 W
WVespertilionidae is a family of microbats, of the order Chiroptera, flying, insect-eating mammals variously described as the common, vesper, or simple nosed bats. The vespertilionid family is the most diverse and widely distributed of bat families, specialised in many forms to occupy a range of habitats and ecological circumstances, and it is frequently observed or the subject of research. The facial features of the species are often simple, as they mainly rely on vocally emitted echolocation. The tails of the species are enclosed by the lower flight membranes between the legs. Over 300 species are distributed all over the world, on every continent except Antarctica. It owes its name to the genus Vespertilio, which takes its name from a word for bat, vespertilio, derived from the Latin term vesper meaning 'evening'; they are termed as evening bats and once referred to as 'evening birds'.
 W
WAeorestes is a genus of vesper bat commonly known as the hoary bats. This genus includes species that were formerly included in the genus Lasiurus.
 W
WAllen's big-eared bat is a species of vesper bat in the monotypic genus Idionycteris. It occurs in Mexico and in Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Colorado in the United States.
 W
WAntrozoini is a tribe of bats in the subfamily Vespertilioninae of the family Vespertilionidae. It includes at least the pallid bat, Van Gelder's bat, and the fossil Anzanycteris; some classifications also include the genera Rhogeessa and Baeodon.
 W
WThe pallid bat is a species of bat that ranges from western Canada to central Mexico. It is the sole species of its genus and is closely related to Van Gelder's bat, which is sometimes included in Antrozous. Although it has in the past been placed in its own subfamily (Antrozoinae) or even family (Antrozoidae), it is now considered part of the subfamily Vespertilioninae and the tribe Antrozoini.
 W
WAllen's yellow bat is a species of vesper bat. There is some taxonomic debate surrounding this species, with some authors considering Baeodon a genus rather than a subgenus. It is endemic to Mexico.
 W
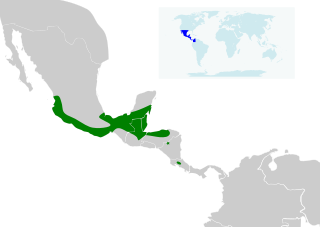
WVan Gelder's bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found in Belize, Costa Rica, Honduras, and Mexico. The species is monotypic within its genus. It is part of the tribe Antrozoini within the subfamily Vespertilioninae and is related to the pallid bat. The bat is found in forest habitat from sea level to elevations as high as 2300 m, although not usually above 1300 m, and is insectivorous and crepuscular. It apparently has a fragmented distribution, and is threatened by deforestation.
 W
WThe canyon bat, also known as the western pipistrelle, is a species of vesper bat. It is found in Mexico and in the western United States. The species has historically been placed in the genus Pipistrellus, but molecular evidence does not show any close relationship with that genus, and accordingly it was classified into its own genus, Parastrellus, in 2006.
 W
WThe spotted bat is a species of vesper bat and the only species of the genus Euderma.
 W
WThe great evening bat is the largest bat in the vesper bat family (Vespertilionidae) and the only living species in the genus Ia. It is common to Eastern and Southeastern Asia, mainly living in areas with limestone caves at altitudes of 400–1,700 metres (0.25–1.06 mi). Their roost sites have been found both near the cave entrances and up to 1.5 kilometres (0.93 mi) within the cave systems.
 W
WThe harlequin bat is a species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae, the vesper bats. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Scotomanes.
 W
WAllen's big-eared bat is a species of vesper bat in the monotypic genus Idionycteris. It occurs in Mexico and in Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Colorado in the United States.
 W
WThe silver-haired bat is a solitary migratory species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae and the only member of the genus Lasionycteris.
 W
WLasiurus is the genus comprising hairy-tailed bats.
 W
WMoloney's mimic bat is a species of vesper bat. It can be found in Angola, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, Mozambique, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, and Zambia. It is found in subtropical or tropical dry or moist forests, subtropical or tropical mangrove forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, dry and moist savanna.
 W
WMoloney's mimic bat is a species of vesper bat. It can be found in Angola, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, Mozambique, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, and Zambia. It is found in subtropical or tropical dry or moist forests, subtropical or tropical mangrove forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, dry and moist savanna.
 W
WThe New Guinea big-eared bat, species Pharotis imogene, is a vespertilionid bat endemic to Papua New Guinea. It is listed as a critically endangered species due to ongoing habitat loss. It is the only known member of the genus Pharotis, which is closely related to Nyctophilus.
 W
WThe pied bat, or badger bat, is a rare species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. If recognised as a valid genus, Niumbaha contains only this species. The distinctive pied bat partly resembles a bee, with light yellow stripes and blotches on its body, the stripes being primarily on its back. Biology professor DeeAnn Reeder, one of the authors of the genus Niumbaha, said, "its cranial characters, its wing characters, its size, the ears – literally everything you look at doesn't fit. It's so unique that we need to create a new genus." However, despite appearances, more recent work shows that superba is deeply embedded within Glauconycteris and should be returned to that genus, making Niumbaha a junior synonym of Glauconycteris.
