 W
WNeuropeptides are small proteins produced by neurons that act on G protein-coupled receptors and are responsible for slow-onset, long-lasting modulation of synaptic transmission. Neuropeptides often coexist with each other or with other neurotransmitters in single neurons. According to their chemical nature, coexisting messengers are localized to different cell compartments: neuropeptides are packaged in large granular vesicles (LGVs), whereas low-molecular weight neurotransmitters are stored in small synaptic vesicles.
 W
WN-Acetylaspartylglutamic acid is a peptide neurotransmitter and the third-most-prevalent neurotransmitter in the mammalian nervous system. NAAG consists of N-acetylaspartic acid (NAA) and glutamic acid coupled via a peptide bond.
 W
WAgouti-related protein (AgRP), also called agouti-related peptide, is a neuropeptide produced in the brain by the AgRP/NPY neuron. It is synthesized only in neuropeptide Y (NPY)-containing cell bodies located in the ventromedial part of the arcuate nucleus in the hypothalamus. AgRP is co-expressed with NPY and acts to increase appetite and decrease metabolism and energy expenditure. It is one of the most potent and long-lasting of appetite stimulators. In humans, the agouti-related peptide is encoded by the AGRP gene.
 W
WCholecystokinin is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat and protein. Cholecystokinin, officially called pancreozymin, is synthesized and secreted by enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum, the first segment of the small intestine. Its presence causes the release of digestive enzymes and bile from the pancreas and gallbladder, respectively, and also acts as a hunger suppressant.
 W
WPrecortistatin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CORT gene. The 105 amino acid residue human precortistatin in turn is cleaved into cortistatin-17 and cortistatin-29. Cortistatin-17 is the only active peptide derived from the precursor. Cortistatin is a neuropeptide that is expressed in inhibitory neurons of the cerebral cortex, and which has a strong structural similarity to somatostatin. Unlike somatostatin, when infused into the brain, it enhances slow-wave sleep. It binds to sites in the cortex, hippocampus and the amygdala.
 W
WDynorphin A is a dynorphin, an endogenous opioid peptide with the amino acid sequence: Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys.
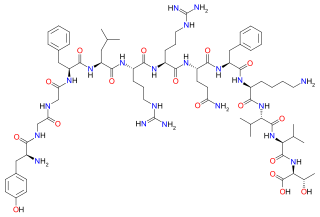 W
WDynorphin B, also known as rimorphin, is a form of dynorphin and an endogenous opioid peptide with the amino acid sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Gln-Phe-Lys-Val-Val-Thr. Dynorphin B is generated as a proteolyic cleavage product of leumorphin, which in turn is a cleavage product of preproenkephalin B (prodynorphin).
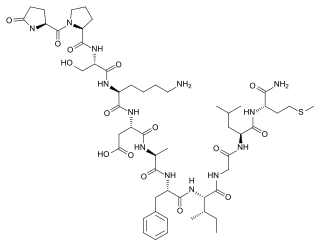 W
WEledoisin is an undecapeptide of mollusk origin, belonging to the tachykinin family of neuropeptides.
 W
WEndomorphin-1 (EM-1) (amino acid sequence Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2) is an endogenous opioid peptide and one of the two endomorphins. It is a high affinity, highly selective agonist of the μ-opioid receptor, and along with endomorphin-2 (EM-2), has been proposed to be the actual endogenous ligand of the μ-receptor. EM-1 produces analgesia in animals and is equipotent with morphine in this regard. The gene encoding for EM-1 has not yet been identified, and it has been suggested that endomorphins could be synthesized by an enzymatic, non-ribosomal mechanism.
 W
WEndomorphin-2 (EM-2) is an endogenous opioid peptide and one of the two endomorphins. It has the amino acid sequence Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2. It is a high affinity, highly selective agonist of the μ-opioid receptor, and along with endomorphin-1 (EM-1), has been proposed to be the actual endogenous ligand of this receptor (that is, rather than the endorphins). Like EM-1, EM-2 produces analgesia in animals, but whereas EM-1 is more prevalent in the brain, EM-2 is more prevalent in the spinal cord. In addition, the action of EM-2 differs from that of EM-1 somewhat, because EM-2 additionally induces the release of dynorphin A and [Met]enkephalin in the spinal cord and brain by an unknown mechanism, which in turn go on to activate the κ- and δ-opioid receptors, respectively, and a portion of the analgesic effects of EM-2 is dependent on this action. Moreover, while EM-1 produces conditioned place preference, a measure of drug reward, EM-2 produces conditioned place aversion, an effect which is dynorphin A-dependent. Similarly to the case of EM-1, the gene encoding for EM-2 has not yet been identified.
