 W
WChild labour refers to the exploitation of children through any form of work that deprives children of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend regular school, and is mentally, physically, socially or morally harmful. Such exploitation is prohibited by legislation worldwide, although these laws do not consider all work by children as child labour; exceptions include work by child artists, family duties, supervised training, and some forms of child work practiced by Amish children, as well as by indigenous children in the Americas.
 W
WA breaker boy was a coal-mining worker in the United States and United Kingdom whose job was to separate impurities from coal by hand in a coal breaker. Although breaker boys were primarily children, elderly coal miners who could no longer work in the mines because of age, disease, or accident were also sometimes employed as breaker boys. The use of breaker boys began in the mid-1860s. Although public disapproval of the employment of children as breaker boys existed by the mid-1880s, the practice did not end until the 1920s.
 W
WA cabin boy or ship's boy is a boy who waits on the officers and passengers of a ship, especially running errands for the captain. The modern merchant navy successor to the cabin boy is the steward's assistant.
 W
WCamel racing is a popular sport in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Pakistan, Mongolia and Australia. Professional camel racing, like horse racing, is an event for betting and tourist attraction. Camels can run at speeds up to 65 km/h in short sprints and they can maintain a speed of 40 km/h for an hour. Camels are often controlled by child jockeys, but allegations of human rights abuses have led to nationwide bans on underage labor in the UAE and Qatar. In modern camel racing, camels are often controlled by remote controlled robotic whips.
 W
WChild labour in Africa is generally defined based on two factors: type of work and minimum appropriate age of the work. If a child is involved in an activity that is harmful to his/her physical and mental development, he/she is generally considered as a child labourer. That is, Any work that is mentally, physically, socially or morally dangerous and harmful to children, and interferes with their schooling by depriving them of the opportunity to attend school or requiring them to attempt to combine school attendance with excessively long and heavy work. Appropriate minimum age for each work depends on the effects of the work on the physical health and mental development of children. ILO Convention No. 138 suggests the following minimum age for admission to employment under which, if a child works, he/she is considered as a child laborer: 18 years old for hazardous works, and 13–15 years old for light works, although 12–14 years old may be permitted for light works under strict conditions in very poor countries. Another definition proposed by ILO’s Statistical Information and Monitoring Program on Child Labor (SIMPOC) defines a child as a child labourer if he/she is involved in an economic activity, and is under 12 years old and works one or more hours per week, or is 14 years old or under and works at least 14 hours per week, or is 14 years old or under and works at least one hour per week in activities that are hazardous, or is 17 or under and works in an “unconditional worst form of child labor”.
 W
WCôte d’Ivoire and Ghana, together, produce nearly 60% of the world’s cocoa each year. During the 2018/19 cocoa-growing season, research commissioned by the U.S Department of Labor was conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago in these two countries and found that 1.48 million children are engaged in hazardous work on cocoa farms including working with sharp tools and agricultural chemicals and carrying heavy loads. That number of children is significant, representing 43 percent of all children living in agricultural households in cocoa growing areas. During the same period cocoa production in Cote d’Ivoire and Ghana increased 62 percent while the prevalence of child labor in cocoa production among all agricultural households increased 14 percentage points. Attention on this subject has focused on West Africa, which collectively supplies 69% of the world's cocoa, Côte d'Ivoire in particular, supplying 35%. The 2016 Global Estimates of Child Labour indicate that one-fifth of all African children are involved in child labor. Nine percent of African children are in hazardous work. It is estimated that more than 1.8 million children in West Africa are involved in growing cocoa. A 2013-14 survey commissioned by the Department of Labor and conducted by Tulane University found that an estimated 1.4 million children aged 5 years old to 11 years old worked in agriculture in cocoa-growing areas, while approximately 800,000 of them were engaged in hazardous work, including working with sharp tools and agricultural chemicals and carrying heavy loads. According to the NORC study, methodological differences between the 2018/9 survey and earlier ones, together with errors in the administration of the 2013/4 survey have made it challenging to document changes in the number of children engaged in child labor over the past five years.
