 W
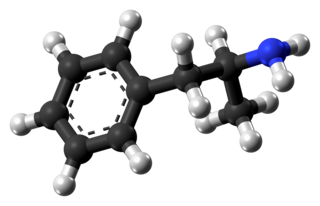
WAmphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant marketed under the brand name Evekeo, among others. It is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. Amphetamine was discovered in 1887 and exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers, levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine, in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.
 W
WAdderall and Mydayis are trade names for a combination drug containing four salts of amphetamine. The mixture is composed of equal parts racemic amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, which produces a (3:1) ratio between dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine, the two enantiomers of amphetamine. Both enantiomers are stimulants, but differ enough to give Adderall an effects profile distinct from those of racemic amphetamine or dextroamphetamine, which are marketed as Evekeo and Dexedrine/Zenzedi, respectively. Adderall is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance enhancer, cognitive enhancer, appetite suppressant, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the phenethylamine class.
 W
WAttention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, or excessive activity and impulsivity, which are otherwise not appropriate for a person's age. Some individuals with ADHD also display difficulty regulating emotions or problems with executive function. For a diagnosis, the symptoms should appear before a person is twelve years old, be present for more than six months, and cause problems in at least two settings. In children, problems paying attention may result in poor school performance. Additionally, there is an association with other mental disorders and substance misuse. Although it causes impairment, particularly in modern society, many people with ADHD can have sustained attention for tasks they find interesting or rewarding.
 W
WCocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript, also known as CART, is a neuropeptide protein that in humans is encoded by the CARTPT gene. CART appears to have roles in reward, feeding, and stress, and it has the functional properties of an endogenous psychostimulant.
 W
WCytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP2D6 gene. CYP2D6 is primarily expressed in the liver. It is also highly expressed in areas of the central nervous system, including the substantia nigra.
 W
WProtein fosB, also known as FosB and G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 3 (G0S3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (FOSB) gene.
 W
WDextroamphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and an amphetamine enantiomer that is prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. Dextroamphetamine was also used in the past by some countries' military forces to fight fatigue during extended combat operations.
 W
WDopamine is a hormone and a neurotransmitter that plays several important roles in the brain and body. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor chemical L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons to send signals to other nerve cells. The brain includes several distinct dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward-motivated behavior. The anticipation of most types of rewards increases the level of dopamine in the brain, and many addictive drugs increase dopamine release or block its reuptake into neurons following release. Other brain dopamine pathways are involved in motor control and in controlling the release of various hormones. These pathways and cell groups form a dopamine system which is neuromodulatory.
 W
WDopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH), also known as dopamine beta-monooxygenase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DBH gene. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase catalyzes the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine.
 W
WThe dopamine transporter is a membrane-spanning protein that pumps the neurotransmitter dopamine out of the synaptic cleft back into cytosol. In the cytosol, other transporters sequester the dopamine into vesicles for storage and later release. Dopamine reuptake via DAT provides the primary mechanism through which dopamine is cleared from synapses, although there may be an exception in the prefrontal cortex, where evidence points to a possibly larger role of the norepinephrine transporter.
 W
WExcitatory amino acid transporter 3 (EAAT3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC1A1 gene.
 W
WFlavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), also known as dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 3 and trimethylamine monooxygenase, is a flavoprotein enzyme (EC 1.14.13.148) that in humans is encoded by the FMO3 gene. This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction:trimethylamine + NADPH + H+ + O2 trimethylamine N-oxide + NADP+ + H2O
 W
WFormetorex (INN), also known as formetamide or N-formylamphetamine, is a substituted amphetamine described as an anorectic which does not appear to have ever been marketed.
 W
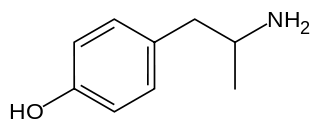
W4-Hydroxyamphetamine (4HA), also known as hydroxyamfetamine, hydroxyamphetamine, oxamphetamine, norpholedrine, para-hydroxyamphetamine, and α-methyltyramine, is a drug that stimulates the sympathetic nervous system.
