 W
WArius manillensis is a species of marine catfish endemic to the island of Luzon, Philippines. It is commonly known as the Manila sea catfish or kanduli. It is fished commercially.
 W
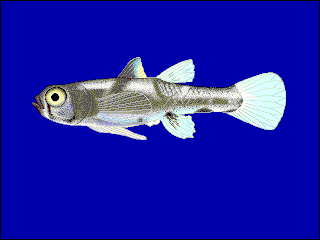
WThe shovelnose sea catfish, also called the short-nosed catfish or the marine catfish, is a species of sea catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1840. It is a non-migratory species which inhabits tropical marine and brackish waters in the Indo-western Pacific region, including Indonesia, India, Pakistan, the Philippines and Thailand. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 20 m. It reaches a maximum NG length of 39.5 cm (15.6 in), while commonly reaching a total length of 12 cm (4.7 in).
 W
WRedigobius bikolanus, the Speckled goby, is a species of goby native to marine, fresh and brackish waters along the coasts of Asia from Japan to Australia out to the Pacific islands of New Caledonia and Vanuatu and along the coast of South Africa and the Seychelles. This species inhabits streams, creeks and estuaries, often being found upstream beyond the tidal zones of rivers. This fish can reach a length of 4.2 centimetres (1.7 in) SL.
 W
WCanthidermis maculata, also known as rough triggerfish or spotted oceanic triggerfish, is a species of triggerfish native to the tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide. Unlike most triggerfish, they are mostly pelagic.
 W
WThe brownspotted catshark is a rare catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae, found in the Indo-West Pacific between latitudes 11° N and 12° S. Its juvenile length is about 38 cm, but its adult size is mostly unknown. The reproduction of this catshark is oviparous.
 W
WThe onefin catshark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae. It is the only member of its genus.
 W
WThe blacktip sawtail catshark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, found off the coasts of Taiwan and the Philippines. It is demersal in nature and occurs deeper than 60 m (200 ft). Growing up to 46 cm (18 in) long, this slim-bodied species is characterized by its plain brownish dorsal coloration with dark tips on the dorsal and caudal fins, and a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles on the upper edge of the caudal fin. It is oviparous, with females producing encapsulated eggs two at a time year-round. The blacktip sawtail catshark is caught incidentally in bottom trawls and used for fishmeal in Taiwan. However, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) currently lacks enough information to assess its conservation status.
 W
WThe dwarf sawtail catshark is a little-known species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, found exclusively in the deep waters off Luzon in the Philippines. Unlike other members of its genus, this slender, diminutive shark has a short, rounded snout and very short furrows at the corners of its jaws. It has indistinct darker saddles beneath each dorsal fin and two dark bands on the caudal fin, as well as a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the upper caudal fin margin. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) does not currently have sufficient information to assess the conservation status of this species.
 W
WChanna striata, the striped snakehead, is a species of snakehead fish. It is also known as the common snakehead, chevron snakehead, or snakehead murrel and generally referred simply as mudfish. It is native to South and Southeast Asia, and has been introduced to some Pacific Islands. Reports from Madagascar and Hawaii are misidentifications of C. maculata.
 W
WChrysiptera springeri is a species of damselfish known by the common name Springer's demoiselle. It is native to the western Pacific Ocean, where it occurs in the tropical waters of Indonesia and the Philippines. It reaches 5.5 centimeters in length and is variable in color. The specific name honours the ichthyologist Victor G. Springer who collected the type in the Moluccas.
 W
WThe dagger-tooth pike conger is a species of eel. They primarily live on soft bottoms in marine and brackish waters down to a depth of 800 m (2,600 ft), but may enter freshwater. They are common to about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length, but may grow as long as 2.2 m (7.2 ft). Dagger-tooth pike congers occur in the Red Sea, on the coast of the northern Indian Ocean, and in the West Pacific from Indochina to Japan. It has also invaded the Mediterranean through the Suez Canal.
