 W
WChampsocephalus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. They are native to the Southern Ocean.
 W
WAntarctic fish is a common name for a variety of fish that inhabit the Southern Ocean. There are relatively few families in this region, the most species-rich being the Liparidae (snailfishes), followed by Nototheniidae. The latter is one of five different families that belong to the suborder Notothenioidei of the order Perciformes. The other four are Artedidraconidae, Bathydraconidae, Channichthyidae and Harpagiferidae. They are also called notothenioids, but this name is also used to describe the other three, non-Antarctic families and some of the non-Antarctic genera in the mainly Antarctic families belonging to the suborder.
 W
WThe blackfin icefish, also known as the Scotia Sea icefish, is a species of crocodile icefish belonging to the family Channichthyidae. The blackfin icefish belongs to Notothenioidei, a suborder of fishes that accounts for 90% of the fish fauna on the Antarctic continental shelf. Icefishes, also called white-blooded fishes, are a unique family in that they are the only known vertebrates to lack haemoglobin, making their blood oxygen carrying capacity just 10% that of other teleosts. Icefishes have translucent blood and creamy white gills.
 W
WChannichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. They are native to the Southern Ocean.
 W
WChannichthys irinae, the pygmy icefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is endemic to the Kerguelen Islands in the Southern Ocean.
 W
WChannichthys mithridatis, the green icefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is endemic to the Kerguelen Islands in the Southern Ocean.
 W
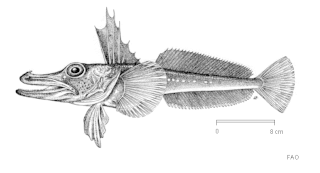
WChannichthys panticapaei, the charcoal icefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is endemic to the Kerguelen Islands area in the Southern Ocean. This demersal species is found at depths of 112–154 m (367–505 ft) and is sometimes caught in bottom trawls. However, it is not targeted and is of no interest to commercial fisheries at present. It is dark gray to uniformly blackish with long first to third dorsal fin spines. The charcoal icefish reaches lengths of up to 40.2 cm (15.8 in), with females generally being smaller. This planktivorous (plankton-eating) species likely spawns from June to July, with maturity reached at 30 cm TL / 27 cm SL.
 W
WChannichthys rhinoceratus, the unicorn icefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is endemic to the Kerguelen-Heard Plateau in the Southern Ocean. It is a demersal species living from surface waters to depths up to 750 m (2,460 ft). It is considered by some researchers as the only species in the genus Channichthys.
 W
WChannichthys richardsoni, the robust icefish, is a demersal species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is endemic to the shelf waters of the Kerguelen Islands in the Southern Ocean. It lives at depths of 126–310 metres (413–1,017 ft).
 W
WChannichthys velifer, or the sail icefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is endemic to the Kerguelen Plateau area of the Southern Ocean. This demersal species lives at depths of 125 to 150 m. It is described to have a light brownish-olive or grayish-olive color, with a white belly and dark spots on the caudal and dorsal fins forming brush-like patterns. The anal fins are whitish and dark brown spots are sometimes present. Preservation in formalin results in a reddish color. The granulation is moderate, and is better expressed in larger specimens. The dorsal fin membranes are high and there is a large number of dorsal fin rays, distinguishing it from similar Channichthys species. Furthermore, C.velifer has more pectoral fin rays than C.rugosus. This species feeds on fishes and cephalopods and is of no interest to commercial fisheries.
 W
WChionobathyscus is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes, its only member is Chionobathyscus dewitti. This species is found in the Southern Ocean.
 W
WChionodraco hamatus is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is found in the Southern Ocean.
 W
WThe ocellated icefish is a fish of the family Channichthyidae. It lives in the cold waters off Antarctica and is known for having transparent haemoglobin-free blood.
 W
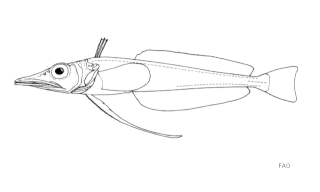
WCryodraco is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. They are found in the Southern Ocean. While C. antarcticus has minor commercial importance, C. atkinsoni and C. pappenheimi are of no interest to commercial fisheries.
 W
WCryodraco antarcticus, the long-fingered icefish, is a demersal species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It occurs only in deep waters of the Southern Ocean.
 W
WCryodraco atkinsoni is a bathydemersal species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is endemic to the waters of the eastern part of the Southern Ocean.
 W
WDacodraco is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes, its only member is Dacodraco hunteri. This species is found in the Southern Ocean.
 W
WThe Antarctic lanternfish or Electrona antarctica mainly inhabits the Antarctic deep, warm waters. It is the dominant species in the Southern Ocean. Their life span is about 4–5 years and they mature after 2–3 years. Their maximum length is 12.5 cm. Their feeding depends upon area to area. Small fish primarily feed on copepods, euphausiid larvae, and hyperiids. This species is mainly the nektonic prey species of seabirds in open water. It is an important krill predator and serves as prey for a majority of seabirds. It is one of the southernmost fish species, being recorded as far south as 74°40′S in the Ross Sea.
