 W
WAcanthocephala is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described.
 W
WThe annelids, also known as the ringed worms or segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments.
 W
WAn arthropod is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Euarthropoda, which includes insects, arachnids, myriapods, and crustaceans. The term Arthropoda as originally proposed refers to a proposed grouping of Euarthropods and the phylum Onychophora.
 W
WBrachiopods, phylum Brachiopoda, are a group of lophotrochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major groups are recognized, articulate and inarticulate. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove features of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic feature (fossilizable), by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple opening and closing muscles, while inarticulate brachiopods have untoothed hinges and a more complex system of muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In a typical brachiopod a stalk-like pedicle projects from an opening in one of the valves near the hinges, known as the pedicle valve, keeping the animal anchored to the seabed but clear of silt that would obstruct the opening.
 W
WBryozoa are a phylum of aquatic invertebrate animals. Typically about 0.5 millimetres long, they are filter feeders that sieve food particles out of the water using a retractable lophophore, a "crown" of tentacles lined with cilia. Most marine species live in tropical waters, but a few occur in oceanic trenches, and others are found in polar waters. One class lives only in a variety of freshwater environments, and a few members of a mostly marine class prefer brackish water. 5869 living species are known. One genus is solitary and the rest are colonial.
 W
WChaetognatha is a phylum of predatory marine worms that are a major component of plankton worldwide. Commonly known as arrow worms, about 20% of the known Chaetognatha species are benthic, and can attach to algae and rocks. They are found in all marine waters, from surface tropical waters and shallow tide pools to the deep sea and polar regions. Most chaetognaths are transparent and are torpedo shaped, but some deep-sea species are orange. They range in size from 2 to 120 millimetres.
 W
WA chordate is an animal of the phylum Chordata. During some period of their life cycle, chordates possess a notochord, a dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail: these four anatomical features define this phylum. Chordates are also bilaterally symmetric, and have a coelom, metameric segmentation, and circulatory system.
 W
WCnidaria is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
 W
WCtenophora comprise a phylum of invertebrate animals that live in marine waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming, and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to 1.5 m in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless platyctenids, and the large-mouthed beroids, which prey on other ctenophores.
 W
WDicyemida, also known as Rhombozoa, is a phylum of tiny parasites that live in the renal appendages of cephalopods.
 W
WEchinoderm is the common name given to any member of the phylum Echinodermata of marine animals. The adults are recognizable by their radial symmetry, and include starfish, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea lilies or "stone lilies". Echinoderms are found at every ocean depth, from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7000 living species, making it the second-largest grouping of deuterostomes, after the chordates. Echinoderms are also the largest phylum that has no freshwater or terrestrial (land-based) representatives.
 W
WEntoprocta, whose name means "anus inside", or Kamptozoa, is a phylum of mostly sessile aquatic animals, ranging from 0.1 to 7 millimetres long. Mature individuals are goblet-shaped, on relatively long stalks. They have a "crown" of solid tentacles whose cilia generate water currents that draw food particles towards the mouth, and both the mouth and anus lie inside the "crown". The superficially similar Bryozoa (Ectoprocta) have the anus outside a "crown" of hollow tentacles. Most families of entoprocts are colonial, and all but 2 of the 150 species are marine. A few solitary species can move slowly.
 W
WThe gastrotrichs, commonly referred to as hairybellies or hairybacks, are a group of microscopic (0.06-3.0 mm), worm-like, pseudocoelomate animals, and are widely distributed and abundant in freshwater and marine environments. They are mostly benthic and live within the periphyton, the layer of tiny organisms and detritus that is found on the seabed and the beds of other water bodies. The majority live on and between particles of sediment or on other submerged surfaces, but a few species are terrestrial and live on land in the film of water surrounding grains of soil. Gastrotrichs are divided into two orders, the Macrodasyida which are marine, and the Chaetonotida, some of which are marine and some freshwater. Nearly 800 species of gastrotrich have been described.