 W
Wp-Hydroxynorephedrine (PHN), or 4-hydroxynorephedrine, is the para-hydroxy analog of norephedrine and an active sympathomimetic metabolite of amphetamine in humans. When it occurs as a metabolite of amphetamine, it is produced from both p-hydroxyamphetamine and norephedrine.
 W
WLevoamphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant known to increase wakefulness and concentration in association with decreased appetite and fatigue. Pharmaceuticals that contain levoamphetamine are currently indicated and prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obesity, and narcolepsy in some countries.
 W
WLisdexamfetamine, sold under the brand name Vyvanse among others, is a medication that is a derivative of amphetamine. It is mainly used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in people over the age of five as well as moderate-to-severe binge eating disorder in adults. Lisdexamfetamine is taken by mouth. In the United Kingdom it is usually less preferred than methylphenidate. Its effects generally begin within 2 hours and last for up to 12 hours.
 W
WN-Methylphenethylamine (NMPEA) is a naturally occurring trace amine neuromodulator in humans that is derived from the trace amine, phenethylamine (PEA). It has been detected in human urine and is produced by phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase with phenethylamine as a substrate. PEA and NMPEA are both alkaloids that are found in a number of different plant species as well. Some Acacia species, such as A. rigidula, contain remarkably high levels of NMPEA. NMPEA is also present at low concentrations in a wide range of foodstuffs.
 W
WMonoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
 W
WMonoamine oxidases (MAO) are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group. They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body. The first such enzyme was discovered in 1928 by Mary Bernheim in the liver and was named tyramine oxidase. The MAOs belong to the protein family of flavin-containing amine oxidoreductases.
 W
WNarcolepsy is a long-term neurological disorder that involves a decreased ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. Symptoms often include periods of excessive daytime sleepiness and brief involuntary sleep episodes. About 70% of those affected also experience episodes of sudden loss of muscle strength, known as cataplexy. These experiences can be brought on by strong emotions. Less commonly, there may be vivid hallucinations or an inability to move while falling asleep or waking up. People with narcolepsy tend to sleep about the same number of hours per day as people without, but the quality of sleep tends to be lessened.
 W
WThe neurobiological effects of physical exercise are numerous and involve a wide range of interrelated effects on brain structure, brain function, and cognition. A large body of research in humans has demonstrated that consistent aerobic exercise induces persistent improvements in certain cognitive functions, healthy alterations in gene expression in the brain, and beneficial forms of neuroplasticity and behavioral plasticity; some of these long-term effects include: increased neuron growth, increased neurological activity, improved stress coping, enhanced cognitive control of behavior, improved declarative, spatial, and working memory, and structural and functional improvements in brain structures and pathways associated with cognitive control and memory. The effects of exercise on cognition have important implications for improving academic performance in children and college students, improving adult productivity, preserving cognitive function in old age, preventing or treating certain neurological disorders, and improving overall quality of life.
 W
WNootropics are drugs, supplements, and other substances that claim to improve cognitive function, particularly executive functions, memory, creativity, or motivation, in healthy individuals. While many substances are purported to improve cognition, research is at a preliminary stage as of 2020, and the effects of the majority of these agents are not fully determined.
 W
WPhenylpropanolamine (PPA) is a sympathomimetic agent which is used as a decongestant and appetite suppressant. It was commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter cough and cold preparations. In veterinary medicine, it is used to control urinary incontinence in dogs.
 W
WNorepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline", derived from Latin roots meaning "at/alongside the kidneys", is more commonly used in the United Kingdom; in the United States, "norepinephrine", derived from Greek roots having that same meaning, is usually preferred. "Norepinephrine" is also the international nonproprietary name given to the drug. Regardless of which name is used for the substance itself, parts of the body that produce or are affected by it are referred to as noradrenergic.
 W
WThe norepinephrine transporter (NET), also known as noradrenaline transporter (NAT) and solute carrier family 6 member 2 (SLC6A2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A2 gene.
 W
WObesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to an extent that it may have a negative effect on health. People are generally considered obese when their body mass index (BMI), a measurement obtained by dividing a person's weight by the square of the person's height—despite known allometric inaccuracies—is over 30 kg/m2; the range 25–30 kg/m2 is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values. Obesity is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. High BMI is a marker of risk, but not proven to be a direct cause, for diseases caused by diet, physical activity, and environmental factors. A reciprocal link has been found between obesity and depression, with obesity increasing the risk of clinical depression and also depression leading to a higher chance of developing obesity.
