 W
WPlanktology is the study of plankton, various small drifting plants, animals and microorganisms that inhabit bodies of water. Planktology topics include primary production, energy flow and the carbon cycle.
 W
WPlankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water that are unable to propel themselves against a current. The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales.
 W
WAeroplankton are tiny lifeforms that float and drift in the air, carried by the current of the wind; they are the atmospheric analogue to oceanic plankton.
 W
WAn algae scrubber is a water filtering device which uses light to grow algae; in this process, undesirable chemicals are removed from the water. Algae scrubbers allow saltwater, freshwater and pond hobbyists to operate their tanks using natural filtration in the form of primary production, much like oceans and lakes.
 W
WThe Australian Continuous Plankton Recorder (AusCPR) survey is a joint project of the CSIRO and the Australian Antarctic Division, DEWHA, to monitor plankton communities as a guide to the health of Australia's oceans.
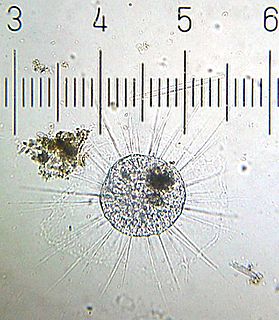 W
WThe axodines are a group of unicellular heterokont algae, previously classified in the Chrysophyceae.
 W
WBacterioplankton refers to the bacterial component of the plankton that drifts in the water column. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word πλανκτος, meaning "wanderer" or "drifter", and bacterium, a Latin term coined in the 19th century by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg. They are found in both seawater and freshwater.
 W
WChaetognatha is a phylum of predatory marine worms that are a major component of plankton worldwide. Commonly known as arrow worms, about 20% of the known Chaetognatha species are benthic, and can attach to algae and rocks. They are found in all marine waters, from surface tropical waters and shallow tide pools to the deep sea and polar regions. Most chaetognaths are transparent and are torpedo shaped, but some deep-sea species are orange. They range in size from 2 to 120 millimetres.
 W
WChemotrophs are organisms that obtain energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic (chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic (chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototrophs, which use solar energy. Chemotrophs can be either autotrophic or heterotrophic. Chemotrophs are found in ocean floors where sunlight cannot reach them because of the great depth and all the levels of water inbetween them and the sun. They evolved to not be dependent on solar energy. Ocean floors often contain underwater volcanos that can provide heat as a substitute for sunlight's warmth.
 W
WA coccolithophore is a unicellular, eukaryotic phytoplankton (alga). They belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker's Five kingdom classification, or clade Hacrobia, according to the newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophorids are in the phylum or division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae. Coccolithophorids are distinguished by special calcium carbonate plates of uncertain function called coccoliths, which are also important microfossils. However, there are Prymnesiophyceae species lacking coccoliths, so not every member of Prymnesiophyceae is a coccolithophorid. Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine and are found in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean.
 W
WDiel vertical migration (DVM), also known as diurnal vertical migration, is a pattern of movement used by some organisms, such as copepods, living in the ocean and in lakes. The migration occurs when organisms move up to the uppermost layer of the sea at night and return to the bottom of the daylight zone of the oceans or to the dense, bottom layer of lakes during the day. The word diel comes from the Latin dies day, and means a 24-hour period. In terms of biomass, it is the greatest migration in the world. It is not restricted to any one taxon as examples are known from crustaceans (copepods), molluscs (squid), and ray-finned fishes (trout). Various stimuli are responsible for this phenomenon, the most prominent being response to changes in light intensity, though evidence suggests that biological clocks are an underlying stimulus as well. The phenomenon may arise for a number of reasons, though it is most typically to access food and avoid predators. While this mass migration is generally nocturnal, with the animals ascending from the depths at nightfall and descending at sunrise, the timing can be altered in response to the different cues and stimuli that trigger it. Some unusual events impact vertical migration: DVM is absent during the midnight sun in Arctic regions and vertical migration can occur suddenly during a solar eclipse.