 W
WThe arrowhead dogfish is a small little known deepwater dogfish of the family Centrophoridae.
 W
WThe dwarf pygmy goby or Philippine goby is a tropical species of fish in the subfamily Gobionellinae from brackish water and mangrove areas in Southeast Asia. It is one of the smallest fish species in the world. Males reach maturity at a standard length of 0.9 cm (0.35 in) and can reach up to 1.1 cm (0.43 in) in standard length, while the females can grow up to 1.5 centimetres (0.59 in) in total length. Adults weigh around 4 milligrams (0.00015 oz). It is known as bia and tabios in the Philippines.
 W
WGadomus colletti is a species of rattail. This deep-water fish is found in the waters around Japan, the Philippines, and northern Taiwan.
 W
WThe longnose houndshark is a houndshark of the family Triakidae. It is found in the western Pacific off northern Australia and Vanuatu, between latitudes 9° S and 26° S, at depths between 250 and 475 m. It can grow up to a length of 75 cm.
 W
WHymenocephalus lethonemus is a species of rattail. It occurs at depths of up to 485 m (1591 ft) in the waters off southern Japan, the Philippines and northern Taiwan.
 W
WLutjanus lemniscatus, commonly known as the yellowstreaked snapper, is a marine fish native to the western Pacific and Indian Oceans, from Mozambique to the Philippines.
 W
WThe milkfish is the sole living species in the family Chanidae. However, there are at least five extinct genera from the Cretaceous.
 W
WNematabramis alestes is a species of cyprinid found in Zamboanga, Basilan, Palawan, and Busuanga in the Philippines. It belongs to the genus Nematabramis. It reaches up to 10.1 cm (4.0 in) in length.
 W
WThe Bloch's gizzard shad, also known as gizzard shad, hairback, long-finned gizzard shad, long-ray bony bream and thread-finned gizzard shad, are a widespread and common, small to medium-sized anadromous fish found in all marine, freshwater and brackish waters throughout Indo-West Pacific, towards eastward of Andaman Sea, South China Sea and the Philippines to Korean peninsula. Single specimen recorded from waters of South Africa. It was described by Marcus Elieser Bloch in 1795.
 W
WNeovespicula depressifrons is a species of waspfish found in coastal habitats of the Indo-West Pacific region.
 W
WOxyurichthys microlepis, the maned goby, is a species of goby native to tropical marine and brackish waters along the coasts of the Indian Ocean from Africa to the western Pacific Ocean where it occurs in estuaries and inshore waters to depths of about 75 metres (246 ft). It occurs in the Mekong Delta and is suspected to use the tidal flow up the river to reach as far inland as Cambodia. This species can reach a length of 13.5 centimetres (5.3 in) TL. It is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries and can also be found in the aquarium trade.
 W
WThe paradise threadfin is a species of catadromous ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae which is found in south and southeast Asia in freshwater rivers where it is a valued food fish.
 W
WPentapodus setosus, commonly known as the butterfly whiptail, is a marine fish native to the western Pacific Ocean.
 W
WPhotocorynus spiniceps is a species of anglerfish in the family Linophrynidae. It is in the monotypic genus Photocorynus.
 W
WThe picturesque dragonet is a brightly colored member of the dragonet family native to the Indo-West Pacific: Philippines, eastern Indonesia and northwest Australia. It occasionally makes its way into the aquarium trade, where it is commonly known as the spotted mandarin, psychedelic mandarin or target mandarin.
 W
WPleurosicya mossambica, also known as the toothy goby or the Mozambique ghost goby, is a small species of goby native to the tropical Indo-West Pacific region. It was first described by South African ichthyologist J.L.B. Smith in 1959. Like many other gobies, it forms commensal relationships with several other marine invertebrates, including soft corals and sponges.
 W
WPolydactylus sextarius, the blackspot threadfin, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae which is native to the western Pacific and eastern Indian Oceans.