 W
WHemichordata is a phylum of marine deuterostome animals, generally considered the sister group of the echinoderms. They appear in the Lower or Middle Cambrian and include two main classes: Enteropneusta, and Pterobranchia. A third class, Planctosphaeroidea, is known only from the larva of a single species, Planctosphaera pelagica. The extinct class Graptolithina is closely related to the pterobranchs.
 W
WHyoliths are animals with small conical shells, known as fossils from the Palaeozoic Era. They are lophophorates, a group which includes the brachiopods.
 W
WKinorhyncha is a phylum of small marine invertebrates that are widespread in mud or sand at all depths as part of the meiobenthos. They are also called mud dragons. Modern species are 1 mm or less, but Cambrian forms could reach 4 cm.
 W
WLoricifera is a phylum of very small to microscopic marine cycloneuralian sediment-dwelling animals with 37 described species, in nine genera. Aside from these described species, there are approximately 100 more that have been collected and not yet described. Their sizes range from 100 μm to ca. 1 mm. They are characterised by a protective outer case called a lorica and their habitat is in the spaces between marine gravel to which they attach themselves. The phylum was discovered in 1983 by Reinhardt Kristensen, in Roscoff, France. They are among the most recently discovered groups of Metazoans. They attach themselves quite firmly to the substrate, and hence remained undiscovered for so long. The first specimen was collected in the 1970s, and later described in 1983. They are found at all depths, in different sediment types, and in all latitudes.
 W
WMollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda. The members are known as molluscs or mollusks. Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied.
 W
WSalinella salve is a dubious species of very simple animal that may not exist, but which some have named as the sole member of the phylum Monoblastozoa. It was discovered in 1892 by Johannes Frenzel in the salt pans of Argentina and cultivated in a laboratory by him. This animal has not been found since and its real existence is considered as doubtful.
 W
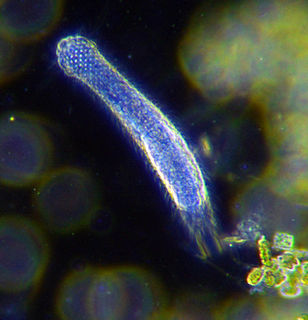
WThe nematodes or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda, with plant-parasitic nematodes being known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Taxonomically, they are classified along with insects and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but as their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, it shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum.
 W
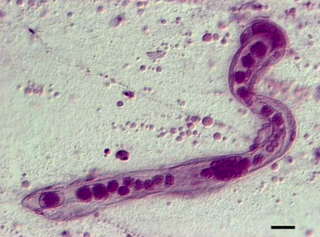
WNematomorpha are a phylum of parasitoid animals superficially similar to nematode worms in morphology, hence the name. Most species range in size from 50 to 100 millimetres long, reaching 2 metres in extreme cases, and 1 to 3 millimetres in diameter. Horsehair worms can be discovered in damp areas, such as watering troughs, swimming pools, streams, puddles, and cisterns. The adult worms are free-living, but the larvae are parasitic on arthropods, such as beetles, cockroaches, mantids, orthopterans, and crustaceans. About 351 freshwater species are known and a conservative estimate suggests that there may be about 2000 freshwater species worldwide. The name "Gordian" stems from the legendary Gordian knot. This relates to the fact that nematomorphs often tie themselves in knots.
 W
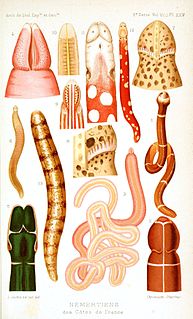
WNemertea is a phylum of invertebrate animals also known as ribbon worms or proboscis worms. Alternative names for the phylum have included Nemertini, Nemertinea and Rhynchocoela. Most are very slim, usually only a few millimeters wide, although a few have relatively short but wide bodies. Many have patterns of yellow, orange, red and green coloration. The foregut, stomach and intestine run a little below the midline of the body, the anus is at the tip of the tail, and the mouth is under the front. A little above the gut is the rhynchocoel, a cavity which mostly runs above the midline and ends a little short of the rear of the body. All species have a proboscis which lies in the rhynchocoel when inactive but everts to emerge just above the mouth and capture the animal's prey with venom. A highly extensible muscle in the back of the rhynchocoel pulls the proboscis in when an attack ends. A few species with stubby bodies filter feed and have suckers at the front and back ends, with which they attach to a host.