 W
WDimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2S+CH2CH2COO−. This zwitterionic metabolite can be found in marine phytoplankton, seaweeds, and some species of terrestrial and aquatic vascular plants. It functions as an osmolyte as well as several other physiological and environmental roles have also been identified. DMSP was first identified in the marine red alga Polysiphonia fastigiata.
 W
WGelatinous zooplankton are fragile animals that live in the water column in the ocean. Their delicate bodies have no hard parts and are easily damaged or destroyed. Gelatinous zooplankton are often transparent. All jellyfish are gelatinous zooplankton, but not all gelatinous zooplankton are jellyfish. The most commonly encountered organisms include ctenophores, medusae, salps, and Chaetognatha in coastal waters. However, almost all marine phyla, including Annelida, Mollusca and Arthropoda, contain gelatinous species, but many of those odd species live in the open ocean and the deep sea and are less available to the casual ocean observer. Many gelatinous plankters utilize mucous structures in order to filter feed. Gelatinous zooplankton have also been called "Gelata".
 W
WHoloplankton are organisms that are planktic for their entire life cycle. Holoplankton can be contrasted with meroplankton, which are planktic organisms that spend part of their life cycle in the benthic zone. Examples of holoplankton include some diatoms, radiolarians, some dinoflagellates, foraminifera, amphipods, krill, copepods, and salps, as well as some gastropod mollusk species. Holoplankton dwell in the pelagic zone as opposed to the benthic zone. Holoplankton include both phytoplankton and zooplankton and vary in size. The most common plankton are protists.
 W
WIchthyoplankton are the eggs and larvae of fish. They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epipelagic or photic zone. Ichthyoplankton are planktonic, meaning they cannot swim effectively under their own power, but must drift with the ocean currents. Fish eggs cannot swim at all, and are unambiguously planktonic. Early stage larvae swim poorly, but later stage larvae swim better and cease to be planktonic as they grow into juveniles. Fish larvae are part of the zooplankton that eat smaller plankton, while fish eggs carry their own food supply. Both eggs and larvae are themselves eaten by larger animals.
 W
WThe Journal of Plankton Research is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on plankton. It is published by Oxford University Press and the editor-in-chief is John R. Dolan. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2018 impact factor of 2.209.
 W
WMarine microorganisms are defined by their habitat as the microorganisms living in a marine environment, that is, in the saltwater of a sea or ocean or the brackish water of a coastal estuary. A microorganism is any microscopic living organism, that is, any life form too small for the naked human eye to really see, needing a microscope. Microorganisms are very diverse. They can be single-celled or multicellular and include all bacteria and archaea and most protozoa, as well as some species of fungi, algae, and certain microscopic animals, such as rotifers and copepods. Many macroscopic animals and plants have microscopic juvenile stages. Some microbiologists also classify biologically active entities such as viruses and viroids as microorganisms, but others consider these as non-living.
 W
WMarine prokaryotes are marine bacteria and marine archaea. They are defined by their habitat as prokaryotes that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. All cellular life forms can be divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, whereas prokaryotes are the organisms that do not have a nucleus enclosed within a membrane. The three-domain system of classifying life adds another division: the prokaryotes are divided into two domains of life, the microscopic bacteria and the microscopic archaea, while everything else, the eukaryotes, become the third domain.
 W
WMarine protists are defined by their habitat as protists that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. Life originated as single-celled prokaryotes and later evolved into more complex eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are the more developed life forms known as plants, animals, fungi and protists. Protists are the eukaryotes that cannot be classified as plants, fungi or animals. They are usually single-celled and microscopic. The term protist came into use historically as a term of convenience for eukaryotes that cannot be strictly classified as plants, animals or fungi. They are not a part of modern cladistics, because they are paraphyletic.
