 W
WCarbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Their clinical use has been established as anti-glaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, gastric and duodenal ulcers, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, neurological disorders, or osteoporosis.
 W
WAcetazolamide, sold under the trade name Diamox among others, is a medication used to treat glaucoma, epilepsy, altitude sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, and heart failure. It may be used long term for the treatment of open angle glaucoma and short term for acute angle closure glaucoma until surgery can be carried out. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein.
 W
WBendroflumethiazide, formerly bendrofluazide, trade name Aprinox, is a thiazide diuretic used to treat hypertension.
 W
WBenzthiazide is a thiazide diuretic used in the treatment of high blood pressure and edema. It is no longer available in the United States.
 W
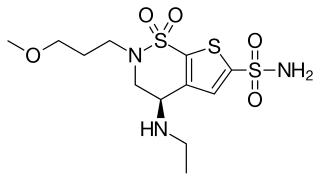
WBrinzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to lower intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
 W
WBumetanide, sold under the trade name Bumex among others, is a medication used to treat swelling and high blood pressure. This includes swelling as a result of heart failure, liver failure, or kidney problems. It may work for swelling when other medications have not. For high blood pressure it is not a preferred treatment. It is taken by mouth, or by injection into a vein or muscle. Effects generally begin within an hour and lasts for about six hours.
 W
WCasuarinin is an ellagitannin. It is found in the pericarp of pomegranates. It is also found in Casuarina and Stachyurus species and in Alnus sieboldiana.
 W
WChlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Diuril among others, is an organic compound used as a diuretic and as an antihypertensive.
 W
WChlortalidone, also known as chlorthalidone, is a diuretic medication used to treat high blood pressure, swelling including that due to heart failure, liver failure, and nephrotic syndrome, diabetes insipidus, and renal tubular acidosis. In high blood pressure it is a preferred initial treatment. It is also used to prevent calcium-based kidney stones. It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin within three hours and last for up to three days.
 W
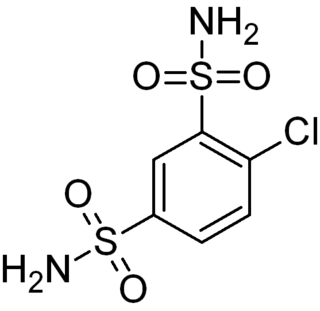
WClofenamide is a low-ceiling sulfonamide diuretic.
 W
WClopamide is a piperidine diuretic.
 W
WCyclothiazide, sometimes abbreviated CTZ, is a benzothiadiazide (thiazide) diuretic and antihypertensive that was originally introduced in the United States in 1963 by Eli Lilly and was subsequently also marketed in Europe and Japan. Related drugs include diazoxide, hydrochlorothiazide, and chlorothiazide.
 W
WDiazoxide, sold under the brand name Proglycem, is a medication used to treat low blood sugar due to a number of specific causes. This includes islet cell tumors that cannot be removed and leucine sensitivity. It can also be used in refractory cases of sulfonylurea toxicity. It is generally taken by mouth.
 W
WDiclofenamide is a sulfonamide and a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor of the meta-disulfamoylbenzene class.
 W
WDorzolamide, sold under the brand name Trusopt among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. It is used as an eye drop. Effects begin within three hours and lasts for at least eight hours. It is also available as the combination dorzolamide/timolol.
 W
WEtacrynic acid (INN) or ethacrynic acid (USAN), trade name Edecrin, is a loop diuretic used to treat high blood pressure and the swelling caused by diseases like congestive heart failure, liver failure, and kidney failure.
 W
WEthoxzolamide is a sulfonamide medication that functions as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. It is used in the treatment of glaucoma and duodenal ulcers, and as a diuretic. It may also be used in the treatment of some forms of epilepsy.
 W
WFurosemide, sold under the brand name Lasix among others, is a medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mouth. When taken by mouth, it typically begins working within an hour, while intravenously, it typically begins working within five minutes.
 W
WGranatin B is an ellagitannin found in the fruit of Punica granatum (pomegranate). It is a molecule having an enantiomeric dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl group.
 W
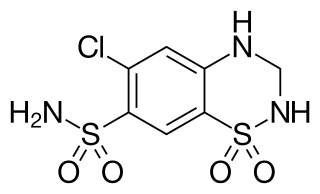
WHydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic medication often used to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build up. Other uses include treating diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. For high blood pressure it is sometimes considered as a first-line treatment. HCTZ is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness.
 W
WHydroflumethiazide is a diuretic.
 W
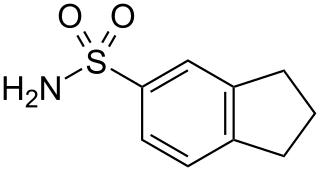
WIndane-5-sulfonamide is the base structure of indanesulfonamides. Indane-5-sulfonamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
 W
WIndapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic drug generally used in the treatment of hypertension, as well as decompensated heart failure. Combination preparations with perindopril are also available. Thiazide-like diuretics appear to be more effective than the thiazide-type diuretics (hydrochlorothiazide) in reducing risk of major cardiovascular events and heart failure in persons with high blood pressure. In terms of risk of stroke, both thiazide-type and thiazide-like diuretic are effective in reducing it. Both drug classes also appear to have similar rates of adverse effects when compared to other classes of anti-hypertensives.