 W
Wγ-Endorphin is an opioid peptide that is characterized by the presence of 17 amino acids. The first 16 amino acids are identical to α-endorphin with Leucine added at the end; or alternatively, γ-Endorphin is equal to the first 17 amino acids of beta-Endorphin. Similar to other endorphins, research focusing upon γ-endorphin has been ongoing since its discovery in the 1970s. Yet, most of the information about the substance’s exact role within the body is speculation that has yet to be proven. Some studies have indicated, however, that the polypeptide has antipsychotic effects on a certain category of patients suffering from schizophrenia, while others suggest that gamma-endorphin may act to help regulate blood pressure. Further research is needed, but if γ-endorphin does indeed possess such characteristics, the substance could eventually be utilized as a useful means of medical treatment.
 W
WGalanin is a neuropeptide encoded by the GAL gene, that is widely expressed in the brain, spinal cord, and gut of humans as well as other mammals. Galanin signaling occurs through three G protein-coupled receptors.
 W
WGalmic is a drug which acts as a selective, non-peptide agonist at the galanin receptors GALR. It has anticonvulsant, antidepressant and analgesic effects in animal studies, but also inhibits memory functions.
 W
WGalnon is a drug which acts as a selective, non-peptide agonist at the galanin receptors GALR. It has anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, anorectic and amnestic effects in animal studies.
 W
WGhrelin is a hormone produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases food intake. Blood levels of ghrelin are highest before meals when hungry, returning to lower levels after mealtimes. Ghrelin may help prepare for food intake by increasing gastric motility and gastric acid secretion.
 W
WKisspeptins are proteins encoded by the KISS1 gene in humans. Kisspeptins are ligands of the G-protein coupled receptor, GPR54. Kiss1 was originally identified as a human metastasis suppressor gene that has the ability to suppress melanoma and breast cancer metastasis. Kisspeptin-GPR54 signaling has an important role in initiating secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) at puberty, the extent of which is an area of ongoing research. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone is released from the hypothalamus to act on the anterior pituitary triggering the release of luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). These gonadotropic hormones lead to sexual maturation and gametogenesis. Disrupting GPR54 signaling can cause hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism in rodents and humans. The Kiss1 gene is located on chromosome 1. It is transcribed in the brain, adrenal gland, and pancreas.
 W
WNeurokinin B (NKB) belongs in the family of tachykinin peptides. Neurokinin B is implicated in a variety of human functions and pathways such as the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Additionally, NKB is associated with pregnancy in females and maturation in young adults. Reproductive function is highly dependent on levels of both neurokinin B and also the G-protein coupled receptor ligand kisspeptin. The first NKB studies done attempted to resolve why high levels of the peptide may be implicated in pre-eclampsia during pregnancy. NKB, kisspeptin, and dynorphin together are found in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) known as the KNDy subpopulation. This subpopulation is targeted by many steroid hormones and works to form a network that feeds back to GnRH pulse generator.
 W
WNeuromedin N is a neuropeptide derived from the same precursor polypeptide as neurotensin, and with similar but subtly distinct expression and effects.
 W
WNeuropeptide B is a short biologically active peptide whose precursor in humans is encoded by the NBP gene. Neuropeptide B acts via two G protein-coupled receptors, neuropeptide B/W receptors, called NPBW1 and NPBW2 encoded by the genes NPBWR1 and NPBWR2, respectively. Neuropeptide B is thought to be associated with the regulation of feeding, neuroendocrine system, memory, learning and in the afferent pain pathway. It is expressed throughout the CNS with high levels in the substantia nigra, hypothalamus, hippocampus, and spinal cord.