 W
WChild slavery is the slavery of children. The enslavement of children can be traced back through history. Even after the abolition of slavery, children continue to be enslaved and trafficked in modern times, which is a particular problem in developing countries.
 W
WA chimney sweep is a person who clears ash and soot from chimneys. The chimney uses the pressure difference caused by a hot column of gas to create a draught and draw air over the hot coals or wood enabling continued combustion. Chimneys may be straight or contain many changes of direction. During normal operation, a layer of creosote builds up on the inside of the chimney, restricting the flow. The creosote can also catch fire, setting the chimney and the building alight. The chimney must be swept to remove the soot. This was done by the master sweep.
 W
WCobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. Like nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.
 W
WColtan is a dull black metallic ore from which are extracted the elements niobium and tantalum. The niobium-dominant mineral in coltan is columbite, and the tantalum-dominant mineral is the tantalite.
 W
WCommercial sexual exploitation of children (CSEC) is a commercial transaction that involves the sexual exploitation of a child, such as the prostitution of children, child pornography, including live streaming sexual abuse, and the sale and trafficking of children. CSEC may involve coercion and violence against children, economic exploitation, forced labour, contemporary slavery
 W
WA crossing sweeper was a person working as a street sweeper who would sweep a path ahead of people crossing dirty urban streets in exchange for a gratuity. This practice was an informal occupation among the urban poor, primarily during the 19th century. It was the focus of fairly intense study and commentary, and attitudes toward the presence of crossing sweepers on city streets varied greatly among urban residents, ranging from appreciation for their work to feelings that they were a public nuisance. Crossing sweepers also found their way into 19th-century fiction and artwork, including a novel by Charles Dickens and a popular painting by William Powell Frith.
 W
WPeonage, also known as debt slavery or bonded labour, is the pledge of a person's services as security for the repayment for a debt or other obligation, where the terms of the repayment are not clearly or reasonably stated, and the person who is holding the debt thus has some control over the laborer. Freedom is assumed on debt repayment. The services required to repay the debt may be undefined, and the services' duration may be undefined, thus allowing the person supposedly owed the debt to demand services indefinitely. Debt bondage can be passed on from generation to generation.
 W
WDetasseling corn is removing the immature pollen-producing bodies, the tassel, from the tops of corn (maize) plants and placing them on the ground. It is a form of pollination control, employed to cross-breed, or hybridize, two varieties of corn.
 W
WThe Devil's Miner is a 2005 documentary film directed by independent film directors Kief Davidson and Richard Ladkani. The film follows a fourteen-year-old Bolivian boy named Basilio Vargas who along with his twelve-year-old brother Bernardino work in the mines near the city of Potosí. The film includes many subtle realities of the miner's lives such as the need to chew coca leaves to numb the pain of hunger and the long shifts they work regardless of age. The film made its world premier at the Rotterdam film festival and its U.S. debut at the Tribeca Film Festival.
 W
WWilliam Dodd was an Englishman who came to notice when he described his work and growing disability as a child worker during the Industrial Revolution. He was employed by the reformer Earl of Shaftesbury after writing about child workers in the textile industry, but Shaftesbury later sacked him after accusations were made that Dodd was lying and was a disgruntled employee. He wrote one more book on a related subject that was written and published in America.
 W
WA doffer is someone who removes ("doffs") bobbins, pirns or spindles holding spun fiber such as cotton or wool from a spinning frame and replaces them with empty ones. Historically, spinners, doffers, and sweepers each had separate tasks that were required in the manufacture of spun textiles. From the early days of the industrial revolution, this work, which requires speed and dexterity rather than strength, was often done by children. After World War I, the practice of employing children declined, ending in the United States in 1933. In modern textile mills, doffing machines have now replaced humans.
 W
WA drummer was responsible for the army drums for use on the battlefield. Drums were part of the field music for hundreds of years, being introduced by the Ottomans to Europe. Chinese armies however had used drums even before that. With the professionalization of armies, military music was developed as well. Drums were not only used for the men to march in step, but were an important part of the battlefield communications system, with various drum rudiments used to signal different commands from officers to troops. By the second half of the 18th century, most Western armies had a standardized set of marches and signals to be played, often accompanied by fifers.