 W
WLana's sawshark or the Philippine sawshark, is a sawshark of the family Pristiophoridae, found in the Philippines off Apo Island and southern Luzon at depths of between 230 and 590 m. Its length is up to 73 cm.
 W
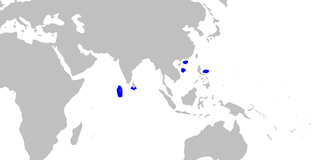
WSecutor insidiator, the barred ponyfish or pugnose ponyfish, is a species of bony fish in the slipmouths family. The barred ponyfish's mineralized skeleton contains apatite and the mineralized tissue contains hydroxylapatite. They have bare heads with nuchal spines and their bodies are a distinctive, reflective silver, frequently imitated by fishermen using silver lures. They have a protracted mouth pointing upward and the tip of the maxilla reaches well below the level of the lower margin of the eye. Barred ponyfish feed on zooplankton, including larval fishes and crustaceans. Body depth is twice or slightly more than standard length, which measures 11.3 cm from the tip of the snout to last vertebra. The lateral line ends before the dorsal fin.
 W
WThe blackfin gulper shark is a dogfish of the family Centrophoridae in the Northwest Pacific. Threats are not entirely clear but they may be bycatching from deepwater trawling and line fisheries and may also be used for cod liver oil and fish meal.
 W
WThe leafscale gulper shark is a dogfish of the family Centrophoridae. C. squamosus is reported to have a lifespan of approximately 70 years, based on otolith ring counts. It was the first described species in the genus Centrophorus, which now contains 13 species.
 W
WThe smallfin gulper shark is a medium-sized deepwater dogfish in the family Centrophoridae.
 W
WThe shovelnose sea catfish, also called the short-nosed catfish or the marine catfish, is a species of sea catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1840. It is a non-migratory species which inhabits tropical marine and brackish waters in the Indo-western Pacific region, including Indonesia, India, Pakistan, the Philippines and Thailand. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 20 m. It reaches a maximum NG length of 39.5 cm (15.6 in), while commonly reaching a total length of 12 cm (4.7 in).
 W
WTilapia is the common name for nearly a hundred species of cichlid fish from the coelotilapine, coptodonine, heterotilapine, oreochromine, pelmatolapiine and tilapiine tribes, with the economically most important species placed in Coptodonini and Oreochromini. Tilapia are mainly freshwater fish inhabiting shallow streams, ponds, rivers, and lakes, and less commonly found living in brackish water. Historically, they have been of major importance in artisanal fishing in Africa, and they are of increasing importance in aquaculture and aquaponics. Tilapia can become a problematic invasive species in new warm-water habitats such as Australia, whether deliberately or accidentally introduced, but generally not in temperate climates due to their inability to survive in cold water.
 W
WThe whitefin topeshark is a houndshark of the family Triakidae, found only in the tropical waters of the Philippines between latitudes 20° N and 5° N. They inhabit the coastal areas. They can grow up to a length of 96 cm. Adolescent specimens have dark areas on their caudal fins. The reproduction of this shark is ovoviviparous.
 W
WThe walking catfish is a species of freshwater airbreathing catfish native to Southeast Asia. It is named for its ability to "walk" and wiggle across dry land, to find food or suitable environments. While truly, it does not walk as most bipeds or quadrupeds do, it has the ability to use its pectoral fins to keep it upright as it makes a wiggling motion with snakelike movements to traverse land. This fish normally lives in slow-moving and often stagnant waters in ponds, swamps, streams, and rivers, as well as in flooded rice paddies, or temporary pools that may dry up. When this happens, its "walking" skill allows the fish to move to other aquatic environments. Considerable taxonomic confusion surrounds this species and it has frequently been confused with other close relatives. One main distinction between the walking catfish and the native North American ictalurid catfish with which it sometimes is confused, is that the walking catfish lacks an adipose fin.