 W
WNeuropeptide S (NPS) is a neuropeptide found in human and mammalian brain, mainly produced by neurons in the amygdala and between Barrington's nucleus and the locus coeruleus, although NPS-responsive neurons extend projections into many other brain areas. NPS binds specifically to a G protein-coupled receptor, NPSR. Animal studies show that NPS suppresses anxiety and appetite, induces wakefulness and hyperactivity, including hyper-sexuality, and plays a significant role in the extinction of conditioned fear. It has also been shown to significantly enhance dopamine activity in the mesolimbic pathway, and inhibits motility and increases permeability in neurocrine fashion acting through NO in the myenteric plexus in rats and humans.
 W
WNeuropeptide W or preprotein L8 is a short human neuropeptide. Neuropeptide W acts as a ligand for two neuropeptide B/W receptors, NPBWR1 and NPBWR2, which are integrated in GPCRs family of alpha-helical transmembrane proteins.
 W
WNeuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36 amino-acid neuropeptide that is involved in various physiological and homeostatic processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. NPY has been identified as the most abundant peptide present in the mammalian central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is secreted alongside other neurotransmitters such as GABA and glutamate.
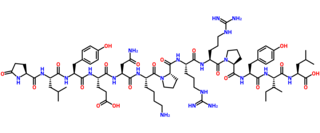 W
WNeurotensin is a 13 amino acid neuropeptide that is implicated in the regulation of luteinizing hormone and prolactin release and has significant interaction with the dopaminergic system. Neurotensin was first isolated from extracts of bovine hypothalamus based on its ability to cause a visible vasodilation in the exposed cutaneous regions of anesthetized rats.
 W
WNociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ), a 17-amino acid neuropeptide, is the endogenous ligand for the nociceptin receptor, and initiates its function to act on numerous brain activities such as pain sensation and fear learning. It is derived from the prepronociceptin protein, as are a further 2 peptides, nocistatin & NocII, which inhibit the N/OFQ receptor function. Nociceptin itself acts as a potent anti-analgesic, effectively counteracting the effect of pain-relievers. The gene coding for prepronociceptin is located on Ch8p21 in humans. Nociceptin acts at the Nociceptin receptor formerly known as ORL1. Nociceptin is the first example of reverse pharmacology; the NOP receptor was discovered before the endogenous ligand which was discovered by two separate groups in 1995.
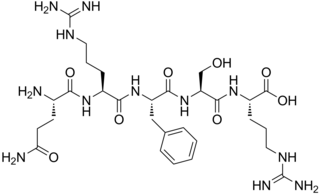 W
WOpiorphin is an endogenous chemical compound first isolated from human saliva. Initial research with mice shows the compound has a painkilling effect greater than that of morphine. It works by stopping the normal breakup of enkephalins, natural pain-killing opioids in the spinal cord. It is a relatively simple molecule consisting of a five-amino acid polypeptide, Gln-Arg-Phe-Ser-Arg.
 W
WOrexin, also known as hypocretin, is a neuropeptide that regulates arousal, wakefulness, and appetite. The least common form of narcolepsy, type 1, in which the sufferer experiences brief losses of muscle tone (cataplexy), is caused by a lack of orexin in the brain due to destruction of the cells that produce it.
 W
WOxytocin (Oxt) is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide. It is normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. It plays a role in social bonding, reproduction, childbirth, and the period after childbirth. Oxytocin is released into the bloodstream as a hormone in response to love and in labor. This helps with birth, bonding with the baby, and milk production.
 W
WPhenypressin (Phe2-Arg8-vasopressin) is an oxytocin neuropeptide belonging to the vertebrae vasopressin family and has similar pharmacological properties as arginine vasopressin. The name phenypressin came about because there is a substitution of phenylalanine that makes it different from arginine vasopressin in the second residue and that is the only difference. It belongs to the family, neurohypophysial hormones, named after the fact that they are secreted by the neurohypophysis which is a neural projection from the hypothalamus. It has mostly been found to be present is some species belonging to the family, Macropodidae, particularly eastern gray kangaroos[3], red kangaroos, tammar wallaby, and the quokka wallaby. In other marsupial families, Phenypressin has not yet specifically been identified, but they do have other vasopressin-like peptides present.
 W
WPhysalaemin is a tachykinin peptide obtained from the Physalaemus frog, closely related to substance P. Its structure was first elucidated in 1964.