 W
WThe Factory Acts were a series of acts passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom to regulate the conditions of industrial employment.
 W
WThe Harvest is a 2010 documentary film about agricultural child labor in America. The film depicts children as young as 12 years of age who work as many as 12 hours a day, six months a year, subject to hazardous conditions: heat exposure, pesticides, and dangerous work. The agriculture industry has been subject to significantly more lenient labor laws than any other occupation in the United States. As a result, lack of consistent schooling significantly limits their opportunities of succeeding in high school or more. The hazardous conditions threaten their health and lives. The purpose of the documentary is to bring awareness of the harsh working conditions which tens of thousands of children face in the fields of the United States each year and to enact the Children's Act for Responsible Employment which will bring parity of labor conditions to field workers that are afforded to minors in other occupations.
 W
WThe Health and Morals of Apprentices Act 1802, sometimes known as the Factory Act 1802, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom designed to improve conditions for apprentices working in cotton mills. The Act was introduced by Sir Robert Peel, who had become concerned in the issue after a 1784 outbreak of a "malignant fever" at one of his cotton mills, which he later blamed on 'gross mismanagement' by his subordinates.
 W
WChildren in the military are children who are associated with military organizations, such as state armed forces and non-state armed groups. Throughout history and in many cultures, children have been involved in military campaigns. For example, thousands of children participated on all sides of the First World War and the Second World War. Children may be trained and used for combat, assigned to support roles such as porters or messengers, or used for tactical advantage as human shields or for political advantage in propaganda.
 W
WA hurrier, also sometimes called a coal drawer or coal thruster, was a child or woman employed by a collier to transport the coal that they had mined. Women would normally get the children to help them because of the difficulty of carrying the coal. Common particularly in the early 19th century, the hurrier pulled a corf full of coal along roadways as small as 0.4 metres (16 in) in height. They would often work 12-hour shifts, making several runs down to the coal face and back to the surface again.
 W
WThe International Cocoa Initiative (ICI) is a Geneva-based nonprofit funded by major chocolate makers that focuses on addressing child labour in cocoa production in West Africa. ICI works with communities, farmers, unions, the cocoa and chocolate industry, civil society and national governments in cocoa-producing countries to improve the lives of children involved in cocoa production. The secretariat of the International Cocoa Initiative is in Geneva, Switzerland. The organisation has two national offices in Abidjan and Accra.
 W
WA lemonade stand is a business that is commonly owned and operated by a child or children, to sell lemonade. The concept has become iconic of youthful summertime Americana to the degree that parodies and variations on the concept exist across media. The term may also be used to refer to stands that sell similar beverages like iced tea. In the United States, unlicensed lemonade stands have gotten in trouble with rules about permits.
 W
WA link-boy was a boy who carried a flaming torch to light the way for pedestrians at night. Linkboys were common in London in the days before street lighting. The linkboy's fee was commonly one farthing, and the torch was often made from burning pitch and tow.
 W
WOwen Reed Lovejoy, Jr. was a minister who opposed child labor. He was known as the "children's statesman". He served as the general secretary of the National Child Labor Committee from 1907 to 1926.
 W
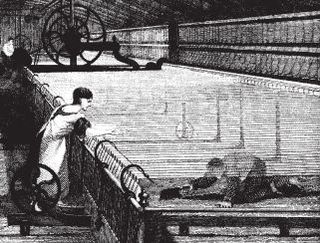
WMines Regulation Act of 1860 is an act of Parliament of the United Kingdom to raise the age of children working in coal mines from 10 to 12 years of age. There were exceptions if the boys could read and write or attended school for six hours per week. The act also improved safety rules.
 W
WScavengers were employed in 18th and 19th century in cotton mills, predominantly in the UK and the United States, to clean and recoup the area underneath a spinning mule. The cotton wastage that gathered on the floor was seen as too valuable for the owners to leave and one of the simplest solutions was to employ young children to work under the machinery. Many children suffered serious injuries while under the mules, with fingers, hands, and sometimes heads crushed by the heavy moving parts. Legislation introduced in 1819 tried to reduce working hours and improve conditions but there were still deaths recorded well beyond the middle of the 19th century.
