 W
WNeurocritical care is a medical field that treats life-threatening diseases of the nervous system and identifies, prevents/treats secondary brain injury.
 W
WNeurology is a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Neurology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the central and peripheral nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue, such as muscle. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system.
 W
WAdipsia, also known as hypodipsia, is a symptom of inappropriately decreased or absent feelings of thirst. It involves an increased osmolality or concentration of solute in the urine, which stimulates secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the hypothalamus to the kidneys. This causes the person to retain water and ultimately become unable to feel thirst. Due to its rarity, the disorder has not been the subject of many research studies.
 W
WAlcohol-related brain damage alters both the structure and function of the brain as a result of the direct neurotoxic effects of alcohol intoxication or acute alcohol withdrawal. Increased alcohol intake is associated with damage to brain regions including the frontal lobe, limbic system, and cerebellum, with widespread cerebral atrophy, or brain shrinkage caused by neuron degeneration. This damage can be seen on neuroimaging scans.
 W
WAstrogliosis is an abnormal increase in the number of astrocytes due to the destruction of nearby neurons from central nervous system (CNS) trauma, infection, ischemia, stroke, autoimmune responses or neurodegenerative disease. In healthy neural tissue, astrocytes play critical roles in energy provision, regulation of blood flow, homeostasis of extracellular fluid, homeostasis of ions and transmitters, regulation of synapse function and synaptic remodeling. Astrogliosis changes the molecular expression and morphology of astrocytes, causing scar formation and, in severe cases, inhibition of axon regeneration.
 W
WThe auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
 W
WThe blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from non-selectively crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where neurons reside. The blood-brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose, water and amino acids that are crucial to neural function.
 W
WCerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. Arteries deliver oxygenated blood, glucose and other nutrients to the brain. Veins carry "used or spent" blood back to the heart, to remove carbon dioxide, lactic acid, and other metabolic products.
 W
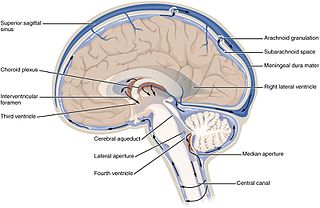
WCerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found in the brain and spinal cord. It is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. There is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immunological protection to the brain inside the skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow.
 W
WIn medicine, confusion is the quality or state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion" is often used interchangeably with delirium in the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems and the Medical Subject Headings publications to describe the pathology. These refer to the loss of orientation, or the ability to place oneself correctly in the world by time, location and personal identity. Mental confusion is sometimes accompanied by disordered consciousness and memory loss. The term is from Latin: confusĭo, -ōnis, from confundere: "to pour together", "to mingle together", "to confuse".
 W
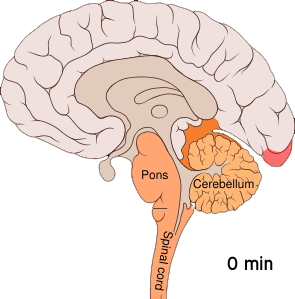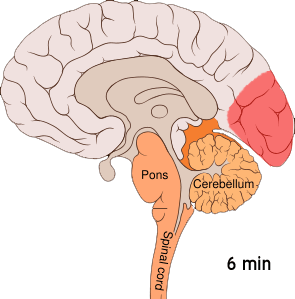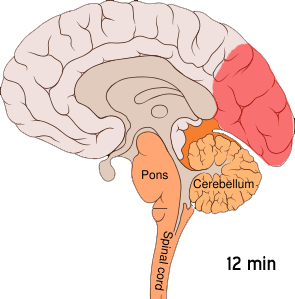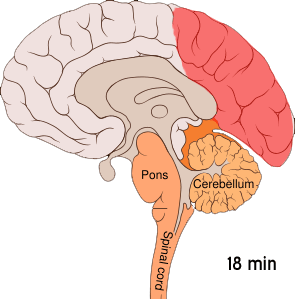
WCortical spreading depression (CSD) or spreading depolarization is a wave of electrophysiological hyperactivity followed by a wave of inhibition. Spreading depolarization describes a phenomenon characterized by the appearance of depolarization waves of the neurons and neuroglia that propagates across the cortex at a velocity of 1.5–9.5 mm/min. CSD can be induced by hypoxic conditions and facilitates neuronal death in energy-compromised tissue. CSD has also been implicated in migraine aura, where CSD is assumed to ascend in well-nourished tissue and is typically benign in most of the cases, although it may increase the probability in migraine patients to develop a stroke. Spreading depolarization within brainstem tissues regulating functions crucial for life has been implicated in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy, by way of ion channel mutations such as those seen in Dravet syndrome, a particularly severe form of childhood epilepsy that appears to carry an unusually high risk of SUDEP.