 W
WPro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is a precursor polypeptide with 241 amino acid residues. POMC is synthesized in corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary from the 285-amino-acid-long polypeptide precursor pre-pro-opiomelanocortin (pre-POMC), by the removal of a 44-amino-acid-long signal peptide sequence during translation. POMC is part of the central melanocortin system.
 W
WRelaxin-3 is a neuropeptide that was discovered in 2001, and which is highly conserved in species ranging from flies, fish, rodents and humans. Relaxin-3 is a member and ancestral gene of the relaxin family of peptides, which includes the namesake hormone relaxin which mediates peripheral actions during pregnancy and which was found to relax the pelvic ligament in guinea pigs almost a century ago. The cognate receptor for relaxin-3 is the G-protein coupled receptor RXFP3, however relaxin-3 is pharmacologically able to also cross react with RXFP1 and RXFP3.
 W
WSomatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion.
 W
WSubstance P (SP) is an undecapeptide member of the tachykinin neuropeptide family. It is a neuropeptide, acting as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. Substance P and its closely related neurokinin A (NKA) are produced from a polyprotein precursor after differential splicing of the preprotachykinin A gene. The deduced amino acid sequence of substance P is as follows:Arg Pro Lys Pro Gln Gln Phe Phe Gly Leu Met (RPKPQQFFGLM)
 W
WPreprotachykinin-1,, is a precursor protein that in humans is encoded by the TAC1 gene.
 W
WTachykinin peptides are one of the largest families of neuropeptides, found from amphibians to mammals. They were so named due to their ability to rapidly induce contraction of gut tissue. The tachykinin family is characterized by a common C-terminal sequence, Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, where X is either an Aromatic or an Aliphatic amino acid. The genes that produce tachykinins encode precursor proteins called preprotachykinins, which are chopped apart into smaller peptides by posttranslational proteolytic processing. The genes also code for multiple splice forms that are made up of different sets of peptides.
 W
WUrotensin II-related peptide (URP) is a cyclic neuropeptide that is found in all vertebrates that have been genome sequenced so far. It has a long lasting hypotensive effect and may also regulate reproduction. It is part of the Urotensin II system and is one of the two endogenous ligands for rats, mice, and possibly humans.
 W
WVasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon of that cell, which terminates in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity (hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure.
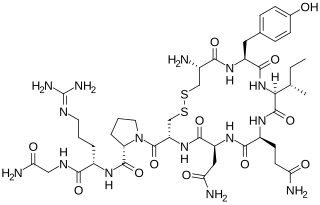 W
WVasotocin is an oligopeptide homologous to oxytocin and vasopressin found in all non-mammalian vertebrates and possibly in mammals during the fetal stage of development. Arginine vasotocin (AVT), a hormone produced by neurosecretory cells within the posterior pituitary gland (neurohypophysis) of the brain, is a major endocrine regulator of water balance and osmotic homoeostasis and is involved in social and sexual behavior in non-mammalian vertebrates. In mammals, it appears to have biological properties similar to those of oxytocin and vasopressin. It has been found to have effects on the regulation of REM sleep. Evidence for the existence of endogenous vasotocin in mammals is limited and no mammalian gene encoding vasotocin has been confirmed.
 W
WVGF or VGF nerve growth factor inducible is a secreted protein and neuropeptide precursor that may play a role in regulating energy homeostasis, metabolism and synaptic plasticity. The protein was first discovered in 1985 by Levi et al. in an experiment with PC12 cells and its name is non-acronymic. VGF gene encodes a precursor which is divided by proteolysis to polypeptides of different mass, which have a variety of functions, the best studied of which are the roles of TLQP-21 in the control of appetite and inflammation., and TLQP-62 as well as AQEE-30 in regulating depression-like behaviors and memory The expression of VGF and VGF-derived peptides is detected in a subset of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems and specific populations of endocrine cells in the adenohypophysis, adrenal medulla, gastrointestinal tract, and pancreas. VGF expression is induced by NGF, CREB and BDNF and regulated by neurotrophin-3. Physical exercise significantly increases VGF expression in mice hippocampal tissue and upregulates a neurotrophic signaling cascade thought to underlie the action of antidepressants.