 W
WMytilidae are a family of small to large marine and brackish-water bivalve molluscs in the order Mytilida. One of the genera, Limnoperna, even inhabits freshwater environments. The order has only this one family which contains some 52 genera.
 W
WAdipicola pelagica is a species of saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. It is a deepwater species and is found attached to the bones and tissues of whales that have died and sunk to the seabed, and sometimes to fragments of decomposing carcases which have sloughed off and floated to the surface.
 W
WAmygdalum is a genus of saltwater mussels, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Mytilidae, the true mussels.
 W
WArcuatula is a genus of mussels from the family Mytilidae.
 W
WArcuatula senhousia, commonly known as the Asian date mussel, Asian mussel or bag mussel, is a small saltwater mussel, a marine bivalve mollusk species in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. Other common names for this species include: the Japanese mussel, Senhouse's mussel, the green mussel, and the green bagmussel. It is harvested for human consumption in China.
 W
WBotula fusca, or the cinnamon mussel, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from North Carolina to the West Indies and Bermuda.
 W
WBrachidontes is a genus of mussels in the family Mytilidae.
 W
WBrachidontes crebristriatus, also known as the Hawaiian mussel, nahawele liʻiliʻi or kio-nawahele, is a bivalve known only from Hawaiʻi.
 W
WBrachidontes exustus, or the scorched mussel, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Cape Hatteras to the West Indies and Brazil.
 W
WBrachidontes modiolus, or the yellow mussel, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Florida to the West Indies.
 W
WBrachidontes pharaonis is a species of mussel from the family Mytilidae. It is native to the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, and has colonised the Mediterranean Sea where it is regarded as an invasive species.
 W
WChoromytilus is a genus of mussel, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae.
 W
WChoromytilus chorus, common name Chorus mussel or Choro mussel, is a species of mussel, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae.
 W
WChoromytilus meridionalis, the black mussel, is a species of bivalve. It is a marine mollusc in the family Mytilidae.
 W
WGeukensia is a genus of marine bivalve mollusc in the Mytilidae family, naturally found in the western Atlantic.
 W
WGeukensia demissa is a species of mussel, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Mytilidae, the true mussels. This species is native to the Atlantic coast of North America. The common names for this species include ribbed mussel, Atlantic ribbed marsh mussel and ribbed horsemussel. However, the common name ribbed mussel is also used for the Southern Hemisphere mussel Aulacomya atra. The appearance of the shell is grooved and oval in shape. The interior of this mussel is tinted purple
 W
WGibbomodiola is a genus of bivalves belonging to the family Mytilidae.
 W
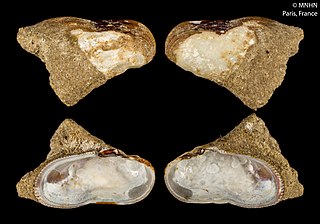
WGibbomodiola adriatica is a species of mussel commonly known as the Adriatic mussel. It can be found in: France, Ireland, the Mediterranean Sea, the North Atlantic Ocean, Sweden, Ukraine, and the United Kingdom.
 W
WGregariella is a genus of mussels in the family Mytilidae.
 W
WIdas is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae, the mussels.
 W
WIdas simpsoni, previously known as Adipicola simpsoni, is a species of saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. It is a deepwater species and is only found attached to the bones of dead whales.
 W
WIschadium is a monotypic genus of mussels in the family Mytilidae. The sole species is Ischadium recurvum, known as the "hooked mussel" or "bent mussel". It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Cape Cod to the West Indies. They are often found growing on Eastern oysters, either intertidal or subtidal. They also attach to other hard substrates, including artificial reefs and dead shells of brackish water clams, Rangia cuneata.
 W
WLimnoperna fortunei, the golden mussel, is a medium-sized freshwater bivalve mollusc of the family Mytilidae. The native range of the species is China, but it has accidentally been introduced to South America and several Asian countries where it has become an invasive species. It is considered to be an ecosystem engineer because it alters the nature of the water and the bottom habitats of lakes and rivers and modifies the associated invertebrate communities. It also has strong effects on the properties of the water column, modifying nutrient proportions and concentrations, increasing water transparency, decreasing phytoplankton and zooplankton densities, on which it feeds, and enhancing the growth of aquatic macrophytes. Because mussels attach to hard substrata, including the components of industrial, water-treatment and power plants, they have become a major biofouling problem in the areas invaded.
 W
WLioberus is a genus of mussels in the family Mytilidae.
 W
WModiolarca, is a genus of medium-sized marine bivalve molluscs in the Family Mytilidae, the mussels.
 W
WModiolarca impacta is a species of saltwater clam, a mussel, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Mytilidae, the mussels.
 W
WMusculus somaliensis is an extinct species of small saltwater mussel, a fossil marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. The size, shape and sometimes color of these fossils are reminiscent of a pistachio nut.
 W
WMytella is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae, the mussels.
 W
WMytella charruana is a bivalve, commonly known as the charru mussel. This species was discovered in Central and South America and by Alcide d'Orbigny, A French naturalist in 1842. They are less than an inch long (2.5 cm), and range from brown to black in color.
 W
WMytella guyanensis is a species of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae, the mussels.
 W
WPerna is a genus of mussels, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae.
 W
WPerna canaliculus, the New Zealand green-lipped mussel, also known as the New Zealand mussel, the greenshell mussel, kuku, and kutai, is a bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae. P. canaliculus has economic importance as a cultivated species in New Zealand.
 W
WPerna perna, the brown mussel, is an economically important mussel, a bivalve mollusc belonging to the family Mytilidae. It is harvested as a food source but is also known to harbor toxins and cause damage to marine structures. It is native to the waters of Africa, Europe, and South America and was introduced in the waters of North America.
 W
WPerna viridis, known as the Asian green mussel, is an economically important mussel, a bivalve belonging to the family Mytilidae. It is harvested for food but is also known to harbor toxins and cause damage to submerged structures such as drainage pipes. It is native in the Asia-Pacific region but has been introduced in the Caribbean, and in the waters around Japan, North America, and South America.
 W
WPerumytilus is a monotypic genus of bivalves belonging to the family Mytilidae. The only species is Perumytilus purpuratus.
 W
WSemimytilus is a genus in the family Mytilidae. The genus is also connected with freshwater habitats.
 W
WSemimytilus algosus is a species of mussels. A common name for this species is Bisexual mussel, or Dwarf mussel. It is the first species where trioecy was reported in the phylum Mollusca.
 W
WSeptifer is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae, the mussels.
 W
WSeptifer bilocularis is a marine bivalve species in the family Mytilidae, the mussels.
 W
WTrichomya is a monotypic genus of marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. The only species is Trichomya hirsuta which is endemic to southern and eastern Australia. Its common names include the hairy mussel, the greenling and the kelp greenling.