 W
WMarimo is a rare growth form of Aegagropila linnaei in which the algae grow into large green balls with a velvety appearance.
 W
WAmphora is a major genus of marine and freshwater diatoms. With over 1000 species, it is one of the largest genera of diatoms. These diatoms are recognized by their strongly dorsiventral frustules, which means that their ridges lie close to the ventral margin of the valve, and their girdle is much wider on the dorsal side.
 W
WAnadyomenaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Cladophorales.
 W
WBiddulphiaceae is a family of diatom in the order Biddulphiales. The Biddulphiaceae are distinguished from the Eupodiscaceae by their pseudocelli, where the Eupodiscaceae have fully developed ocelli. Both families commonly inhabit the littoral zone of the ocean, close to the shore. Sixteen species of Biddulphiaceae are found on the west coast of India.
 W
WBlidingia minima is a species of seaweed in the Kornmanniaceae family. It was described by Johann Kylin in 1947.
 W
WBotryococcus is a genus of green algae. The cells form an irregularly shaped aggregate. Thin filaments connect the cells. The cell body is ovoid, 6 to 10 μm long, and 3 to 6 μm wide.
 W
WBotryococcus braunii is a green, pyramid-shaped planktonic microalga that is of potentially great importance in the field of biotechnology. Colonies held together by a lipid biofilm matrix can be found in temperate or tropical oligotrophic lakes and estuaries, and will bloom when in the presence of elevated levels of dissolved inorganic phosphorus. The species is notable for its ability to produce high amounts of hydrocarbons, especially oils in the form of Triterpenes, that are typically around 30–40% of their dry weight. Compared to other green alge species it has a relatively thick cell wall that is accumulated from previous cellular divisions; making extraction of cytoplasmic components rather difficult. Much of the useful hydrocarbon oil is outside of the cell.
 W
WCallophyllis is a red algae genus in the family Kallymeniaceae. Several species are exploited as edible seaweeds under the common name carola, most commonly Callophyllis variegata.
 W
WCallophyllis variegata, commonly known as carola, is a type of edible seaweed, a member of the genus Callophyllis. Callophyllis variegata occurs in Concepción de Chile and other parts of South America such as Peru, the Falkland Islands, Tierra del Fuego. But also in New Guinea, South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, Alaska, St. Paul Island, Antarctic and subantarctic islands such as the Graham Land, Kerguelen, Macquarie Island, South Georgia, and the South Orkney Islands.
 W
WChaetomorpha is a genus of green algae in the family Cladophoraceae. Members of this genus may be referred to by the common name sea emerald.
 W
WChaetomorpha aerea is a species of green algae of the family Cladophoraceae.
 W
WChaetomorpha antennina is a species of green algae of the family Cladophoraceae.
 W
WChaetomorpha linum is a species of green algae in the family Cladophoraceae.
 W
WChaetomorpha melagonium is a species of green algae of the family Cladophoraceae.
 W
WChara virgata is slender, branched freshwater green alga.
 W
WChondracanthus is a red algae genus in the family Gigartinaceae. The name Chondracanthus is from χόνδρος} meaning 'cartilage' and ακανϑα meaning 'spine or thorn,' together meaning 'with cartilaginous spines.' This refers to the rubbery papillae on the surface of the blades containing the reproductive structures.
 W
WCladophora is a genus of reticulated filamentous Ulvophyceae. The genus Cladophora contains many species that are very hard to tell apart and classify, mainly because of the great variation in their appearances, which is affected by habitat, age and environmental conditions. Unlike Spirogyra the filaments of Cladophora branch and do not undergo conjugation. There are two multicellular stages in its life cycle - a haploid gametophyte and a diploid sporophyte - which look highly similar. The only way to tell the two stages apart is to either count their chromosomes, or examine their offspring. The haploid gametophyte produces haploid gametes by mitosis and the diploid sporophyte produces haploid spores by meiosis. The only visible difference between the gametes and spores of Cladophora is that the gametes have two flagella and the spores have four. The Cladophora species can be a major nuisance causing major alteration to benthic conditions linked particularly with increased phosphorus loading.
