 W
WThe cerebellum is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans.
 W
WThe central lobule is a small square lobule, situated in the anterior cerebellar notch. It overlaps the lingula, from which it is separated by the precentral fissure; laterally, it extends along the upper and anterior part of each hemisphere, where it forms a wing-like prolongation (ala), on each side, as the alae of the central lobule or alae lobuli centralis.
 W
WThe anatomy of the cerebellum can be viewed at three levels. At the level of gross anatomy, the cerebellum consists of a tightly folded and crumpled layer of cortex, with white matter underneath, several deep nuclei embedded in the white matter, and a fluid-filled ventricle in the middle. At the intermediate level, the cerebellum and its auxiliary structures can be broken down into several hundred or thousand independently functioning modules or compartments known as microzones. At the microscopic level, each module consists of the same small set of neuronal elements, laid out with a highly stereotyped geometry.
 W
WThe anterior lobe of cerebellum is the portion of the cerebellum responsible for mediating unconscious proprioception. Inputs into the anterior lobe of the cerebellum are mainly from the spinal cord.
 W
WAutosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia type 1 (ARCA1) is a condition characterized by progressive problems with movement. Signs and symptoms of the disorder first appear in early to mid-adulthood. People with this condition initially experience impaired speech (dysarthria), problems with coordination and balance (ataxia), or both. They may also have difficulty with movements that involve judging distance or scale (dysmetria). Other features of ARCA1 include abnormal eye movements (nystagmus) and problems following the movements of objects with their eyes. The movement problems are slowly progressive, often resulting in the need for a cane, walker, or wheelchair.
 W
WThe biventer lobule is a region of the cerebellum. It is triangular in shape; its apex points backward, and is joined by the gray band to the pyramid.
 W
WCerebellar degeneration is a condition in which cerebellar cells, otherwise known as neurons, become damaged and progressively weaken in the cerebellum. There are two types of cerebellar degeneration; paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, and alcoholic or nutritional cerebellar degeneration. As the cerebellum contributes to the coordination and regulation of motor activities, as well as controlling equilibrium of the human body, any degeneration to this part of the organ can be life-threatening. Cerebellar degeneration can result in disorders in fine movement, posture, and motor learning in humans, due to a disturbance of the vestibular system. This condition may not only cause cerebellar damage on a temporary or permanent basis, but can also affect other tissues of the central nervous system, those including the cerebral cortex, spinal cord and the brainstem.
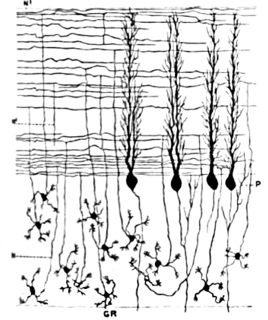 W
WCerebellar granule cells form the thick granular layer of the cerebellar cortex and are among the smallest neurons in the brain. Cerebellar granule cells are also the most numerous neurons in the brain: in humans, estimates of their total number average around 50 billion, which means that they constitute about 3/4 of the brain's neurons.
 W
WThe cerebellum consists of three parts, a median and two lateral, which are continuous with each other, and are substantially the same in structure. The median portion is constricted, and is called the vermis, from its annulated appearance which it owes to the transverse ridges and furrows upon it; the lateral expanded portions are named the hemispheres.
 W
WThe cerebellar tonsil is analogous to a rounded lobule on the undersurface of each cerebellar hemisphere, continuous medially with the uvula of the cerebellar vermis and superiorly by the flocculonodular lobe. Synonyms include: tonsilla cerebelli, amygdala cerebelli, the latter of which is not to be confused with the cerebral tonsils or amygdala nuclei located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The flocculonodular lobe of the cerebellum which can also be confused for the cerebellar tonsils, is one of three lobes that make up the overall composition of the cerebellum. The cerebellum consists of three anatomical and functional lobes: anterior lobe, posterior lobe, and flocculonodular lobe.
 W
WThe cerebellar vermis is located in the medial, cortico-nuclear zone of the cerebellum, which is in the posterior fossa of the cranium. The primary fissure in the vermis curves ventrolaterally to the superior surface of the cerebellum, dividing it into anterior and posterior lobes. Functionally, the vermis is associated with bodily posture and locomotion. The vermis is included within the spinocerebellum and receives somatic sensory input from the head and proximal body parts via ascending spinal pathways.