 W
WPhenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and inhibiting vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) in monoamine neurons. To a lesser extent, it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system. In mammals, phenethylamine is produced from the amino acid L-phenylalanine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase via enzymatic decarboxylation. In addition to its presence in mammals, phenethylamine is found in many other organisms and foods, such as chocolate, especially after microbial fermentation.
 W
WPhentermine (phenyl-tertiary-butylamine), sold under the brand name Ionamin among others, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is taken by mouth for up to a few weeks. After a few weeks the beneficial effects no longer occur. It is also available as the combination phentermine/topiramate.
 W
WPhenylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2COCH3. It is a colorless oil that is soluble in organic solvents. This substance is used in the manufacture of methamphetamine and amphetamine, where it is commonly known as P2P. Due to the illicit uses in clandestine chemistry, it was declared a schedule II controlled substance in the United States in 1980. In humans, phenylacetone occurs as a metabolite of amphetamine and methamphetamine via FMO3-mediated oxidative deamination.
 W
WThe serotonin transporter also known as the sodium-dependent serotonin transporter and solute carrier family 6 member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A4 gene. SERT is a type of monoamine transporter protein that transports serotonin from the synaptic cleft back to the presynaptic neuron.
 W
WSolute carrier family 22 member 3 (SLC22A3) also known as the organic cation transporter 3 (OCT3) or extraneuronal monoamine transporter (EMT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC22A3 gene.
 W
WSLC22A5 is a membrane transport protein associated with primary carnitine deficiency. This protein is involved in the active cellular uptake of carnitine. It acts a symporter, moving sodium ions and other organic cations across the membrane along with carnitine. Such polyspecific organic cation transporters in the liver, kidney, intestine, and other organs are critical for the elimination of many endogenous small organic cations as well as a wide array of drugs and environmental toxins. Mutations in the SLC22A5 gene cause systemic primary carnitine deficiency, which can lead to heart failure.
 W
WTrace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) is a trace amine-associated receptor (TAAR) protein that in humans is encoded by the TAAR1 gene. TAAR1 is an intracellular amine-activated Gs-coupled and Gq-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is primarily expressed in several peripheral organs and cells, astrocytes, and in the intracellular milieu within the presynaptic plasma membrane of monoamine neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). TAAR1 was discovered in 2001 by two independent groups of investigators, Borowski et al. and Bunzow et al. TAAR1 is one of six functional human trace amine-associated receptors, which are so named for their ability to bind endogenous amines that occur in tissues at trace concentrations. TAAR1 plays a significant role in regulating neurotransmission in dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin neurons in the CNS; it also affects immune system and neuroimmune system function through different mechanisms.
 W
WTrace amines are an endogenous group of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonists – and hence, monoaminergic neuromodulators – that are structurally and metabolically related to classical monoamine neurotransmitters. Compared to the classical monoamines, they are present in trace concentrations. They are distributed heterogeneously throughout the mammalian brain and peripheral nervous tissues and exhibit high rates of metabolism. Although they can be synthesized within parent monoamine neurotransmitter systems, there is evidence that suggests that some of them may comprise their own independent neurotransmitter systems.
 W
WVesicular monoamine transporter 1 (VMAT1) also known as chromaffin granule amine transporter (CGAT) or solute carrier family 18 member 1 (SLC18A1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC18A1 gene. VMAT1 is an integral membrane protein, which is embedded in synaptic vesicles and serves to transfer monoamines, such as norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin, between the cytosol and synaptic vesicles. SLC18A1 is an isoform of the vesicular monoamine transporter.
 W
WThe vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) also known as solute carrier family 18 member 2 (SLC18A2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC18A2 gene. VMAT2 is an integral membrane protein that transports monoamines—particularly neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and histamine—from cellular cytosol into synaptic vesicles. In nigrostriatal pathway and mesolimbic pathway dopamine-releasing neurons, VMAT2 function is also necessary for the vesicular release of the neurotransmitter GABA.