 W
WDominican amber is amber from the Dominican Republic derived from resin of the extinct tree Hymenaea protera.
 W
WBlue amber is a rare variety of amber resin that exhibits a blue coloration. Blue amber has been found only in the Dominican Republic—especially in the amber mines around the city of Santiago and, less commonly, in the eastern half of the country. In the modern age, it was discovered at about the same time as Dominican amber.
 W
WThe El Mamey Formation is a geologic formation in the Dominican Republic. The formation consists of shales and sandstones interspersed with a conglomerate of well-rounded pebbles, deposited in a fluvio-deltaic environment. El Mamey Formation is one of the formations containing Dominican amber and preserves fossils dating back to the Burdigalian to Langhian period.
 W
WThe La Toca Formation is a geologic formation in the northern and eastern part of the Dominican Republic. The formation, predominantly an alternating sequence of marls and turbiditic sandstones, breccias and conglomerates, is renowned for the preservation of insects and other arthropods in amber, known as Dominican amber. The formation is dated to the Burdigalian to Langhian stages of the Miocene period.
 W
WThe Yanigua Formation is a geologic formation in Dominican Republic. The lagoonal claystones and marls preserve fossils dating back to the Miocene period. The formation hosts Dominican amber.
 W
WAcanthostichus hispaniolicus is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Dorylinae known from a group of possibly Miocene fossils found on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola. A. hispaniolicus is the first species of the ant genus Acanthostichus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber, and is the only species of Acanthostichus found in the West Indies.
 W
WAcropyga glaesaria is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Formicinae known from a group of possibly Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. A. glaesaria is the first species of the ant genus Acropyga to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is the one of several species of Acropyga found in the West Indies. As with other members of the genus, A. glaesaria was most likely trophobiotic.
 W
WAnochetus ambiguus is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from two possibly Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. A. ambiguus is one of eight species in the ant genus Anochetus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Anochetus species found in the Greater Antillies.
 W
WAnochetus conisquamis is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from one possibly Miocene fossil found on Hispaniola. A. conisquamis is one of eight species in the ant genus Anochetus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Anochetus species found in the Greater Antilles.
 W
WAnochetus corayi is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from one possibly Miocene fossil found on Hispaniola. A. corayi is one of eight species in the ant genus Anochetus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Anochetus species found in the Greater Antillies.
 W
WAnochetus dubius is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from two possibly Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. A. dubius is one of eight species in the ant genus Anochetus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Anochetus species found in the Greater Antillies.
 W
WAnochetus exstinctus is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from two possibly Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. A. exstinctus is one of eight species in the ant genus Anochetus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Anochetus species found in the Greater Antillies.
 W
WAnochetus intermedius is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from two possibly Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. A. intermedius is one of eight species in the ant genus Anochetus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Anochetus species found in the Greater Antilles.
 W
WAnochetus lucidus is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from two possibly Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. A. lucidus is one of eight species in the ant genus Anochetus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Anochetus species found in the Greater Antillies.
 W
WAraneagryllus is an extinct monotypic genus of cricket in the subfamily Phalangopsinae with the sole species Araneagryllus dylani. The fossil was recovered in the Dominican Republic from early Miocene Burdigalian stage Dominican amber deposits on the island of Hispaniola. Araneagryllus is the first Phalangopsinae cricket to be described from the fossil record.
 W
WAzteca alpha is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Dolichoderinae known from possibly Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. A. alpha is one of only two species in the genus Azteca to have been described from fossils, both found in Dominican amber. It is the host for a fossil nematode, and has been preserved with scale insects.
 W
WCephalotes alveolatus is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae known from a single Middle Miocene fossil found in amber on Hispaniola. At the time of description C. alveolatus was one of seven fossil ant species placed in the Cephalotes coffeae clade.
 W
WCephalotes caribicus is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae known from two Middle Miocene fossils found in amber on Hispaniola. At the time of description C. caribicus was one of nine ant species placed in the Cephalotes pinelii clade.
 W
WCephalotes dieteri is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae known from two Middle Miocene fossils found in amber on Hispaniola. At the time of description, C. dieteri was one of seven fossil ant species placed in the Cephalotes coffeae clade.
 W
WCephalotes hispaniolicus is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae known from a single Middle Miocene fossil found in amber on Hispaniola. At the time of description C. hispaniolicus was one of six ant species placed in the Cephalotes multispinosus clade.