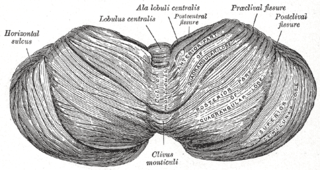 W
WThe culmen is the portion of the anterior vermis adjacent to the primary fissure of cerebellum.
 W
WThe cerebellum has four deep cerebellar nuclei embedded in the white matter in its center.
 W
WThe dentate nucleus is a cluster of neurons, or nerve cells, in the central nervous system that has a dentate – tooth-like or serrated – edge. It is located within the deep white matter of each cerebellar hemisphere, and it is the largest single structure linking the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. It is the largest and most lateral, or farthest from the midline, of the four pairs of deep cerebellar nuclei, the others being the globose and emboliform nuclei, which together are referred to as the interposed nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus. The dentate nucleus is responsible for the planning, initiation and control of voluntary movements. The dorsal region of the dentate nucleus contains output channels involved in motor function, which is the movement of skeletal muscle, while the ventral region contains output channels involved in nonmotor function, such as conscious thought and visuospatial function.
 W
WThe emboliform nucleus is a deep cerebellar nucleus that lies immediately to the medial side of the nucleus dentatus, and partly covering its hilum. It is one among the four pairs of deep cerebellar nuclei, which are from lateral to medial: the dentate, interposed, and fastigial nuclei. These nuclei can be seen using Weigert's elastic stain.
 W
WThe fastigial nucleus is located in the cerebellum. It is one of the four deep cerebellar nuclei, and is grey matter embedded in the white matter of the cerebellum.
 W
WThe flocculonodular lobe (vestibulocerebellum) is a lobe of the cerebellum consisting of the nodule and the flocculus. The two flocculi are connected to the midline structure called the nodulus by thin pedicles. It is placed on the anteroinferior surface of cerebellum.
 W
WThe flocculus is a small lobe of the cerebellum at the posterior border of the middle cerebellar peduncle anterior to the biventer lobule. Like other parts of the cerebellum, the flocculus is involved in motor control. It is an essential part of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, and aids in the learning of basic motor skills in the brain.
 W
WThe folium vermis is a short, narrow, concealed band at the posterior extremity of the vermis, consisting apparently of a single folium, but in reality marked on its upper and under surfaces by secondary fissures.
 W
WFronto-cerebellar dissociation is the disconnection and independent function of frontal and cerebellar regions of the brain. It is characterized by inhibited communication between the two regions, and is notably observed in cases of ADHD, schizophrenia, alcohol abuse, and heroin abuse. The frontal and cerebellar regions make distinctive contributions to cognitive performance, with the left-frontal activations being responsible for selecting a response to a stimulus, while the right-cerebellar activation is responsible for the search for a given response to a stimulus. Left-frontal activation increases when there are many appropriate responses to a stimulus, and right-cerebellar activation increases when there is a single appropriate response to a stimulus. A person with dissociated frontal and cerebellar regions may have difficulties with selecting a response to a stimuli, or difficulties with response initiation. Fronto-cerebellar dissociation can often result in either the frontal lobe or the cerebellum becoming more active in place of the less active region as a compensatory effect.
 W
WThe globose nucleus is one of the deep cerebellar nuclei. It is located medial to the emboliform nucleus and lateral to the fastigial nucleus. This nucleus contains primarily large and small multipolar neurons.
 W
WThe cerebellar glomerulus is a small, intertwined mass of nerve fiber terminals in the granular layer of the cerebellar cortex. It consists of post-synaptic granule cell dendrites and pre-synaptic Golgi cell axon terminals surrounding the pre-synaptic terminals of mossy fibers.
 W
WIn neuroscience, Golgi cells are inhibitory interneurons found within the granular layer of the cerebellum. They were first identified as inhibitory by Eccles et al. in 1964. It was also the first example of an inhibitory feed back network, where the inhibitory interneuron was identified anatomically. These cells synapse onto the dendrite of granule cells and unipolar brush cells. They receive excitatory input from mossy fibres, also synapsing on granule cells, and parallel fibers, which are long granule cell axons. Thereby this circuitry allows for feed-forward and feed-back inhibition of granule cells.