 W
WCladophora socialis is a species of green algae.
 W
WCodium arabicum, commonly known as green sea cushion, is a species of seaweed in the Codiaceae family.
 W
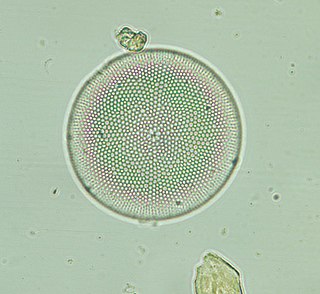
WCoscinodiscaceae is a diatom family in the order Coscinodiscales.
 W
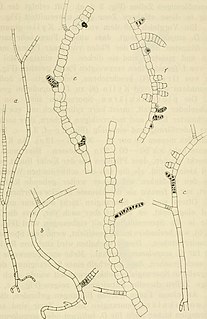
WThe Dasycladaceae is one of the two extinct families of green algae of the order Dasycladales. When found in Palaeozoic limestones, they typically indicate depositional depth of less than 5m.
 W
WDesmotrichum is a genus of brown algae. One species is accepted in AlgaeBase, Desmotrichum plumosum.
 W
WThe Gelidiaceae is a small family of red algae containing eight genera. Many species of this algae are used to make agar.
 W
WGeosiphon is a genus of fungus in the family Geosiphonaceae. The genus is monotypic, containing the single species Geosiphon pyriformis, first described by Kützing in 1849 as Botrydium pyriforme. In 1915, Von Wettstein characterized Geosiphon pyriforme as a multinucleate alga containing endosymbiotic cyanobacteria, although he also noted the presence of chitin, a component of fungal cell walls. In 1933, Knapp was the first to suggest the fungal origin of the species and described it as a lichen with endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. It is the only member of the Glomeromycota known to not form a symbiosis with terrestrial plants in the form of arbuscular mycorrhiza.
 W
WGigartinaceae is a red algae family in the order Gigartinales.
 W
WLaverbread is a food product, made from an edible seaweed, consumed mainly in Wales as part of local traditional cuisine. The seaweed is commonly found around the west coast of Great Britain and east coast of Ireland along the Irish Sea, where it is known as slake. It is smooth in texture and forms delicate, sheetlike thalli, often clinging to rocks. The principal variety is Porphyra umbilicalis. Porphyra is classified as red algae; it tends to be a brownish colour, but boils down to a dark green pulp when prepared. Laver seaweed has a high content of dietary minerals, particularly iodine and iron. The high iodine content gives the seaweed a distinctive flavour in common with olives and oysters.
 W
WMarimo is a rare growth form of Aegagropila linnaei in which the algae grow into large green balls with a velvety appearance.
 W
WNaviculaceae is a diatom family in the order Naviculales.
 W
WLaverbread is a food product, made from an edible seaweed, consumed mainly in Wales as part of local traditional cuisine. The seaweed is commonly found around the west coast of Great Britain and east coast of Ireland along the Irish Sea, where it is known as slake. It is smooth in texture and forms delicate, sheetlike thalli, often clinging to rocks. The principal variety is Porphyra umbilicalis. Porphyra is classified as red algae; it tends to be a brownish colour, but boils down to a dark green pulp when prepared. Laver seaweed has a high content of dietary minerals, particularly iodine and iron. The high iodine content gives the seaweed a distinctive flavour in common with olives and oysters.
 W
WSaprolegniaceae is a family of freshwater mould. Mycologist James Ellis Humphrey did significant work on this family.
 W
WSyringodium is a genus in the family Cymodoceaceae described as a genus in 1860. It is found along shorelines of tropical and subtropical marine environments.
 W
WSyringodium filiforme, commonly known as manatee grass, is a species of marine seagrass. It forms meadows in shallow sandy or muddy locations in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, and is also found in the Bahamas and Bermuda.
 W
WUlothrix is a genus of green algae in the family Ulotrichaceae.
 W
WUlotrichaceae is a family of green algae in the order Ulotrichales.