 W
WMafenide is a sulfonamide-type medication used as an antibiotic. It was approved by the FDA in 1948.
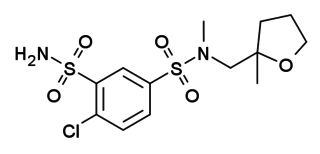 W
WMefruside (INN) is a diuretic indicated for the treatment of edema and hypertension.
 W
WMethazolamide is a potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. It is indicated in the treatment of increased intraocular pressure (IOP) in chronic open-angle glaucoma and secondary glaucoma. Also it is used preoperatively in acute angle-closure (narrow-angle) glaucoma where lowering the IOP is desired before surgery.
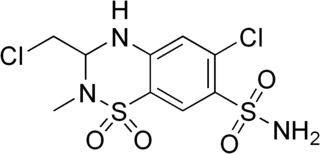 W
WMethyclothiazide is a thiazide diuretic.
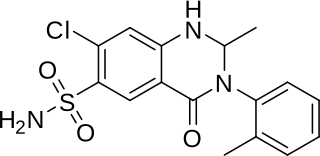 W
WMetolazone is a thiazide-like diuretic marketed under the brand names Zytanix, Metoz, Zaroxolyn, and Mykrox. It is primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure. Metolazone indirectly decreases the amount of water reabsorbed into the bloodstream by the kidney, so that blood volume decreases and urine volume increases. This lowers blood pressure and prevents excess fluid accumulation in heart failure. Metolazone is sometimes used together with loop diuretics such as furosemide or bumetanide, but these highly effective combinations can lead to dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities.
 W
WPedunculagin is an ellagitannin. It is formed from casuarictin via the loss of a gallate group.
 W
WPiretanide is a loop diuretic compound by using a then-new method for introducing cyclic amine residues in an aromatic nucleus in the presence of other aromatically bonded functional groups. Studies of piretanide in rats and dogs in comparison with other high-ceiling diuretics such as furosemide and bumetanide found a more suitable dose/response rate and a more favourable sodium/potassium excretion ratio. These findings led eventually to studies in man and finally to the introduction as a saluretic and antihypertensive medication in Germany, France, Italy and other countries.
 W
WPolythiazide is a thiazide diuretic. A diuretic is any substance that promotes the production of urine.
 W
WPunicalagin is an ellagitannin, a type of phenolic compound. It is found in forms alpha and beta in pomegranates, in Terminalia catappa and Terminalia myriocarpa, and in Combretum molle, the velvet bushwillow, a plant species found in South Africa. These three genera are all Myrtales and the last two are both Combretaceae.
 W
WPunicalin is an ellagitannin. It can be found in Punica granatum (pomegranate) or in the leaves of Terminalia catappa, a plant used to treat dermatitis and hepatitis. It is also reported in Combretum glutinosum, all three species being Myrtales, the two last being Combretaceae.
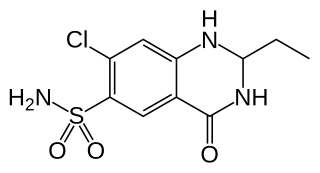 W
WQuinethazone is a thiazide-like diuretic used to treat hypertension. Common side effects include dizziness, dry mouth, nausea, and low potassium levels.
 W
WSultiame, also known as sulthiame, is a sulfonamide and inhibitor of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. It is used as an anticonvulsant.
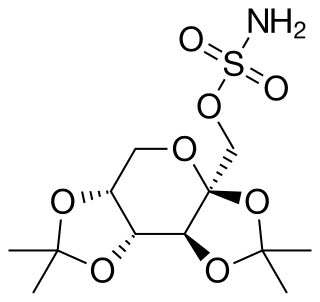 W
WTopiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used in alcohol dependence. For epilepsy this includes treatment for generalized or focal seizures. It is taken by mouth.
 W
WTorasemide, also known as torsemide, is a diuretic medication used to treat fluid overload due to heart failure, kidney disease, and liver disease and high blood pressure. It is a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
 W
WTrichlormethiazide is a diuretic with properties similar to those of hydrochlorothiazide. It is usually administered for the treatment of oedema and hypertension. In veterinary medicine, trichlormethiazide can be combined with dexamethasone to be used on horses with mild swelling of distal limbs and general bruising.
 W
WXipamide is a sulfonamide diuretic drug marketed by Eli Lilly under the trade names Aquaphor and Aquaphoril. It is used for the treatment of oedema and hypertension.
 W
WZonisamide is a medication used to treat the symptoms of epilepsy and Parkinson's disease. Chemically it is a sulfonamide. It serves as an anticonvulsant used primarily as an adjunctive therapy in adults with Parkinson's disease, partial-onset seizures; infantile spasm, mixed seizure types of Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, myoclonic and generalized tonic clonic seizure. Despite this it is also sometimes used as a monotherapy for partial-onset seizures.