakhand state in India, most known for an ashram by the same name, set up by Sri Yashoda Ma, a housewife turned ascetic in the 1930, along with her disciple Sri Krishna Prem (1898–1965), a mystic of the 20th Century. The ashram was later run by his disciple, Sri Madhava Ashish (1920–1997), another Englishman, who also later settled in India.
 W
WMoon magic is associated with the Moon. There is a belief common to many cultures that working rituals at the time of different phases of the moon can bring about physical or psychological change or transformation. These rituals have historically occurred on or around the full moon and to a lesser extent the new moon. Such practices are common amongst adherents of neopagan and witchcraft systems such as Wicca. Witches in Greek and Roman literature, particularly those from Thessaly, were regularly accused of "drawing down the Moon" by use of a magic spell. The trick serves to demonstrate their powers, to perform a love spell or to extract a magical juice from the Moon. These beliefs would seem to be consistent with many other cultures traditions, for instance; casting of the i ching is often done during the full moon's apex.
 W
WMysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in ultimate or hidden truths, and to human transformation supported by various practices and experiences.
 W
WNambassa was a series of hippie-conceived festivals held between 1976 and 1981 on large farms around Waihi and Waikino in New Zealand. They were music, arts and alternatives festivals that focused on peace, love, and an environmentally friendly lifestyle. In addition to popular entertainment, they featured workshops and displays advocating alternative lifestyle and holistic health issues, alternative medicine, clean and sustainable energy, and unadulterated foods.
 W
WA near-birth experience is an alleged recollected event which occurred before or during one's own birth, or during the pregnancy, an alleged remembering of one's own pre-existence, or an alleged encounter with the unborn child experienced by relatives or close family friends. Under this usage, the term "near-birth experience" is analogous to the term "near-death experience."
 W
WNew Age travellers or New Travellers, often referred to as crusties, are people in the United Kingdom generally espousing New Age beliefs along with the hippie culture of the 1960s, and who used to travel between free music festivals and fairs prior to crackdown in the 1990s, who now congregate in community with others who hold similar beliefs on various authorised and unauthorised sites.
 W
WThe Odic force is the name given in the mid-19th century to a hypothetical vital energy or life force by Baron Carl von Reichenbach. Von Reichenbach coined the name from that of the Norse god Odin in 1845. The study of Odic force is called odology.
 W
WPost-Islamism is a neologism in political science, the definition and applicability of which has led to an intellectual debate. Asef Bayat and Olivier Roy are among the main architects of the idea.
 W
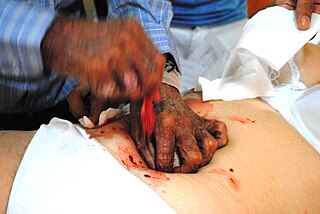
WPsychic surgery is a pseudoscientific medical fraud in which practitioners create the illusion of performing surgery with their bare hands and use sleight of hand, fake blood, and animal parts to convince the patient that diseased lesions have been removed and that the incision has spontaneously healed.
 W
WPyramidology refers to various religious or pseudoscientific speculations regarding pyramids, most often the Giza pyramid complex and the Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt. Some "pyramidologists" also concern themselves with the monumental structures of pre-Columbian America, and the temples of Southeast Asia.
 W
WThe Radical Faeries are a loosely affiliated worldwide network and countercultural movement seeking to redefine queer consciousness through secular spirituality. Sometimes deemed a form of modern Paganism, the movement also adopts elements from anarchism and environmentalism.
 W
WThe meaning of spirituality has developed and expanded over time, and various connotations can be found alongside each other. Traditionally, spirituality referred to a religious process of re-formation which "aims to recover the original shape of man", oriented at "the image of God" as exemplified by the founders and sacred texts of the religions of the world. The term was used within early Christianity to refer to a life oriented toward the Holy Spirit and broadened during the Late Middle Ages to include mental aspects of life. In modern times, the term both spread to other religious traditions and broadened to refer to a wider range of experience, including a range of esoteric traditions and religious traditions. Modern usages tend to refer to a subjective experience of a sacred dimension and the "deepest values and meanings by which people live", often in a context separate from organized religious institutions, such as a belief in a supernatural realm, personal growth, a quest for an ultimate or sacred meaning, religious experience, or an encounter with one's own "inner dimension".
 W
WCount Saint Germain is a legendary spiritual master of the ancient wisdom in various Theosophical and post-Theosophical teachings, said to be responsible for the New Age culture of the Age of Aquarius and identified with the Count Saint Germain, who has been variously described as a courtier, adventurer, inventor, alchemist, pianist, violinist, and amateur composer.
 W
WSummum is a religion and philosophy that began in 1975 as a result of American citizen Claude "Corky" Nowell's claimed encounter with beings he described as "Summa Individuals". According to Nowell, these beings presented him with concepts regarding the nature of creation, concepts that have always existed and are continually re-introduced to humankind by advanced beings who work along the pathways of creation. As a result of his experience, Nowell founded Summum in order to share the "gift" he received with others. In 1980, as a reflection of his newfound path, he changed his name to Summum Bonum Amon Ra, but news stories indicate he went by Corky Ra. Summum religious practices draw upon both Ancient Egyptian religion and the Hebrew prophet Moses.
 W
WThe Temples of Humankind are a collection of subterranean temples buried 30 metres (100 ft) underground built by the Federation of Damanhur. They are decorated in several motifs stressing peaceful human collaboration. The Temples are located in the foothills of the Alps in northern Italy, 50 kilometres (30 mi) from Turin, in the valley of Valchiusella.
 W
WThe third eye is a mystical and esoteric concept of a speculative invisible eye, usually depicted as located on the forehead, which provides perception beyond ordinary sight.