 W
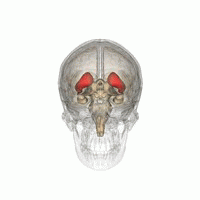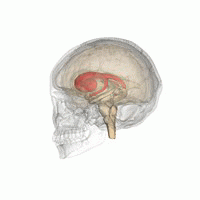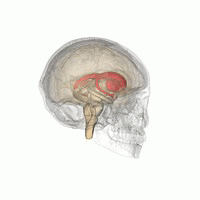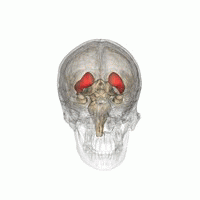
WDaT Scan commonly refers to a diagnostic method to investigate if there is a loss of dopaminergic neurons in striatum. The term may also refer to a brand name of Ioflupane (123I) which is used for the study. The scan principle is based on use of the radiopharmaceutical Ioflupane (123I) which binds to dopamine transporters (DaT). The signal from them is then detected by the use of single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) which uses special gamma-cameras to create a pictographic representation of the distribution of dopamine transporters in the brain.
 W
WA dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by afferent nerve fibres from the dorsal root of any given spinal nerve. There are 8 cervical nerves , 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves and 5 sacral nerves. Each of these nerves relays sensation from a particular region of skin to the brain.
 W
WDescartes' Error: Emotion, Reason, and the Human Brain is a 1994 book by neurologist António Damásio, in part a treatment of the mind/body dualism question. Damásio presents the "somatic marker hypothesis", a proposed mechanism by which emotions guide behavior and decision-making, and positing that rationality requires emotional input. He argues that René Descartes' "error" was the dualist separation of mind and body, rationality and emotion.
 W
WDiscoid meniscus is a rare human anatomic variant that usually affects the lateral meniscus of the knee. Usually a person with this anomaly has no complaints; however, it may present as pain, swelling, or a snapping sound heard from the affected knee. Strong suggestive findings on magnetic resonance imaging includes a thickened meniscal body seen on more than two contiguous sagittal slices.
 W
WThe field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation.
 W
WA grid cell is a type of neuron within the entorhinal cortex that fires at regular intervals as an animal navigates an open area, allowing it to understand its position in space by storing and integrating information about location, distance, and direction. Grid cells have been found in many animals, including rats, mice, bats, monkeys, and humans.
 W
WSynaptic plasticity refers to a chemical synapse's ability to undergo changes in strength. Synaptic plasticity is typically input-specific, meaning that the activity in a particular neuron alters the efficacy of a synaptic connection between that neuron and its target. However, in the case of heterosynaptic plasticity, the activity of a particular neuron leads to input unspecific changes in the strength of synaptic connections from other unactivated neurons. A number of distinct forms of heterosynaptic plasticity have been found in a variety of brain regions and organisms. These different forms of heterosynaptic plasticity contribute to a variety of neural processes including associative learning, the development of neural circuits, and homeostasis of synaptic input.
 W
WIn human brain anatomy, the lateral prefrontal cortex (LPFC) is part of the prefrontal cortex (PFC). According to Striedter the PFC of humans can be delineated into two functionally, morphologically, and evolutionarily different regions: the ventromedial PFC (vmPFC) present in all mammals and the LPFC present only in primates. The LPFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA45, BA46, and BA47. Some researchers also include BA44.
 W
WA lower motor neuron lesion is a lesion which affects nerve fibers traveling from the lower motor neuron(s) in the anterior horn/anterior grey column of the spinal cord, or in the motor nuclei of the cranial nerves, to the relevant muscle(s).
 W
WThe McDonald criteria are diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis (MS). These criteria are named after neurologist W. Ian McDonald who directed an international panel in association with the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS) of America and recommended revised diagnostic criteria for MS in April 2001. These new criteria intended to replace the Poser criteria and the older Schumacher criteria. They have undergone revisions in 2005, 2010 and 2017.
 W
WMidline shift is a shift of the brain past its center line. The sign may be evident on neuroimaging such as CT scanning. The sign is considered ominous because it is commonly associated with a distortion of the brain stem that can cause serious dysfunction evidenced by abnormal posturing and failure of the pupils to constrict in response to light. Midline shift is often associated with high intracranial pressure (ICP), which can be deadly. In fact, midline shift is a measure of ICP; presence of the former is an indication of the latter. Presence of midline shift is an indication for neurosurgeons to take measures to monitor and control ICP. Immediate surgery may be indicated when there is a midline shift of over 5 mm. The sign can be caused by conditions including traumatic brain injury,stroke, hematoma, or birth deformity that leads to a raised intracranial pressure.