 W
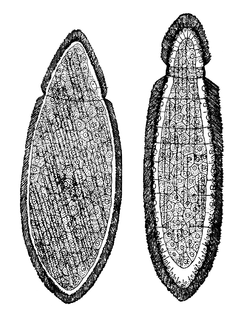
WOnychophora, commonly known as velvet worms or more ambiguously as peripatus, is a phylum of elongate, soft-bodied, many-legged panarthropods. In appearance they have variously been compared to worms with legs, caterpillars, and slugs. They prey upon smaller animals such as insects, which they catch by squirting an adhesive slime.
 W
WOrthonectida is a small phylum of poorly known parasites of marine invertebrates that are among the simplest of multi-cellular organisms. Members of this phylum are known as orthonectids.
 W
WPhoronids are a small phylum of marine animals that filter-feed with a lophophore, and build upright tubes of chitin to support and protect their soft bodies. They live in most of the oceans and seas, including the Arctic Ocean but excluding the Antarctic Ocean, and between the intertidal zone and about 400 meters down. Most adult phoronids are 2 cm long and about 1.5 mm wide, although the largest are 50 cm long.
 W
WThe Placozoa are a basal form of marine free-living (non-parasitic) multicellular organism. They are the simplest in structure of all animals. Three genera have been found: the classical Trichoplax adhaerens, Hoilungia hongkongensis, and Polyplacotoma mediterranea, where the last appears most basal. The last two have been found only since 2017. Although the Placozoa were first discovered in 1883 by the German zoologist, Franz Eilhard Schulze (1840–1921) and since the 1970s more systematically analyzed by the German protozoologist, Karl Gottlieb Grell (1912–1994), a common name does not yet exist for the taxon; the scientific name means "flat animals".
 W
WThe flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, Plathelminthes, or platyhelminths are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates, and have no specialized circulatory and respiratory organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion and egestion ; as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously.
 W
WSponges, the members of the phylum Porifera, are a basal Metazoa (animal) clade as a sister of the Diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. The branch of zoology that studies sponges is known as spongiology.
 W
WPriapulida, sometimes referred to as penis worms, is a phylum of unsegmented marine worms. The name of the phylum relates to the Greek god of fertility, because their general shape and their extensible spiny introvert may recall the shape of a penis. They live in the mud and in comparatively shallow waters up to 90 metres (300 ft) deep. Some species show a remarkable tolerance for hydrogen sulfide and anoxia. They can be quite abundant in some areas. In an Alaskan bay as many as 85 adult individuals of Priapulus caudatus per square meter has been recorded, while the density of its larvae can be as high as 58,000 per square meter.
 W
WProarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately 567 to 550 million years ago. The name comes from the Greek προ = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as Dickinsonia, Vendia, Cephalonega, Praecambridium and currently many other Proarticulata are described.
 W
WThe rotifers, commonly called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals.
 W
WTardigrades, known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them little water bears. In 1777, the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani named them Tardigrada, which means "slow steppers".
 W
WTrilobozoa is a taxon of extinct organisms which displayed tri-radial symmetry. Fossils of trilobozoans are restricted to marine strata of the Late Ediacaran period — prior to the Cambrian explosion of more modern life forms.
 W
WXenacoelomorpha is a bilaterian phylum of small and very simple animals, grouping the xenoturbellids with the acoelomorphs. This grouping was suggested by morphological synapomorphies, and confirmed by phylogenomic analyses of molecular data.