 W
WCephalotes integerrimus is an extinct species of arboreal ant of the genus Cephalotes, characterized by an odd shaped head and the ability to "parachute" by steering their fall if they drop off of the tree they're on. Giving their name also as gliding ants. Their larger and flatter legs, a trait common with other members of the genus Cephalotes, gave them their gliding abilities.
 W
WCephalotes jansei is an extinct species of arboreal ant of the genus Cephalotes, originally erroneously called Exocryptocerus jansei by its discoverers, characterized by an odd shaped head and the ability to "parachute" by steering their fall if they drop from a tree, giving them the nickname of gliding ants. The species was probably native of Hispaniola, however, lack of more evidence makes this uncertain. Their larger and flatter legs, a trait common with other members of the genus Cephalotes, gave them their gliding abilities.
 W
WElectromyrmococcus is an extinct genus of mealybug in the Pseudococcidae subfamily Rhizoecinae. The genus currently contains three species, all from the early Miocene, Burdigalian stage, Dominican amber deposits on the island of Hispaniola.
 W
WEnischnomyia is an extinct genus of bat fly in the family Streblidae. At the time of its description the new genus comprised a single species, Enischnomyia stegosoma, known from a single Miocene fossil found on Hispaniola. E. stegosoma was the first fossil streblid bat fly described from a fossil, and the only member of the subfamily Nycterophiliinae described from Hispaniola. The species is host for the plasmodiid Vetufebrus ovatus preserved in its salivary glands and midgut.
 W
WFormicodiplogaster is an extinct form genus of nematodes in the family Diplogasteridae which currently includes a single described species Formicodiplogaster myrmenema. The species is known from early Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. F. myrmenema has been preserved in association with Azteca alpha, one of only two known fossil species in the ant genus Azteca.
 W
WMesembrinella caenozoica is an extinct species of blow fly in the family Mesembrinellidae. The species is solely known from the Middle Miocene Dominican amber deposits on the island of Hispaniola.
 W
WNesagapostemon is an extinct monotypic genus of sweat bee in the Halictidae subfamily Halictinae. At present, it contains the single species Nesagapostemon moronei.
 W
WOdontomachus pseudobauri is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from one possibly Miocene fossil found on Hispaniola. O. pseudobauri is one of two species in the ant genus Odontomachus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Odontomachus species found in the Greater Antilles.
 W
WOdontomachus spinifer is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from one possibly Miocene fossil found on Hispaniola. O. spinifer is one of two species in the ant genus Odontomachus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Odontomachus species found in the Greater Antilles.
 W
WOligochlora is an extinct genus of sweat bee in the Halictidae subfamily Halictinae. The genus currently contains six species, all of which are known from the early Miocene Burdigalian stage Dominican amber deposits on the island of Hispaniola.
 W
WPalaeoplethodon hispaniolae is an extinct salamander species found in Miocene Dominican amber from the Dominican Republic. It is so far the only salamander species known to have existed in the Caribbean.
 W
WPaleoleishmania is an extinct genus of kinetoplastids, a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa. At present it is placed in the family Trypanosomatidae. The genus contains two species, Paleoleishmania neotropicum and the type species Paleoleishmania proterus.
 W
WTermitaradus mitnicki is an extinct species of true bug in the family Termitaphididae known only from early Miocene Burdigalian stage Dominican amber deposits on the island of Hispaniola.
 W
WTriatoma dominicana is an extinct species of assassin bug in the subfamily Triatominae, the kissing bugs known from early Miocene Burdigalian stage Dominican amber deposits on the island of Hispaniola.
 W
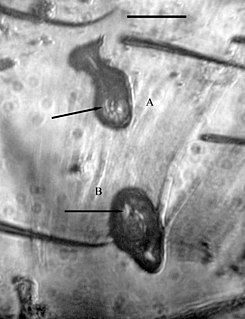
WTrypanosoma antiquus is an extinct species of kinetoplastid, a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa.
 W
WVetufebrus is an extinct genus of haemospororida in the family Plasmodiidae. At the time of its description the new genus comprised a single species Vetufebrus ovatus known from a single Miocene Dominican amber fossil found on Hispaniola. V. ovatus was vectored by Enischnomyia stegosoma, the first fossil streblid bat fly described from a fossil, and the only member of the subfamily Nycterophiliinae described from Hispaniola. V. ovatus is the first instance of a Streblidae bat fly as a host for a malarial parasite.