 W
WSchlieffen's bat or Schlieffen's twilight bat is a species of vesper bat found in Africa. It has been placed in numerous genera since its first description in 1859, but morphological and genetic studies have confirmed it as the only species in the genus Nycticeinops. It is named for the collector of the original specimen, Wilhelm von Schlieffen-Schlieffiennburg.
 W
WThe pallid bat is a species of bat that ranges from western Canada to central Mexico. It is the sole species of its genus and is closely related to Van Gelder's bat, which is sometimes included in Antrozous. Although it has in the past been placed in its own subfamily (Antrozoinae) or even family (Antrozoidae), it is now considered part of the subfamily Vespertilioninae and the tribe Antrozoini.
 W
WThe canyon bat, also known as the western pipistrelle, is a species of vesper bat. It is found in Mexico and in the western United States. The species has historically been placed in the genus Pipistrellus, but molecular evidence does not show any close relationship with that genus, and accordingly it was classified into its own genus, Parastrellus, in 2006.
 W
WThe tricolored bat is a species of microbat native to eastern North America. Formerly known as the eastern pipistrelle, based on the errant belief that it was closely related to European Pipistrellus species, the closest known relative of the tricolored bat is now recognized as the canyon bat. Its common name "tricolored bat" derives from the coloration of the hairs on its back, which have three distinct color bands. It is the smallest bat species in the eastern and midwestern US, with individuals weighing only 4.6–7.9 g (0.16–0.28 oz). This species mates in the fall before hibernation, though due to sperm storage, females do not become pregnant until the spring. Young are born helpless, though rapidly develop, flying and foraging for themselves by four weeks old. It has a relatively long lifespan, and can live nearly fifteen years.
 W
WThe New Guinea big-eared bat, species Pharotis imogene, is a vespertilionid bat endemic to Papua New Guinea. It is listed as a critically endangered species due to ongoing habitat loss. It is the only known member of the genus Pharotis, which is closely related to Nyctophilus.
 W
WRohu's bat is a species of vesper bat. It belongs to the monotypic genus Philetor. It is found in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Nepal, Papua New Guinea, and the Philippines.
 W
WRohu's bat is a species of vesper bat. It belongs to the monotypic genus Philetor. It is found in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Nepal, Papua New Guinea, and the Philippines.
 W
WThe pied bat, or badger bat, is a rare species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. If recognised as a valid genus, Niumbaha contains only this species. The distinctive pied bat partly resembles a bee, with light yellow stripes and blotches on its body, the stripes being primarily on its back. Biology professor DeeAnn Reeder, one of the authors of the genus Niumbaha, said, "its cranial characters, its wing characters, its size, the ears – literally everything you look at doesn't fit. It's so unique that we need to create a new genus." However, despite appearances, more recent work shows that superba is deeply embedded within Glauconycteris and should be returned to that genus, making Niumbaha a junior synonym of Glauconycteris.
 W
WRohu's bat is a species of vesper bat. It belongs to the monotypic genus Philetor. It is found in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Nepal, Papua New Guinea, and the Philippines.
 W
WRüppell's or the greater broad-nosed bat is a species of vespertilionid microbat found in eastern Australia.
 W
WSchlieffen's bat or Schlieffen's twilight bat is a species of vesper bat found in Africa. It has been placed in numerous genera since its first description in 1859, but morphological and genetic studies have confirmed it as the only species in the genus Nycticeinops. It is named for the collector of the original specimen, Wilhelm von Schlieffen-Schlieffiennburg.
 W
WRüppell's or the greater broad-nosed bat is a species of vespertilionid microbat found in eastern Australia.
 W
WThe harlequin bat is a species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae, the vesper bats. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Scotomanes.
 W
WThe silver-haired bat is a solitary migratory species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae and the only member of the genus Lasionycteris.
 W
WThe spotted bat is a species of vesper bat and the only species of the genus Euderma.
 W
WThe tricolored bat is a species of microbat native to eastern North America. Formerly known as the eastern pipistrelle, based on the errant belief that it was closely related to European Pipistrellus species, the closest known relative of the tricolored bat is now recognized as the canyon bat. Its common name "tricolored bat" derives from the coloration of the hairs on its back, which have three distinct color bands. It is the smallest bat species in the eastern and midwestern US, with individuals weighing only 4.6–7.9 g (0.16–0.28 oz). This species mates in the fall before hibernation, though due to sperm storage, females do not become pregnant until the spring. Young are born helpless, though rapidly develop, flying and foraging for themselves by four weeks old. It has a relatively long lifespan, and can live nearly fifteen years.
 W
WVan Gelder's bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found in Belize, Costa Rica, Honduras, and Mexico. The species is monotypic within its genus. It is part of the tribe Antrozoini within the subfamily Vespertilioninae and is related to the pallid bat. The bat is found in forest habitat from sea level to elevations as high as 2300 m, although not usually above 1300 m, and is insectivorous and crepuscular. It apparently has a fragmented distribution, and is threatened by deforestation.
 W
WThe Vespertilioninae are a subfamily of vesper bats from the family Vespertilionidae.