 W
WAncylostoma caninum is a species of nematode known as a hookworm, which principally infects the small intestine of dogs. The result of A. caninum infection ranges from asymptomatic cases to death of the dog; better nourishment, increasing age, prior A. caninum exposure, or vaccination are all linked to improved survival. Other hosts include carnivores such as wolves, foxes, and cats, with a small number of cases having been reported in humans.
 W
WAngiostrongylus cantonensis is a parasitic nematode (roundworm) that causes angiostrongyliasis, the most common cause of eosinophilic meningitis in Southeast Asia and the Pacific Basin. The nematode commonly resides in the pulmonary arteries of rats, giving it the common name rat lungworm. Snails are the primary intermediate hosts, where larvae develop until they are infectious.
 W
WAnisakis is a genus of parasitic nematodes that have life cycles involving fish and marine mammals. They are infective to humans and cause anisakiasis. People who produce immunoglobulin E in response to this parasite may subsequently have an allergic reaction, including anaphylaxis, after eating fish infected with Anisakis species.
 W
WAscaris suum, also known as the large roundworm of pig, is a parasitic nematode that causes ascariasis in pigs. While roundworms in pigs and humans are today considered as two species with different hosts, cross-infection between humans and pigs is possible; some researchers have thus argued they are the same species. Ascariasis is associated with contact to pigs and pig manure in Denmark.
 W
WBrugia is a genus for a group of small roundworms. They are among roundworms that cause the parasitic disease filariasis. Specifically, of the three species known, Brugia malayi and Brugia timori cause lymphatic filariasis in humans; and Brugia pahangi and Brugia patei infect domestic cats, dogs and other animals. They are transmitted by the bite of mosquitos.
 W
WCapillaria is a genus of nematodes in the family Capillariidae .
 W
WCapillaria aerophila is a nematode parasite found in the respiratory tract of foxes, dogs, and various other carnivorous mammals. A few cases of human infestation have also been reported. Though it is sometimes called a "lungworm", this term usually refers to other species of nematodes. Infestation by C. aerophila is referred to as "pulmonary capillariasis", "bronchial capillariasis," or (rarely) "thominxosis." This parasite has a direct life cycle, meaning that the life cycle can be completed in a single host. C. aerophila usually causes only minor clinical symptoms, such as irritation of the respiratory tract and coughing. However, secondary bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, including pneumonia, may develop in heavy infestations. Treatment with anthelmintics, such as levamisole or fenbendazole, is usually sufficient to cure C. aerophila infestations.
 W
WCapillaria feliscati (also known as Pearsonema feliscati, the cat bladder worm is a worm that affects cats, and seldom dogs. Its main final hosts are wild carnivores. It is a urinary tract nematode, though its occurrence is rare. C. feliscati are small, delicate, yellowish, thread-like worms. Adults are approximately between 16 and 53 millimetres in length.
 W
WCapillaria hepatica is a parasitic nematode which causes hepatic capillariasis in rodents and numerous other mammal species, including humans. The life cycle of C. hepatica may be completed in a single host species. However, the eggs, which are laid in the liver, must mature outside of the host body prior to infecting a new host. So the death of the host in which the adults reach sexual maturity, either by being eaten or dying and decomposing, is necessary for completion of the life cycle.
 W
WCooperia oncophora is one of the most common intestinal parasitic nematodes in cattle in temperate regions. Infections with C. oncophora may result in mild clinical symptoms, but can lead to weight loss and damage of the small intestine, especially when co-infections with other nematodes such as O. ostertagi occur. Infections are usually treated with broad-spectrum anthelmintics such as benzimidazole, but resistance to these drugs has developed in the last decades and is now very common. C. oncophora has a direct life cycle. Infective larvae are ingested by the host. The larvae grow to adults, which reproduce in the small intestines. Eggs are shed onto the pasture with the faeces, which leads to new infections. Co-infections with other gastro-intestinal nematodes such as O. ostertagi and H. contortus are common.
 W
WDioctophyme renale, commonly referred to as the giant kidney worm is a parasitic roundworm whose mature form is found in the kidneys of mammals. D. renale is distributed worldwide, but is less common in Africa and Oceania. It affects fish eating mammals, particularly mink and dogs. Human infestation is rare, but results in kidney destruction, usually of one kidney and hence not fatal. A 2019 review listed a total of 37 known human cases of dioctophymiasis in 10 countries with the highest number (22) in China. Upon diagnosis through tissue sampling, the only treatment is surgical excision.
