 W
W2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase subunit alpha, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BCKDHA gene.
 W
W2-Oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase subunit beta, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BCKDHB gene.
 W
WCentrosomal protein 89, also known as Centrosomal protein of 89 kDa (CEP89), Centrosomal protein 123 (CEP123), or Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 123 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP89 gene.
 W
WThe enzyme citrate synthase E.C. 2.3.3.1 ] exists in nearly all living cells and stands as a pace-making enzyme in the first step of the citric acid cycle. Citrate synthase is localized within eukaryotic cells in the mitochondrial matrix, but is encoded by nuclear DNA rather than mitochondrial. It is synthesized using cytoplasmic ribosomes, then transported into the mitochondrial matrix.
 W
WLipoamide acyltransferase component of branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DBT gene.
 W
WDihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD), also known as dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, mitochondrial, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DLD gene. DLD is a flavoprotein enzyme that oxidizes dihydrolipoamide to lipoamide.
 W
WDihydrolipoyl transacetylase is an enzyme component of the multienzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is responsible for the pyruvate decarboxylation step that links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. This involves the transformation of pyruvate from glycolysis into acetyl-CoA which is then used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration.
 W
WDihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase component of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DLST gene.
 W
WE3 binding protein also known as pyruvate dehydrogenase protein X component, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDHX gene. The E3 binding protein is a component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex found only in eukaryotes. Defects in this gene are a cause of pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency which results in neurological dysfunction and lactic acidosis in infancy and early childhood. This protein is also a minor antigen for antimitochondrial antibodies. These autoantibodies are present in nearly 95% of patients with primary biliary cholangitis, an autoimmune disease of the liver. In primary biliary cholangitis, activated T lymphocytes attack and destroy epithelial cells in the bile duct where this protein is abnormally distributed and overexpressed. Primary biliary cholangitis eventually leads to liver failure.
 W
WEnoyl Coenzyme A hydratase, short chain, 1, mitochondrial, also known as ECHS1, is a human gene.
 W
WFAST kinase domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FASTKD1 gene on chromosome 2. This protein is part of the FASTKD family, which is known for regulating the energy balance of mitochondria under stress. FASTKD1 is also an RNA-binding protein and has been associated with endometrial cancer.
 W
WFAST kinase domain-containing protein 2 (FASTKD2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FASTKD2 gene on chromosome 2. This protein is part of the FASTKD family, which is known for regulating the energy balance of mitochondria under stress. FASTKD2 has been implicated in mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, breast cancer, and prostate cancer.
 W
WAspartate aminotransferase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GOT2 gene. Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase is a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme which exists in cytoplasmic and inner-membrane mitochondrial forms, GOT1 and GOT2, respectively. GOT plays a role in amino acid metabolism and the urea and tricarboxylic acid cycles. Also, GOT2 is a major participant in the malate-aspartate shuttle, which is a passage from the cytosol to the mitochondria. The two enzymes are homodimeric and show close homology. GOT2 has been seen to have a role in cell proliferation, especially in terms of tumor growth.
 W
WMitochondrial 70kDa heat shock protein (mtHsp70), also known as mortalin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HSPA9 gene.
 W
WIn enzymology, an isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction3-methylbutanoyl-CoA + acceptor 3-methylbut-2-enoyl-CoA + reduced acceptor
 W
WLeucine zipper-EF-hand containing transmembrane protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LETM1 gene.
 W
WLon protease homolog, mitochondrial is a protease, an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LONP1 gene.
 W
WMalate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial also known as malate dehydrogenase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MDH2 gene.
 W
WMitochondrial intermediate peptidase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MIPEP gene. This protein is a critical component of human mitochondrial protein import machinery involved in the maturing process of nuclear coded mitochondrial proteins that with a mitochondrial translocation peptide, especially those OXPHOS-related proteins.
 W
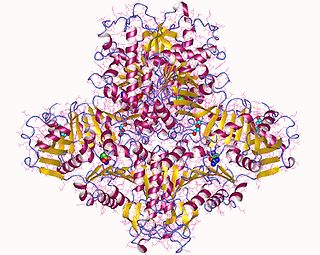
WCytochrome b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MT-CYB gene. Its gene product is a subunit of the respiratory chain protein Ubiquinol Cytochrome c Reductase, which consists of the products of one mitochondrially encoded gene, MT-CYB and ten nuclear genes: UQCRC1, UQCRC2, Cytochrome c1, UQCRFS1, UQCRB, "11kDa protein", UQCRH, Rieske Protein presequence, "cyt. c1 associated protein", and Rieske-associated protein.
 W
WN-Acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) is an enzyme that catalyses the production of N-acetylglutamate (NAG) from glutamate and acetyl-CoA.
