 W
WThe even-toed ungulates are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on one of the five toes: the third toe. Another difference between the two is that even-toed ungulates digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do.
 W
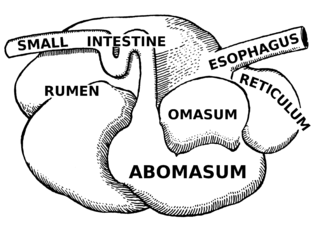
WThe abomasum, also known as the maw, rennet-bag, or reed tripe, is the fourth and final stomach compartment in ruminants. It secretes rennet, which is used in cheese creation.
 W
WAchenodon is an extinct artiodactyl mammal, possibly belonging to the eloiids. It lived in the Mid-To-Upper Eocene and its fossil remains have been found in North America.
 W
WThe pronghorn is a species of artiodactyl mammal indigenous to interior western and central North America. Though not an antelope, it is often known colloquially in North America as the American antelope, prong buck, pronghorn antelope, prairie antelope, or simply antelope because it closely resembles the true antelopes of the Old World and fills a similar ecological niche due to parallel evolution. It is the only surviving member of the family Antilocapridae.
 W
WThe Antilocapridae are a family of artiodactyls endemic to North America. Their closest extant relatives are the giraffids with which they comprise the superfamily Giraffoidea. Only one species, the pronghorn, is living today; all other members of the family are extinct. The living pronghorn is a small ruminant mammal resembling an antelope.
 W
WThe Baja California pronghorn or peninsular pronghorn is a critically endangered subspecies of pronghorn, endemic to Baja California in Mexico. The wild population is estimated at 200.
 W
WChevrotains are small even-toed ungulates that make up the family Tragulidae, the only extant members of the infraorder Tragulina. The 10 extant species are placed in three genera, but several species also are known only from fossils. The extant species are found in forests in South and Southeast Asia, with a single species in the rainforests of Central and West Africa. They are solitary or live in pairs, and feed almost exclusively on plant material. Chevrotains are the smallest hoofed mammals in the world. The Asian species weigh between 0.7 and 8.0 kg, while the African chevrotain is considerably larger at 7–16 kg (15–35 lb).
 W
WChoeropotamidae, also known as aplobunodontids (Haplobunodontidae), are a family of extinct mammals, extinct herbivores, belonging to artiodactyls. They lived between the Eocene lower/middle and the Oligocene lower and their remains were found in Europe and Africa.
 W
WA cloven hoof, cleft hoof, divided hoof or split hoof is a hoof split into two toes. This is found on members of the mammalian order Artiodactyla. Examples of mammals that possess this type of hoof are cattle, deer, pigs, antelopes, gazelles, goats and sheep. In folklore and popular culture, a cloven hoof has long been associated with the Devil.
 W
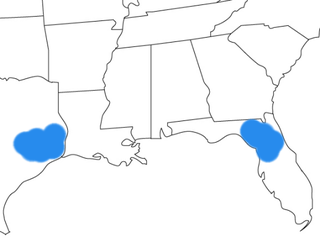
WFloridachoerus olseni is an extinct peccary that lived during the Hemingfordian age of the Early Miocene, and was endemic to North America. F. olseni was in existence for approximately 4.46 million years . Remains of this extinct mammal were located at the fossil rich Thomas Farm site in Gilchrist County, Florida and Toledo Bend site, Newton County, Texas. Floridachoerus olseni was named after Stanley. J. Olsen of the Florida Geological Survey in 1962. Olsen previously worked at the site for Harvard University.
 W
WThe Giraffidae are a family of ruminant artiodactyl mammals that share a common ancestor with cervids and bovids. This family, once a diverse group spread throughout Eurasia and Africa, presently comprises only two extant genera, the giraffe and the okapi. Both are confined to sub-Saharan Africa: the giraffe to the open savannas, and the okapi to the dense rainforest of the Congo. The two genera look very different on first sight, but share a number of common features, including a long, dark-coloured tongue, lobed canine teeth, and horns covered in skin, called ossicones.
 W
WGiraffoidea is a superfamily that includes the families Climacoceratidae, Antilocapridae, and Giraffidae. The only extant members in the superfamily are the pronghorn, giraffe, and okapi. The Climacoceratidae are also placed in the superfamily, but were originally placed within the family Palaeomerycidae.
 W
WHelohyidae were a group of artiodactyl mammals. They were most prominent in the mid-to-upper Eocene, although some fossils were found on land in the upper Oligocene.
 W
WHippopotamuses are stout, naked-skinned, and semiaquatic artiodactyl mammals, possessing three-chambered stomachs and walking on four toes on each foot. While they resemble pigs physiologically, their closest living relatives are the cetaceans. Hippopotamuses are the only living members of the family Hippopotamidae.
 W
WThis is a list of even-toed ungulate species by estimated global population. This list is not comprehensive, as not all ungulates have had their numbers quantified.
 W
WMerycodus is an extinct genus of the artiodactyl family Antilocapridae. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Santa Fe Group of New Mexico.
 W
WMoschidae is a family of pecoran even-toed ungulates, characterized by long 'saber teeth' instead of horns, antlers or ossicones, modest size and a lack of facial glands. The fossil record of the family extends back to the late Oligocene, around 28 million years ago. The group was abundant across Eurasia and North America during the Miocene, but afterwards declined to only the extant genus Moschus by the early Pleistocene.