 W
WGobionotothen gibberifrons, the humped rockcod or the humphead notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the islands of the Scotia Arc, the northern part of the Antarctic Peninsula, and Heard Island in the Southern Ocean. This species inhabits depths of 6-429 m, but is most abundant at depths of 100-400 m, at least around Elephant Island.
 W
WGvozdarus svetovidovi, the naked-head toothfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is found in the Ross and Cooperation Seas, probably south of the Antarctic Polar Front from pelagic waters down to depths of 550 m (1,804 ft), though it is normally found in a pelagic environment.
 W
WThe mackerel icefish is a benthopelagic species of fish found in the Southern Ocean and the southernmost waters of the Atlantic Ocean. They are mainly to be found near Heard and McDonald Islands, Îles Kerguelen and islands in the south Atlantic such as South Georgia and Bouvet Island. The species also inhabits the northern waters of the Antarctic Peninsula. They live at depths of 0–700 metres (0–2,297 ft), but are commonly found at depths of 30 to 250 metres.
 W
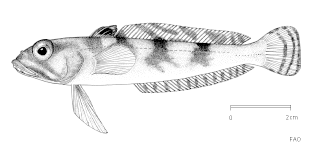
WJonah's icefish is a benthopelagic species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Neopagetopsis. It is found in the Southern Ocean at depths of from 20 to 900 metres. It has a circum-Antarctic distribution on the continental slope and continental shelf, with the northernmost records from the South Shetland and the South Orkney Islands.
 W
WLindbergichthys nudifrons, the yellowfin rockcod, also known as the yellow notie or the gaudy notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean.
 W
WThe longfin icedevil, also known as the threadfin pinhead, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Southern Ocean where it can be found at depths down to 850 metres (2,790 ft). This species grows to a length of 42 centimetres (17 in) TL. This species is the only known member of its genus and is of no interest to commercial fisheries.
 W
WLycodichthys antarcticus is a species of fish of the family Zoarcidae. It occurs in the Southern Ocean. It grows to 24 cm (9.4 in) total length.
 W
WNotothenia coriiceps, also known as the black rockcod, Antarctic yellowbelly rockcod, or Antarctic bullhead notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is widely spread around the Antarctic continent. Like other Antarctic notothenioid fishes, N. coriiceps evolved in the stable, ice-cold environment of the Southern Ocean. It is not currently targeted by commercial fisheries.
 W
WNotothenia cyanobrancha, the blue rockcod, bluegill notothen, or bluegill rockcod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Kerguelen and Heard Islands in the Southern Ocean.
 W
WPagetopsis macropterus species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. This species is found in the Southern Ocean.
 W
WPagetopsis maculata is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is found in the Southern Ocean. It is of no interest to commercial fisheries.
 W
WPagothenia is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. These fishes occur in the Southern Ocean.
 W
WPatagonotothen guntheri, the yellowfin notothen, is a species of notothen found in the Argentinian region of Patagonia, the Falkland Islands, the Burdwood Bank and the Shag Rocks west of South Georgia on the continental shelf at depths of 120-250 m, but may be found in waters deeper than 250 m in the Argentinian region.
 W
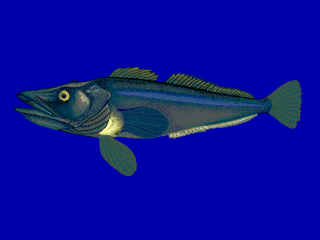
WThe ploughfish is a species of Antarctic dragonfish native to the Southern Ocean around Antarctica. It is found at depths of from 0 to 550 m over the Antarctic continental shelf. This species is the only known member of its genus.
 W
WPseudochaenichthys is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. Its only member is Pseudochaenichthys georgianus, the South Georgia icefish, which is found in the Southern Ocean.
 W
WThe ridge scaled rattail or ridge-scaled grenadier, Macrourus carinatus, is a species of deep-water fish in the family Macrouridae. It has southern circumglobal distribution in temperate to subantarctic waters (34°S–65°S) and is found in the Southern Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans and in the Southern Ocean at depths of about 200–1,200 m (660–3,940 ft).
 W
WThe emerald rockcod, also known as the emerald notothen is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Southern Oceanwhere it is acommercially important species.
 W
WThe marbled rockcod is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Southern Ocean, where it can be found at depths from 5 to 350 m. This is a commercially important species.
 W
WThe Antarctic toothfish is a species of notothen native to the Southern Ocean. It is often mistakenly referred to as an Antarctic cod, consistent with the misnaming of other notothenioid Antarctic fish as rock cods. However, notothenioid fishes are not closely related to cods, which are in another taxonomic order, the Gadiformes. The generic name Dissostichus is from the Greek dissos (twofold) and stichus (line) and refers to the presence of two long lateral lines, which are very important to the species’ ecology. The common name "toothfish" refers to the presence of biserial dentition in the upper jaw, thought to give it a shark-like appearance. The habitat of the Antarctic toothfish is in subzero degree water below latitude 60°S.
 W
WThe Patagonian toothfish is a species of notothen found in cold waters between depths of 45 and 3,850 m in the southern Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans and Southern Ocean on seamounts and continental shelves around most Subantarctic islands.
 W
WTrematomus is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. These fishes occur in the Southern Ocean.