 W
WAngiostrongylus is a genus of parasitic nematodes in the family Metastrongylidae.
 W
WAngiostrongylus costaricensis is a species of parasitic nematode and is the causative agent of abdominal angiostrongyliasis in humans. It occurs in Latin America and the Caribbean.
 W
WAnguina is a genus of plant pathogenic nematodes.
 W
WThe Anisakidae are a family of intestinal nematodes (roundworms). The larvae of these worms can cause anisakiasis when ingested by humans, in raw or insufficiently cooked fish.
 W
WAnisakis simplex, known as the herring worm, is a species of nematodes in the genus Anisakis, which occurs in ocean fish such as herrings. Human infections can cause severe abdominal cramps. The worm drills through the intestinal wall and lodges in muscle tissue.
 W
WAphelenchoididae is a nematode family in the order Aphelenchida.
 W
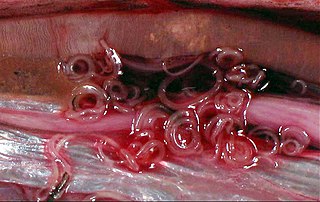
WThe order Ascaridida includes several families of parasitic roundworms with three "lips" on the anterior end. They were formerly placed in the subclass Rhabditia by some, but morphological and DNA sequence data rather unequivocally assign them to the Spiruria. The Oxyurida and Rhigonematida are occasionally placed in the Ascaridida as superfamily Oxyuroidea, but while they seem indeed to be Spiruria, they are not as close to Ascaris as such a treatment would place them. These "worms" contain a number of important parasites of humans and domestic animals.
 W
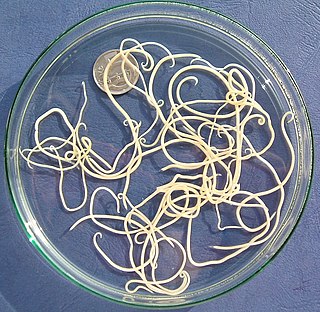
WThe suborder Ascaridina contains the bulk of the Ascaridida, parasitic roundworms with three "lips" on the anterior end. The Ascaridida were formerly placed in the subclass Rhabditia by some, but morphological and DNA sequence data rather unequivocally assigns them to the Spiruria. The Oxyurida and Rhigonematida are occasionally placed in the Ascaridina as superfamily Oxyuroidea, but while they seem indeed to be Spiruria, they are not as close to Ascaris as such a treatment would place them.
 W
WThe Camallanida are an order of nematodes.Parasites of terrestrial and aquatic vertebrates Copepods as obligatory secondary hosts
 W
WCamallanus is a genus of parasitic roundworms in the family Camallanidae.
 W
WDiplogasterida was an order of nematodes. It was sometimes placed in a monotypic subclass Diplogasteria, but molecular phylogenetic evidence has shown it to be embedded in the family Rhabditidae. The confusion of having a hierarchical nesting of groups that were formerly mutually exclusive has led to a profusion of names. Although completely revised taxonomy of nematodes that builds on recent classification systems as well as recent phylogenetic evidence is still necessary, most contemporary taxonomic studies now treat all groups listed under "Diplogasterina" below as a single family, Diplogastridae.
 W
WDitylenchus is a genus of plant pathogenic nematodes.
 W
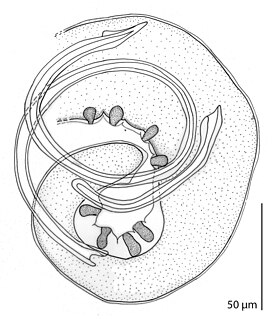
WGongylonema is a genus of thread-like nematode that was described by Molin in 1857. It is the only currently valid genus in the family Gongylonematidae, though the mysterious Spiruroides – usually placed in the Subuluridae, which are not closely related to Gongylonema among the Spiruria – might actually belong here. They are parasites of birds and mammals, transmitted by insects. Some 38 species are known, about 12 of which have been recorded in Europe.
 W
WHabronematoidea is a superfamily of spirurian nematodes in the large order Spirurida. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.
 W
WHeteroderidae is a family of nematodes. The name comes from the Greek heteros = other and deras = skin (derm). This "refers to the different 'skins' of female and cyst."
 W
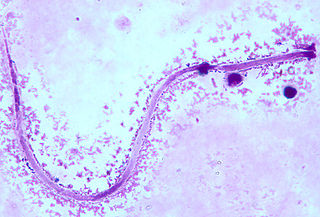
WHeteroderinae is a subfamily of roundworms.