 W
WMuscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle fibers. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding a heavy book or a dumbbell at the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state.
 W
WNeurocriminology is an emerging sub-discipline of biocriminology and criminology that applies brain imaging techniques and principles from neuroscience to understand, predict, and prevent crime.
 W
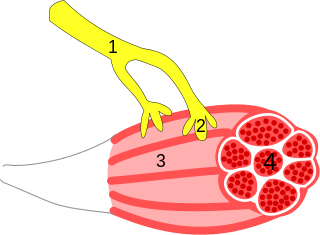
WA neuroeffector junction is a site where a motor neuron releases a neurotransmitter to affect a target—non-neuronal—cell. This junction functions like a synapse. However, unlike most neurons, somatic efferent motor neurons innervate skeletal muscle, and are always excitatory. Visceral efferent neurons innervate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands, and have the ability to be either excitatory or inhibitory in function. Neuroeffector junctions are known as neuromuscular junctions when the target cell is a muscle fiber.
 W
WNeuropathology is the study of disease of nervous system tissue, usually in the form of either small surgical biopsies or whole-body autopsies. Neuropathologists usually work in a department of anatomic pathology, but work closely with the clinical disciplines of neurology, and neurosurgery, which often depend on neuropathology for a diagnosis. Neuropathology also relates to forensic pathology because brain disease or brain injury can be related to cause of death. Neuropathology should not be confused with neuropathy, which refers to disorders of the nerves themselves rather than the tissues. In neuropathology, the branches of the specializations of nervous system as well as the tissues come together into one field of study.
 W
WThe neurotrophic electrode is an intracortical device designed to read the electrical signals that the brain uses to process information. It consists of a small, hollow glass cone attached to several electrically conductive gold wires. The term neurotrophic means "relating to the nutrition and maintenance of nerve tissue" and the device gets its name from the fact that it is coated with Matrigel and nerve growth factor to encourage the expansion of neurites through its tip. It was invented by neurologist Dr. Philip Kennedy and was successfully implanted for the first time in a human patient in 1996 by neurosurgeon Roy Bakay.
 W
WNonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.
 W
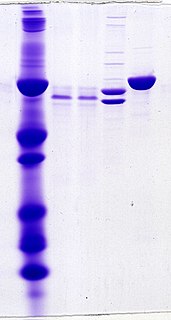
WOligoclonal bands (OCBs) are bands of immunoglobulins that are seen when a patient's blood serum, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is analyzed. They are used in the diagnosis of various neurological and blood diseases, especially in multiple sclerosis.
 W
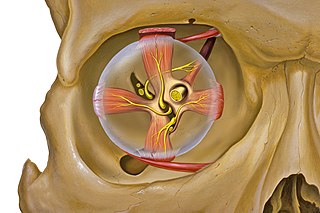
WOrbital apex syndrome, is a collection of cranial nerve deficits associated with a mass lesion near the apex of the orbit of the eye. This syndrome is a separate entity from Rochon–Duvigneaud syndrome, which occurs due to a lesion immediately anterior to the orbital apex. Most commonly optic nerve is involved.
 W
WMultiple sclerosis is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the CNS in which activated immune cells invade the central nervous system and cause inflammation, neurodegeneration, and tissue damage. The underlying cause is currently unknown. Current research in neuropathology, neuroimmunology, neurobiology, and neuroimaging, together with clinical neurology, provide support for the notion that MS is not a single disease but rather a spectrum.
 W
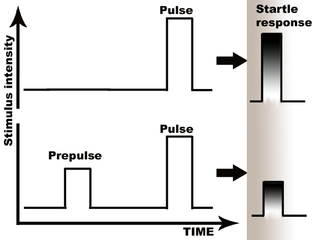
WPrepulse inhibition (PPI) is a neurological phenomenon in which a weaker prestimulus (prepulse) inhibits the reaction of an organism to a subsequent strong reflex-eliciting stimulus (pulse), often using the startle reflex. The stimuli are usually acoustic, but tactile stimuli and light stimuli are also used. When prepulse inhibition is high, the corresponding one-time startle response is reduced.
 W
WPresynaptic inhibition is an inhibitory input to a neuron to make it less likely to fire an action potential and communicate with downstream neurons. Inhibition can be provided both at the postsynapse (IPSP) and the presynapse. Presynaptic inhibition occurs when an inhibitory neurotransmitter, like GABA, acts on GABA receptors on the axon terminal. Presynaptic inhibition is ubiquitous among sensory neurons.