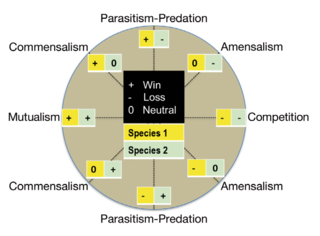 W
WMicrobial symbiosis in marine animals was not discovered until 1981. In the time following, symbiotic relationships between marine invertebrates and chemoautotrophic bacteria have been found in a variety of ecosystems, ranging from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Symbiosis is a way for marine organisms to find creative ways to survive in a very dynamic environment. They are different in relation to how dependent the organisms are on each other or how they are associated. It is also considered a selective force behind evolution in some scientific aspects. The symbiotic relationships of organisms has the ability to change behavior, morphology and metabolic pathways. With increased recognition and research, new terminology also arises, such as holobiont, which the relationship between a host and its symbionts as one grouping. Many scientists will look at the hologenome, which is the combined genetic information of the host and its symbionts. These terms are more commonly used to describe microbial symbionts.
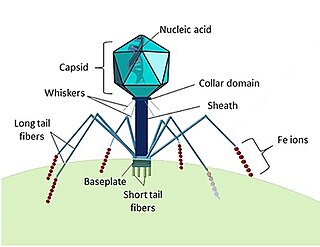 W
WMarine viruses are defined by their habitat as viruses that are found in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. Viruses are small infectious agents that can only replicate inside the living cells of a host organism, because they need the replication machinery of the host to do so. They can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
 W
WMeroplankton are a wide variety of aquatic organisms which have both planktonic and benthic stages in their life cycles. Much of the meroplankton consists of larval stages of larger organism. Meroplankton can be contrasted with holoplankton, which are planktonic organisms that stay in the pelagic zone as plankton throughout their entire life cycle.
 W
WMicroalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae, typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist individually, or in chains or groups. Depending on the species, their sizes can range from a few micrometers (μm) to a few hundred micrometers. Unlike higher plants, microalgae do not have roots, stems, or leaves. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces. Microalgae, capable of performing photosynthesis, are important for life on earth; they produce approximately half of the atmospheric oxygen and use simultaneously the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide to grow photoautotrophically. Microalgae, together with bacteria, form the base of the food web and provide energy for all the trophic levels above them. Microalgae biomass is often measured with chlorophyll a concentrations and can provide a useful index of potential production.
 W
WMycoplankton are saprotropic members of the plankton communities of marine and freshwater ecosystems. They are composed of filamentous free-living fungi and yeasts that are associated with planktonic particles or phytoplankton. Similar to bacterioplankton, these aquatic fungi play a significant role in heterotrophic mineralization and nutrient cycling. Mycoplankton can be up to 20 mm in diameter and over 50 mm in length.
 W
WNanophytoplankton are particularly small phytoplankton with sizes between 2 and 20 µm. They are the autotrophic part of nanoplankton. Like other phytoplankton, nanophytoplankton are microscopic organisms that obtain energy through the process of photosynthesis and must therefore live in the upper sunlit layer of ocean or other bodies of water. These microscopic free-floating organisms, including algae, and cyanobacteria, fix large amounts of carbon which would otherwise be released as carbon dioxide.. The term nanophytoplankton is derived from the far more widely used term nannoplankton/nanoplankton.
 W
WIn aquatic biology, the paradox of the plankton describes the situation in which a limited range of resources supports an unexpectedly wide range of plankton species, apparently flouting the competitive exclusion principle which holds that when two species compete for the same resource, one will be driven to extinction.
 W
WParasagitta elegans is a small arrow worm in the family Sagittidae, previously named Sagitta elegans
 W
WThe order Pennales is a traditional subdivision of the heterokont algae known as diatoms. The order is named for the shape of the cell walls of pennate diatoms, which are elongated in valve view. The valves may be linear or oval in shape, and usually bear bilaterally symmetrical ornamental patterns. These patterns are composed of a series of transverse lines that can appear as rows of dots when viewed with an optical microscope. Some pennate diatoms also exhibit a fissure along their longitudinal axis. This is known as a raphe, and is involved in gliding movements made by diatom cells; motile diatoms always possess a raphe.