 W
WMansonella is a genus of parasitic nematodes responsible for the disease mansonelliasis.
 W
WOnchocerca is a genus of parasitic roundworm. It contains one human parasite – Onchocerca volvulus – which is responsible for the neglected disease Onchocerciasis, also known as "river blindness" because the infected humans tend to live near rivers where host black flies live. Over 40 million people are infected in Africa, Central America, and South America. Other species affect cattle, horses, etc.
 W
WOnchocerca tubingensis is the name of a nematode. It was discovered in 1974 and published by O. Bain und H. Schulz-Key in Tropenmedizin und Parasitologie and named after Tübingen. Red deer are the host of this parasite. The adult worms of Onchocerca tubingensis are found in subcutaneous nodules on the caudal part of the back, while the microfilariae are distributed on the ventral part of the body with maximum densities in the region of the sternum and with lower densities on the inner sides of the hindlegs. The infection rates of 94 red deer investigated in southern Germany during 1907–1974 were 23%.
 W
WOxyurida is an order of nematode worms of the class Secernentea. It consists of four families, one of which contains the human pinworm.
 W
WOxyuridae is a family of nematode worms of the class Secernentea. It consists of eight genera, one of which contains the human pinworm.
 W
WPhilometra cyanopodi is a species of parasitic nematode of fishes, first found off New Caledonia in the South Pacific, in the gonads of Epinephelus cyanopodus. This species is characterized mainly by: length of spicules and length and structure of its gubernaculum; structure of male caudal end; body size; location in host and types of hosts.
 W
WPhilometra fasciati is a species of parasitic nematode of fishes, first found off New Caledonia in the South Pacific, in the gonads Epinephelus fasciatus. This species is characterized mainly by: length of spicules and length and structure of its gubernaculum; structure of male caudal end; body size; location in host and types of hosts.
 W
WPhilometra lethrini is a species of parasitic nematode of fishes, first found off New Caledonia in the South Pacific, in the gonads of Lethrinus genivittatus. This species is characterized mainly by: length of spicules and length and structure of its gubernaculum; structure of male caudal end; body size; location in host and types of hosts.
 W
WPhysalopteridae is a family of spirurian nematodes, which belongs to the superfamily Physalopteroidea. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.
 W
WPratylenchidae is a family of plant pathogenic nematodes.
 W
WPratylenchus coffeae is a plant-pathogenic nematode infecting several hosts including potato, banana, sweet potato, strawberry, Persian violet, peanut and citrus.
 W
WPratylenchus neglectus is a plant-pathogenic nematode infecting potato, alfalfa and mint.
 W
WRasheedia is a genus of nematodes in the order Spirurida. The nematode genus Bulbocephalus Rasheed, 1966 was found to be a homonym of Bulbocephalus Watson, 1916 and, therefore, a new name, Rasheedia n. nom., was proposed in 2018 to substitute it.
 W
WRoot-gall nematodes are plant-parasitic nematodes from the genus Subanguina that affect grasses, including cereals, and some other plants, such as mugwort. They are distinct from the Root-knot nematodes which are from the genus Meloidogyne. So far around twenty-five separate species of Subanguina have been identified, although the most well-known and type species is Subanguina radicicola.
 W
WSecernentea was a class of nematodes in the Classical Phylogeny System and is no longer in use. This morphological-based classification system has been replaced by the Modern Phylogeny system, where taxonomy assignment is based on small subunit ribosomal DNA.
 W
WSubclass Spiruria comprises mostly parasitic secernentean nematodes. In an alternate classification, they are treated as suborder Spirurina, with the orders listed here being ranked as infraorders.
 W
WSpirurida is an order of spirurian nematodes. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.
 W
WSubuluridae is a family of spirurian nematodes which, together with the two species of Maupasinidae, make up the superfamily Subuluroidea. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.
 W
WThelaziidae is a family of spirurian nematodes, which form the mid-sized lineage of the superfamily Thelazioidea. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.
 W
WThelazioidea is a superfamily of spirurian nematodes in the large order Spirurida. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.
 W
WTylenchoidea is a superfamily of roundworms. Its members are either plant parasites or detritivores.
 W
WTylenchus is a genus of nematodes in the family Tylenchidae and subfamily Tylenchinae.