 W
WDirofilaria immitis, also known as heartworm or dog heartworm, is a parasitic roundworm that is a type of filarial worm, a small thread-like worm, that causes dirofilariasis. It is spread from host to host through the bites of mosquitoes. There are four genera of mosquitoes that transmit dirofilariasis, Aedes, Culex, Anopheles, and Mansonia. The definitive host is the dog, but it can also infect cats, wolves, coyotes, jackals, foxes, ferrets, bears, seals, sea lions and, under rare circumstances, humans.
 W
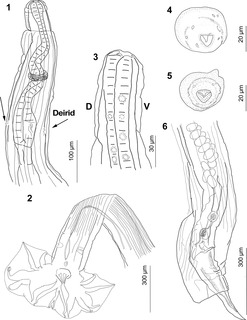
WDracunculus is a genus of spiruroid nematode parasites in the family Dracunculidae. Some species infest humans and alter their hosts’ behaviour in a way that supports the worm's reproductive cycle. Dracunculus causes a blister to form on the host, often on the foot or lower leg, causing severe pain and a boiling sensation. This will cause the human host to dip the affected area in water to soothe the pain which will cause the blister to burst, allowing reproductive larvae into the water where they can await the next host to infect.
 W
WGuerrerostrongylus is a genus of nematode worms. Species of Guerrerostrongylus infect mostly the digestive tract of sigmodontine and caviomorph rodents from South America. The genus is part of the subfamily Nippostrongylinae.
 W
WHaemonchus contortus, also known as the barber's pole worm, is a very common parasite and one of the most pathogenic nematodes of ruminants. Adult worms attach to abomasal mucosa and feed on the blood. This parasite is responsible for anemia, oedema, and death of infected sheep and goats, mainly during summer in warm, humid climates.
 W
WHeligmosomoides polygyrus, previously named Nematospiroides dubius, is a naturally occurring intestinal roundworm of rodents. It belongs to the family Trychostrongylidae, and male and female worms are morphologically distinguishable. The parasite has a direct lifecycle, with its larval form being the infective stage. H. polygyrus has the ability to establish chronic infections in rodents and alter host immune responses. This nematode is widely used as a gastrointestinal parasitic model in immunological, pharmacological, and toxicological studies.
 W
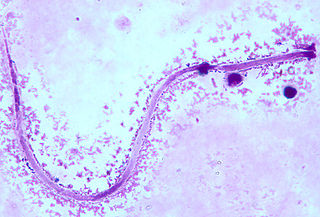
WHookworms are intestinal, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is common in countries with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, and hygiene. In humans, infections are caused by two main species of roundworm, belonging to the genera Ancylostoma and Necator. In other animals the main parasites are species of Ancylostoma.
 W
WMansonella is a genus of parasitic nematodes responsible for the disease mansonelliasis.
 W
WNecator americanus is a species of hookworm commonly known as the New World hookworm. Like other hookworms, it is a member of the phylum Nematoda. It is an obligatory parasitic nematode that lives in the small intestine of human hosts. Necatoriasis—a type of helminthiasis—is the term for the condition of being host to an infestation of a species of Necator. Since N. americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale are the two species of hookworms that most commonly infest humans, they are usually dealt with under the collective heading of "hookworm infection". They differ most obviously in geographical distribution, structure of mouthparts, and relative size.
 W
WNippostrongylus brasiliensis is a type of nematode/gastrointestinal roundworm or nematode that infects rodents, primarily rats. This worm is a widely studied parasite due to its simple lifecycle and its ability to be used in animal models. Its lifecycle similar to the human hookworms Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale which includes five molting stages to become sexually mature.
 W
WOdilia is a genus of nematode worms established by Marie-Claude Durette-Desset in 1973 that infect mostly murid rodents of the Australasian region (species of Melomys, Rattus and Uromys from mainland Australia and Tasmania.
 W
WOnchocerca is a genus of parasitic roundworm. It contains one human parasite – Onchocerca volvulus – which is responsible for the neglected disease Onchocerciasis, also known as "river blindness" because the infected humans tend to live near rivers where host black flies live. Over 40 million people are infected in Africa, Central America, and South America. Other species affect cattle, horses, etc.
 W
WOnchocerca tubingensis is the name of a nematode. It was discovered in 1974 and published by O. Bain und H. Schulz-Key in Tropenmedizin und Parasitologie and named after Tübingen. Red deer are the host of this parasite. The adult worms of Onchocerca tubingensis are found in subcutaneous nodules on the caudal part of the back, while the microfilariae are distributed on the ventral part of the body with maximum densities in the region of the sternum and with lower densities on the inner sides of the hindlegs. The infection rates of 94 red deer investigated in southern Germany during 1907–1974 were 23%.
 W
WThe Onchocercidae are a family of nematodes in the superfamily Filarioidea. This family includes some of the most devastating human parasitic diseases, such as lymphatic filariasis, onchocerciasis, loiasis, and other filariases.