 W
WPhotosynthetic picoplankton or picophytoplankton is the fraction of the phytoplankton performing photosynthesis composed by cells between 0.2 and 2 µm (picoplankton). It is especially important in the central oligotrophic regions of the world oceans that have very low concentration of nutrients.
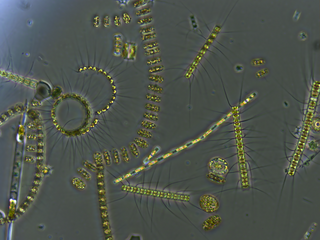 W
WPhytoplankton are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of oceans, seas and freshwater basin ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν (phyton), meaning "plant", and πλαγκτός (planktos), meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye. However, when present in high enough numbers, some varieties may be noticeable as colored patches on the water surface due to the presence of chlorophyll within their cells and accessory pigments in some species. About 1% of the global biomass is due to phytoplankton.
 W
WPicoeukaryotes are picoplanktonic eukaryotic organisms 3.0 µm or less in size. They are distributed throughout the world’s marine and freshwater ecosystems and constitute a significant contribution to autotrophic communities. Though the SI prefix pico- might imply an organism smaller than atomic size, the term was likely used to avoid confusion with existing size classifications of plankton.
 W
WPicoplankton is the fraction of plankton composed by cells between 0.2 and 2 μm that can be either prokaryotic and eukaryotic phototrophs and heterotrophs:photosynthetic heterotrophic
 W
WA Plankton net is equipment used for collecting samples of plankton in standing bodies of water. It consists of a towing line and bridles, nylon mesh net, and a cod end. Plankton nets are considered one of the oldest, simplest and inexpensive methods of sampling plankton. The plankton net can be used for both vertical and horizontal sampling. It allows researchers to analyse plankton both quantitatively and qualitatively in water samples from the environment.
 W
WThe SCAR Southern Ocean Continuous Plankton Recorder (SO-CPR) Survey was established in 1991 by the Australian Antarctic Division,of Environment, Water Heritage and the Arts, to map the spatial-temporal patterns of zooplankton and then to use the sensitivity of plankton to environmental change as early warning indicators of the health of the Southern Ocean. It also serves as reference for other Southern Ocean and Antarctic monitoring programs.
 W
WThin layers are concentrated aggregations of phytoplankton and zooplankton in coastal and offshore waters that are vertically compressed to thicknesses ranging from several centimeters up to a few meters and are horizontally extensive, sometimes for kilometers. Generally, thin layers have three basic criteria: 1) they must be horizontally and temporally persistent; 2) they must not exceed a critical threshold of vertical thickness; and 3) they must exceed a critical threshold of maximum concentration. The precise values for critical thresholds of thin layers has been debated for a long time due to the vast diversity of plankton, instrumentation, and environmental conditions. Thin layers have distinct biological, chemical, optical, and acoustical signatures which are difficult to measure with traditional sampling techniques such as nets and bottles. However, there has been a surge in studies of thin layers within the past two decades due to major advances in technology and instrumentation. Phytoplankton are often measured by optical instruments that can detect fluorescence such as LIDAR, and zooplankton are often measured by acoustic instruments that can detect acoustic backscattering such as ABS. These extraordinary concentrations of plankton have important implications for many aspects of marine ecology, as well as for ocean optics and acoustics. It is important to note that zooplankton thin layers are often found slightly under phytoplankton layers because many feed on them. Thin layers occur in a wide variety of ocean environments, including estuaries, coastal shelves, fjords, bays, and the open ocean, and they are often associated with some form of vertical structure in the water column, such as pycnoclines, and in zones of reduced flow.
 W
WZooplankton are heterotrophic plankton. Plankton are organisms drifting in oceans, seas, and bodies of fresh water. The word zooplankton is derived from the Greek zoon (ζῴον), meaning "animal", and planktos (πλαγκτός), meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Individual zooplankton are usually microscopic, but some are larger and visible to the naked eye.