 W
WThe name granule cell has been used for a number of different types of neuron whose only common feature is that they all have very small cell bodies. Granule cells are found within the granular layer of the cerebellum, the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the superficial layer of the dorsal cochlear nucleus, the olfactory bulb, and the cerebral cortex.
 W
WGranule-cell to Purkinje-cell synapses or gcPc synapses are the junctions that form the synapse in the cerebellum between granule cells and Purkinje cells. These synapses are thought to be a storage site for the information that is required for motor coordination and their misfunctioning is involved with some movement disorders. Glutamate is the neurotransmitter.
 W
WThe largest and deepest fissure in the cerebellum is named the horizontal fissure.
 W
WThe lingula is a small tongue-shaped process, consisting of four or five folia; it lies in front of the lobulus centralis, and is concealed by it.
 W
WThe nodule, or anterior end of the inferior vermis, abuts against the roof of the fourth ventricle, and can only be distinctly seen after the cerebellum has been separated from the medulla oblongata and pons.
 W
WThe posterior lobe of cerebellum or neocerebellum, is the portion of the cerebellum below the primary fissure.
 W
WThe monticulus of the cerebellum is divided by the primary fissure into an anterior, raised part, the culmen or summit, and a posterior sloped part, the clivus; the quadrangular lobule is similarly divided.
 W
WPurkinje cells, or Purkinje neurons, are a class of GABAergic neurons located in the cerebellum. They are named after their discoverer, Czech anatomist Jan Evangelista Purkyně, who characterized the cells in 1839.
 W
WStellate cells are any neuron in the central nervous system that have a star-like shape formed by dendritic processes radiating from the cell body. Many Stellate cells are GABAergic and are located in the molecular layer of the cerebellum. Stellate cells are derived from dividing progenitors in the white matter of postnatal cerebellum. Dendritic trees can vary between neurons. There are two types of dendritic trees in the cerebral cortex, which include pyramidal cells, which are pyramid shaped and stellate cells which are star shaped. Dendrites can also aid neuron classification. Dendrites with spines are classified as spiny, those without spines are classified as aspinous. Stellate cells can be spiny or aspinous, while pyramidal cells are always spiny. Most common stellate cells are the inhibitory interneurons found within the upper half of the molecular layer in the cerebellum. Cerebellar stellate cells synapse onto the dendritic arbors of Purkinje cells and send inhibitory signals. Stellate neurons are sometimes found in other locations in the central nervous system; cortical spiny stellate cells are found in layer IVC of the V1 region in the visual cortex. In the somatosensory barrel cortex of mice and rats, glutamatergic (excitatory) spiny stellate cells are organized in the barrels of layer 4. They receive excitatory synaptic fibres from the thalamus and process feed forward excitation to 2/3 layer of V1 visual cortex to pyramidal cells. Cortical spiny stellate cells have a 'regular' firing pattern. Stellate cells are chromophobes, that is cells that does not stain readily, and thus appears relatively pale under the microscope.
 W
WThe tuber of vermis, the most posterior division of the inferior vermis, is of small size, and laterally spreads out into the large inferior semilunar lobules, which comprise at least two-thirds of the inferior surface of the hemisphere.
Unipolar brush cells (UBCs) are a class of excitatory glutamatergic interneuron found in the granular layer of the cerebellar cortex and also in the granule cell domain of the cochlear nucleus.
 W
WThe uvula forms a considerable portion of the inferior vermis; it is separated on either side from the tonsil by the sulcus vallecula, at the bottom of which it is connected to the tonsil by a ridge of gray matter, indented on its surface by shallow furrows, and hence called the furrowed band.
 W
WOn the superior surface of cerebellum, the vermis protrudes above the level of the hemispheres, but on the inferior surface it is sunk almost out of sight in the bottom of a deep depression between them; this depression is called the vallecula of the cerebellum, and lodges the posterior part of the medulla oblongata and the inferior vermis, which consists of the tuber vermis, pyramid, uvula and nodule.