 W
WMusk deer can refer to any one, or all seven, of the species that make up Moschus, the only extant genus of the family Moschidae. Despite being commonly called deer, they are not true deer belonging to the family Cervidae. The musk deer family differs from cervids, or true deer, by lacking antlers and facial glands and by possessing only a single pair of teats, a gallbladder, a caudal gland, a pair of tusk-like teeth and—of particular economic importance to humans—a musk gland.
 W
WMusk deer can refer to any one, or all seven, of the species that make up Moschus, the only extant genus of the family Moschidae. Despite being commonly called deer, they are not true deer belonging to the family Cervidae. The musk deer family differs from cervids, or true deer, by lacking antlers and facial glands and by possessing only a single pair of teats, a gallbladder, a caudal gland, a pair of tusk-like teeth and—of particular economic importance to humans—a musk gland.
 W
WThe omasum, also known as the bible, the fardel, the manyplies and the psalterium, is the third compartment of the stomach in ruminants. The omasum comes after the rumen and reticulum and before the abomasum. Different ruminants have different omasum structures and function based on the food that they eat and how they developed through evolution.
 W
WA peccary is a medium-sized pig-like hoofed mammal of the family Tayassuidae. They are found throughout Central and South America and in the southwestern area of North America. They usually measure between 90 and 130 cm in length, and a full-grown adult usually weighs about 20 to 40 kg.
 W
WPecora is an infraorder of even-toed hoofed mammals with ruminant digestion. Most members of Pecora have cranial appendages projecting from their frontal bones; only two extant genera lack them, Hydropotes and Moschus. The name “Pecora” comes from the Latin word pecus, which means “horned livestock”. Although most pecorans have cranial appendages, only some of these are properly called “horns”, and many scientists agree that these appendages did not arise from a common ancestor, but instead evolved independently on at least two occasions. Likewise, while Pecora as a group is supported by both molecular and morphological studies, morphological support for interrelationships between pecoran families is disputed.
 W
WPhacochoerini is a tribe of even-toed ungulates which encompasses the warthogs.
 W
WPolycerates are animals with more than two horns.
 W
WThe preorbital gland is a paired exocrine gland found in many species of hoofed animals, which is homologous to the lacrimal gland found in humans. These glands are trenchlike slits of dark blue to black, nearly bare skin extending from the medial canthus of each eye. They are lined by a combination of sebaceous and sudoriferous glands, and they produce secretions which contain pheromones and other semiochemical compounds. Ungulates frequently deposit these secretions on twigs and grass as a means of communication with other animals.
 W
WRuminants are herbivorous mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ruminare, which means "to chew over again".
 W
WRuminantia is a taxon within the order Artiodactyla that includes many of the well-known large grazing or browsing mammals: among them cattle, goats, sheep, deer, and antelope. All members of the Ruminantia employ foregut fermentation and are ruminants: they digest food in two steps, chewing and swallowing in the normal way to begin with, and then regurgitating the semidigested cud to rechew it and thus extract the maximum possible food value.
 W
WThe rut is the mating season of certain mammals, which includes ruminants such as deer, sheep, camels, goats, pronghorns, bison, giraffes and antelopes, and extends to others such as skunks and elephants. The rut is characterized in males by an increase in testosterone, exaggerated sexual dimorphisms and increased aggression and interest in females. The males of the species may mark themselves with mud, undergo physiological changes or perform characteristic displays in order to make themselves more visually appealing to the females. Males also use olfaction to entice females to mate using secretions from glands and soaking in their own urine.
 W
WThe Sonoran pronghorn is an endangered subspecies of pronghorn that is endemic to the Sonoran Desert.
 W
WStockoceros is an extinct genus of the North American artiodactyl family Antilocapridae, known from Mexico and the southwestern United States. Its horns are each divided near their base into two prongs of roughly equal length.
 W
WSuidae is a family of artiodactyl mammals which are commonly called pigs, hogs or boars. In addition to numerous fossil species, 18 extant species are currently recognized, classified into between four and eight genera. Within this family, the genus Sus includes the domestic pig, Sus scrofa domesticus or Sus domesticus, and many species of wild pig from Europe to the Pacific. Other genera include babirusas and warthogs. All suids, or swine, are native to the Old World, ranging from Asia to Europe and Africa.
 W
WThe suborder Suina is a lineage of omnivorous, non-ruminant artiodactyl mammals that includes the pigs and peccaries of the families Suidae and Tayassuidae and their fossil kin. Hippopotamidae had historically been classified among the Suina for morphological reasons, but is now more often classified as the sister group of the whales, or Cetacea.
 W
WTetrameryx is an extinct genus of the North American artiodactyl family Antilocapridae, known from Mexico, the western United States, and Saskatchewan. The name means "four [horned] ruminant", referring to the division of each horn near its base into two prongs; in T. shuleri, the rear prong is much longer.
 W
WTragulina is an infraorder of even-toed ungulates. Only the chevrotains survive to the present, including the genera Tragulus and Hyemoschus.
 W
WTylopoda is a suborder of terrestrial herbivorous even-toed ungulates belonging to the order Artiodactyla. They are found in the wild in their native ranges of South America and Asia, while Australian feral camels are introduced. The group has a long fossil history in North America and Eurasia. Tylopoda appeared during the Eocene around 46.2 million years ago.