 W
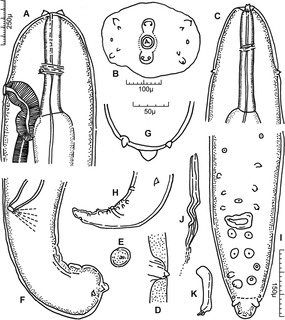
WThe pinworm, also known as threadworm or seatworm, is a parasitic worm. It is a nematode (roundworm) and a common intestinal parasite or helminth, especially in humans. The medical condition associated with pinworm infestation is known as pinworm infection (enterobiasis) or less precisely as oxyuriasis in reference to the family Oxyuridae.
 W
WSetaria is a genus of parasitic roundworms that infect domesticated mammals such as pigs, camels, cattle and horses. Some species also infect wild mammals such as deer and antelope. The genus consists of about 43 species. Members of the genus are uniquely parasites in the abdominal cavity of the body. They are mostly large-sized roundworms, possessing an elaborate head (cephalic) region that is characterised by spines, presence of four lips, and well-guarded mouth. Little is known about their pathogenic effects, but some are known to affect nervous system and eye. The larval infective forms are transmitted from one animal to another by the bite of mosquitoes and flies. In addition Setaria marshalli can be transmitted from the womb to new-born calf.
 W
WSubclass Spiruria comprises mostly parasitic secernentean nematodes. In an alternate classification, they are treated as suborder Spirurina, with the orders listed here being ranked as infraorders.
 W
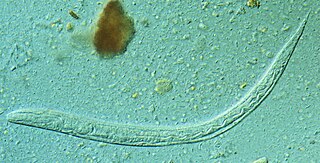
WStrongyles, or alternatively, strongyls, are nematode worms of the family Strongylidae, order Strongylida. They are often parasitic in the gastrointestinal tract of mammals, especially grazers such as sheep, cattle and horses.
 W
WStrongyloides, anguillula, or threadworm is a genus of small nematode parasites, belonging to the family Strongylidae, commonly found in the small intestine of mammals, that are characterized by an unusual lifecycle that involves one or several generations of free-living adult worms.
 W
WStrongyloides stercoralis is a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term threadworm can also refer to nematodes of the genus Enterobius, otherwise known as pinworms.
 W
WStrongylus vulgaris, commonly known as the blood worm, is a common horse parasite in the phylum Nematoda. It looks like a long worm with a large biting mouth. They are usually reddish in color because of all the blood they take from the equine host. This nematode is considered to be one of the "most pathogenic" of the large strongyles subphylum and is distributed worldwide, wherever there are grassland and temperate environments.
 W
WTeladorsagia circumcincta is a nematode that is one of the most important parasites of sheep and goats. It was previously known as Ostertagia circumcincta and is colloquially known as the brown stomach worm. It is common in cool, temperate areas, such as south-eastern and south-western Australia and the United Kingdom. There is considerable variation among lambs and kids in susceptibility to infection. Much of the variation is genetic and influences the immune response. The parasite induces a type I hypersensitivity response which is responsible for the relative protein deficiency which is characteristic of severely infected animals. There are mechanistic mathematical models which can predict the course of infection. There are a variety of ways to control the infection and a combination of control measures is likely to provide the most effective and sustainable control.
 W
WThelazia callipaeda is a parasitic nematode, and the most common cause of thelaziasis in humans, dogs and cats. It was first discovered in the eyes of a dog in China in 1910. By 2000, over 250 human cases had been reported in the medical literature.
 W
WThe Toxocaridae are a zoonotic family of parasitic nematodes that infect canids and felids and which cause toxocariasis in humans. The worms are unable to reproduce in humans.
Trichinella spiralis is a viviparous nematode parasite, occurring in rodents, pigs, bears, hyenas and humans, and is responsible for the disease trichinosis. It is sometimes referred to as the "pork worm" due to it being typically encountered in undercooked pork products. It should not be confused with the distantly related pork tapeworm.
 W
WTrichinosis, also known as trichinellosis, is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the Trichinella type. During the initial infection, invasion of the intestines can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Migration of larvae to muscle, which occurs about a week after being infected, can cause swelling of the face, inflammation of the whites of the eyes, fever, muscle pains, and a rash. Minor infection may be without symptoms. Complications may include inflammation of heart muscle, central nervous system involvement, and inflammation of the lungs.
 W
WTrichuris, often referred to as whipworms, is a genus of parasitic worms from the roundworm family Trichuridae, which are helminths. The name whipworm refers to the shape of the worm; they look like whips with wider "handles" at the posterior end. The name Trichocephalus is sometimes used for this genus.