 W
WA reflex hammer is a medical instrument used by practitioners to test deep tendon reflexes. Testing for reflexes is an important part of the neurological physical examination in order to detect abnormalities in the central or peripheral nervous system.
 W
WRestorative neurology is a branch of neurology dedicated to improving functions of the impaired nervous system through selective structural or functional modification of abnormal neurocontrol according to underlying mechanisms and clinically unrecognized residual functions. When impaired, the body naturally reconstructs new neurological pathways and redirects activity. The field of restorative neurology works to accentuate these new pathways and primarily focuses on the theory of the plasticity of an impaired nervous system. Its main goal is to take a broken down and disordered nervous system and return it to a state of normal function. Certain treatment strategies are used to augment instead of fully replace any performance of surviving and also improving the potential of motor neuron functions. This rehabilitation of motor neurons allows patients a therapeutic approach to recovery opposed to physical structural reconstruction. It is applied in a wide range of disorders of the nervous system, including upper motor neuron dysfunctions like spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis and acquired brain injury including stroke, and neuromuscular diseases as well as for control of pain and spasticity. Instead of applying a reconstructive neurobiological approach, i.e. structural modifications, restorative neurology relies on improving residual function. While subspecialties like neurosurgery and pharmacology exist and are useful in diagnosing and treating conditions of the nervous system, restorative neurology takes a pathophysiological approach. Instead of heavily relying on neurochemistry or perhaps an anatomical discipline, restorative neurology encompasses many fields and blends them together.
 W
WThe Silver Spring monkeys were 17 wild-born macaque monkeys from the Philippines who were kept in the Institute for Behavioral Research in Silver Spring, Maryland. From 1981 until 1991, they became what one writer called the most famous lab animals in history, as a result of a battle between animal researchers, animal advocates, politicians, and the courts over whether to use them in research or release them to a sanctuary. Within the scientific community, the monkeys became known for their use in experiments into neuroplasticity—the ability of the adult primate brain to reorganize itself.
 W
WA synaptosome is an isolated synaptic terminal from a neuron. Synaptosomes are obtained by mild homogenization of nervous tissue under isotonic conditions and subsequent fractionation using differential and density gradient centrifugation. Liquid shear detaches the nerve terminals from the axon and the plasma membrane surrounding the nerve terminal particle reseals. Synaptosomes are osmotically sensitive, contain numerous small clear synaptic vesicles, sometimes larger dense-core vesicles and frequently one or more small mitochondria. They carry the morphological features and most of the chemical properties of the original nerve terminal. Synaptosomes isolated from mammalian brain often retain a piece of the attached postsynaptic membrane, facing the active zone.
 W
WThe visual pathway consists of structures that carry visual information from the retina to the brain. Lesions in that pathway cause a variety of visual field defects. In the visual system of human eye, the visual information processed by retinal photoreceptor cells travel in the following way: Retina→Optic nerve→Optic chiasm →Optic tract→Lateral geniculate nucleus→Optic radiation→Primary and secondary visual cortices.
 W
WVitamin D is a steroid hormone that plays a vital role in calcium and phosphate absorption. In recent studies, several associations between low levels of vitamin D, or hypovitaminosis D, and neuropsychiatric disorders have begun to surface. These disorders include, but are not limited to: Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, schizophrenia, and autism.
 W
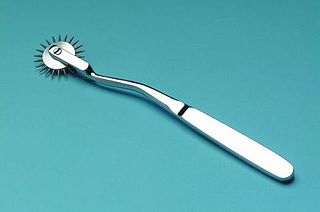
WA Wartenberg wheel, also called a Wartenberg pinwheel or Wartenberg neurowheel, is a medical device for neurological use. Robert Wartenberg (1887–1956) designed the wheel to test nerve reactions (sensitivity) as it rolled systematically across the skin. A Wartenberg wheel is generally made of stainless steel with a handle of approximately 7 inches (18 cm) in length. The wheel, which has evenly spaced radiating sharp pins, rotates as it is rolled across the flesh. A disposable plastic version is available. Because of hygienic concerns, these devices are rarely used for medical purposes any more.
 W
WWorld Federation of Neurology (WFN) was formed in Brussels and Belgium in 1957, as an association of national neurological societies. It is a UK registered charity. with a mission to foster quality neurology and brain health worldwide through promoting global neurological education and training, with the emphasis on under-resourced parts of the world.