 W
WMuro-Ami is a Filipino film. It depicts one of the worst forms of child labor in the illegal fishing system. The film follows the story of Fredo, a ruthless captain of 150 muro-ami divers, who employ illegal fishing practices, such as pounding and crushing corals to scare fish, driving them towards the nets. With a high quota to meet, Fredo forces the divers, who consist mostly of children, to accomplish at least eight dives a day to meet their goal before the millennium. Tired and harassed after the burdensome task being given to them, the children have to make do in subhuman conditions in the Muro Ami boat, The Aurora. They sleep in rat-infested bunks and are fed only twice a day. Life above the water in the boat is much worse than the suffering the children encounter beneath the sea. For every dive, a child's life is perilously in danger.
 W
WA paperboy is someone – often an older child or adolescent – who distributes printed newspapers to homes or offices on a regular route, usually by bicycle or automobile. In Western nations during the heyday of print newspapers during the early 20th century, this was often a young person's first job, perhaps undertaken before or after school. This contrasts with the newsboy or newspaper hawker, now extremely rare in Western nations, who would sell newspapers to passersby on the street, often with very vocal promotion. They were common when multiple daily papers in every city – as many as 50 in New York City alone – competed.
 W
WRitual servitude is a practice in Ghana, Togo, and Benin where traditional religious shrines take human beings, usually young virgin girls, in payment for services, or in religious atonement for alleged misdeeds of a family member. In Ghana and in Togo it is practiced by the Ewe tribe in the Volta region; in Benin it is practiced by the Fon.
 W
WThe Sadler Report – more correctly the Report of the Select Committee on Factory Children's Labour : usually referred to at the time as ”the report of Mr Sadler’s Committee,” - was a report written in 1832 by Michael Sadler., the chairman of a UK Parliamentary committee considering a Bill introduced by Sadler seeking to limit the hours of work of children in textile mills and factories. In committee hearings carried between the passage of the 1832 Reform Act through the Commons and Parliament’s subsequent dissolution Sadler had elicited testimony from factory workers, concerned medical men and other bystanders on bad working conditions and excessive working hours to which children were subjected, highlighting the risks to tired children and the brutality to which they might be subjected. Time prevented balancing or contrary evidence being called before Parliament was dissolved.
 W
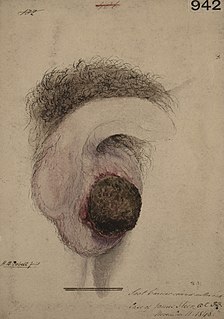
WChimney sweep's cancer, also called soot wart, is a squamous cell carcinoma of the skin of the scrotum. It has the distinction of being the first reported form of occupational cancer, and was initially identified by Percivall Pott in 1775. It was initially noticed as being prevalent amongst chimney sweeps.
 W
WThe Swabian children were peasant children from poor families in the Alps of Austria and Switzerland who went to find work on farms in Upper Swabia and the Swabian Jura. Usually they were sent by their parents to become seasonal workers. They were taken in spring and brought to the child markets in Germany, mainly in Upper Swabia, where they would be purchased or "rented" by farmers for the season. This use of children as workers was most widespread in the 19th century.
 W
WTrafficking of children is a form of human trafficking and is defined by the United Nations as the "recruitment, transportation, transfer, harboring, and/or receipt" kidnapping of a child for the purpose of slavery, forced labor and exploitation. This definition is substantially wider than the same document's definition of "trafficking in persons". Children may also be trafficked for the purpose of adoption.
 W
WValet boy is a term used in some countries to refer to young people who ask for fees from those who park at the roadside. Valet boys usually work in groups, and demand an RM 1-5 "parking fee" from car owners, under an agreement that they will protect the car. It is these very same valets, however, who do the vandalizing should the driver refuse to pay. This "protection" service is a form of extortion. The valet boys do not park the car for the owner; rather they direct drivers into parking lots. This practice has become common in large Brazilian cities, such as São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, where numerous cases of "valet boys" vandalizing cars are reported every day. Similar schemes are also run in other countries although often the person is not a 'boy'. In the Philippines, however, this scheme is mostly run by street children.