 W
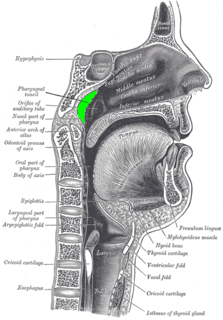
WIn anatomy, the adenoid, also known as the pharyngeal tonsil or nasopharyngeal tonsil, is the superior-most of the tonsils. It is a mass of lymphatic tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof of the nasopharynx, where the nose blends into the throat. In children, it normally forms a soft mound in the roof and back wall of the nasopharynx, just above and behind the uvula.
 W
WThe anterior cervical lymph nodes are a group of nodes found on the anterior part of the neck, in front of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. These can be grouped into a deep and superficial group.
 W
WThe buccinator lymph node or nodes are one or more lymph nodes placed on the Buccinator opposite the angle of the mouth.
 W
WCervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflammation.
 W
WThe deep anterior cervical lymph nodes are found near the middle cricothyroid ligament and the trachea.
 W
WThe deep cervical lymph nodes are a group of cervical lymph nodes found near the internal jugular vein.
 W
WThe deep lateral cervical lymph nodes are found near the upper part of the internal jugular vein in the neck, lateral or posterior to the carotid sheath.
 W
WThe deep parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found below the parotid gland.
 W
WThe facial lymph nodes comprise three groups:(a) infraorbital or maxillary, scattered over the infraorbital region from the groove between the nose and cheek to the zygomatic arch; (b) buccinator, one or more placed on the buccinator muscle opposite the angle of the mouth; (c) supramandibular, on the outer surface of the mandible, in front of the masseter and in contact with the external maxillary artery and anterior facial vein.
 W
WThe inferior deep cervical lymph nodes extend beyond the posterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid muscle into the subclavian triangle, where they are closely related to the brachial plexus and subclavian vein.
 W
WThe infra-auricular deep parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found underneath the ear.
 W
WThe Intraglandular deep parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found inside the parotid gland.
 W
WThe jugular trunk is a lymphatic vessel in the neck. It is formed by vessels that emerge from the superior deep cervical lymph nodes and unite to efferents of the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes.
 W
WThe juguloomohyoid lymph node is related to the intermediate tendon of the omohyoid muscle. It is designated as one of the deep cervical lymph nodes. As it is associated with the lymph drainage of the tongue if enlarged, it can be a sign of a tongue carcinoma.
 W
WThe jugulodigastric lymph nodes are large lymph nodes of the neck.
 W
WThe lateral cervical lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found in the lateral side of the neck.
 W
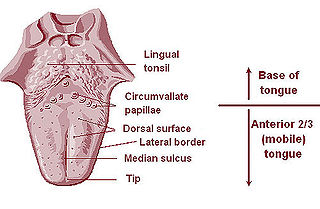
WThe lingual tonsils are a collection of lymphatic tissue located in the lamina propria of the root of the tongue. This lymphatic tissue consists of the lymphatic nodules rich in cells of the immune system (immunocytes). The immunocytes initiate the immune response when the lingual tonsils get in contact with invading microorganisms.
 W
WThe mandibular lymph node is a lymph node found near the jaw.
 W
WThe mastoid lymph nodes are a small group of lymph nodes, usually two in number, located just beneath the ear, on the mastoid insertion of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, beneath the posterior auricular muscle.
 W
WThe nasolabial lymph node is a facial node found near the nose and upper lip.
 W
WThe occipital lymph nodes, one to three in number, are located on the back of the head close to the margin of the trapezius and resting on the insertion of the semispinalis capitis.
 W
WPalatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish lumps. Tonsils only present as "white lumps" if they are inflamed or infected with symptoms of exudates and severe swelling.
 W
WThe right and left paratracheal lymph nodes are groups of lymph nodes located in the throat.
 W
WParotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found near the parotid gland in the immune system.
 W
WThe preauricular deep parotid lymph nodes, from one to three in number, lie immediately in front of the tragus.
 W
WPrelaryngeal lymph nodes are lymph nodes located anterior to the larynx.
 W
WThe pretracheal lymph nodes are lymph nodes located anterior to the trachea.
 W
WThe retropharyngeal lymph nodes, from one to three in number, lie in the buccopharyngeal fascia, behind the upper part of the pharynx and in front of the arch of the atlas, being separated, however, from the latter by the Longus capitis.
 W
WThe submandibular lymph nodes, three to six in number, are lymph nodes beneath the body of the mandible in the submandibular triangle, and rest on the superficial surface of the submandibular gland.
 W
WThe submental glands are situated between the anterior bellies of the digastric muscle and the hyoid bone.
 W
WThe superficial anterior cervical lymph nodes are found in proximity to the anterior jugular vein.
 W
WThe superficial cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes that lie near the surface of the neck.
 W
WThe superficial lateral cervical lymph nodes are found along the course of the external jugular vein, between the inferior aspect of the parotid gland and the supraclavicular nodes. The nodes are intercalated along the course of the vessels draining the parotid nodes and the infraauricular nodes. These nodes drain into the supraclavicular nodes, and on to the jugular trunk, followed by the thoracic duct on the left or the right lymphatic duct.
 W
WThe superficial parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes anterior to the ear.
 W
WThe superior deep cervical lymph nodes lie under the sternocleidomastoid muscle in close relation with the accessory nerve and the internal jugular vein.
 W
WSupraclavicular lymph nodes are lymph nodes found above to the clavicle, that can be felt in the supraclavicular fossa. The supraclavicular lymph nodes on the left side are called Virchow's nodes.
 W
WThe thyroid lymph nodes are deep anterior cervical lymph nodes found near the thyroid gland on the neck.
 W
WThe tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play an important role in the immune system.
 W
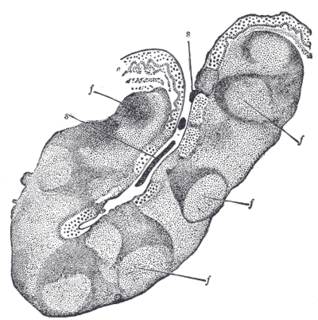
WThe human palatine tonsils (PT) are covered by stratified squamous epithelium that extends into deep and partly branched tonsillar crypts, of which there are about 10 to 30. The crypts greatly increase the contact surface between environmental influences and lymphoid tissue. In an average adult palatine tonsil the estimated epithelial surface area of the crypts is 295 cm2, in addition to the 45 cm2 of epithelium covering the oropharyngeal surface.
 W
WThe tubal tonsil, also known as Gerlach tonsil, is one of the four main tonsil groups comprising Waldeyer's tonsillar ring, which also includes the palatine tonsils, the lingual tonsils, and the pharyngeal tonsils.
 W
WWaldeyer's tonsillar ring is a ringed arrangement of lymphoid organs in the pharynx. Waldeyer's ring surrounds the naso- and oropharynx, with some of its tonsillar tissue located above and some below the soft palate.