 W
WNADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 10 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NDUFA10 gene. The NDUFA10 protein is a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone), which is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and is the largest of the five complexes of the electron transport chain. Mutations in subunits of NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone), also known as Complex I, frequently lead to complex neurodegenerative diseases such as Leigh's syndrome. Furthermore, reduced NDUFA10 expression levels due to FOXM1-directed hypermethylation are associated with human squamous cell carcinoma and may be related to other forms of cancer.
 W
WNADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 5, 16kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NDUFB5 gene. The NDUFB5 protein is a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone), which is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and is the largest of the five complexes of the electron transport chain.
 W
WAlpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase also known as 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase E1 component, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OGDH gene.
 W
WOrnithine aminotransferase (OAT) is an enzyme which is encoded in human by the OAT gene located on chromosome 10.
 W
WMitochondrial-processing peptidase subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PMPCA gene. This gene PMPCA encoded a protein that is a member of the peptidase M16 family. This protein is located in the mitochondrial matrix and catalyzes the cleavage of the leader peptides of precursor proteins newly imported into the mitochondria, though it only functions as part of a heterodimeric complex.
 W
WPyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, somatic form, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDHA1 gene.The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial matrix multienzyme complex that provides the primary link between glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle by catalyzing the irreversible conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA. The PDH complex is composed of multiple copies of 3 enzymes: E1 (PDHA1); dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (DLAT) ; and dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (DLD). The E1 enzyme is a heterotetramer of 2 alpha and 2 beta subunits. The E1-alpha subunit contains the E1 active site and plays a key role in the function of the PDH complex.
 W
WPyruvate dehydrogenase (lipoamide) alpha 2, also known as pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, testis-specific form, mitochondrial or PDHE1-A type II, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDHA2 gene.
 W
WPyruvate dehydrogenase (lipoamide) beta, also known as pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit beta, mitochondrial or PDHE1-B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDHB gene. The pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex is a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial multienzyme complex that catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO2, and provides the primary link between glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The PDH complex is composed of multiple copies of three enzymatic components: pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3). The E1 enzyme is a heterotetramer of two alpha and two beta subunits. This gene encodes the E1 beta subunit. Mutations in this gene are associated with pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-beta deficiency.
 W
WMitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit Tim17-A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TIMM17A gene.
 W
WMitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit Tim22 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TIMM22 gene.
 W
WMitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit Tim23 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TIMM23 gene.
 W
WMitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit TIM44 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TIMM44 gene.
 W
WTranslocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 40 homolog (yeast), also known as TOMM40, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TOMM40 gene.
 W
WThe translocase of the outer membrane (TOM) is a complex of proteins found in the outer mitochondrial membrane of the mitochondria. It allows movement of proteins through this barrier and into the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion. Most of the proteins needed for mitochondrial function are encoded by the nucleus of the cell. The outer membrane of the mitochondrion is impermeable to large molecules greater than 5000 Daltons. The TOM works in conjunction with the translocase of the inner membrane (TIM) to translocate proteins into the mitochondrion. Many of the proteins in the TOM complex, such as TOMM22, were first identified in Neurospora crassa and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
 W
WUbiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex assembly factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UQCC2 gene. Located in the mitochondrial nucleoid, this protein is a complex III assembly factor, playing a role in cytochrome b biogenesis along with the UQCC1 protein. It regulates insulin secretion and mitochondrial ATP production and oxygen consumption. In the sole recorded case, a mutation in the UQCC2 gene caused Complex III deficiency, characterized by intrauterine growth retardation, neonatal lactic acidosis, and renal tubular dysfunction.
 W
WUbiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex assembly factor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UQCC3 gene. Located in mitochondria, this protein is involved in the assembly of mitochondrial Complex III, stabilizing supercomplexes containing Complex III. Mutations in the UQCC3 gene cause Complex III deficiency with symptoms of hypoglycemia, hypotonia, lactic acidosis, and developmental delays. This protein plays an important role as an antiviral factor, bolstering the ability of cells to inhibit viral replication, independent of interferon production. The UQCC3 protein can be cleaved by OMA1 metalloprotease during mitochondrial depolarization, targeting the cell for apoptosis. Depletion of this protein alters cardiolipin composition, causing cellular and mitochondrial defects.
 W
WUbiquinol-cytochrome c reductase binding protein, also known as UQCRB, Complex III subunit 7, QP-C, or Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex 14 kDa protein is a protein which in humans is encoded by the UQCRB gene. This gene encodes a subunit of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductase complex, which consists of one mitochondrial-encoded and 10 nuclear-encoded subunits. Mutations in this gene are associated with mitochondrial complex III deficiency. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. Related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 1, 5 and X.