 W
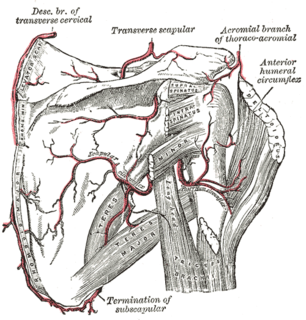
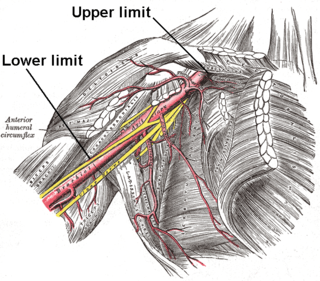
WThe anterior humeral circumflex artery is an artery in the arm. It is one of two circumflexing arteries that branch from the axillary artery, the other being the posterior humeral circumflex artery. The anterior humeral circumflex artery is considerably smaller than the posterior and arises nearly opposite to it, from the lateral side of the axillary artery.
 W
WThe anterior interosseous artery is an artery in the forearm. It is a branch of the common interosseous artery.
 W
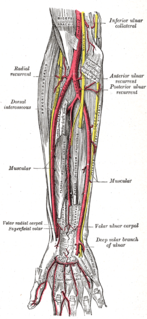
WThe anterior ulnar recurrent artery is an artery in the forearm. It is one of two recurrent arteries that arises from the ulnar artery, the other being the posterior ulnar recurrent artery.
 W
WIn human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.
 W
WThe axillary sheath is a fibrous sheath that encloses the axillary artery and the three cords of the brachial plexus to form the neurovascular bundle. It is surrounded by the axillary fat. It is an extension of the prevertebral fascia of the deep cervical fascia.
 W
WThe brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa at the elbow. It then divides into the radial and ulnar arteries which run down the forearm. In some individuals, the bifurcation occurs much earlier and the ulnar and radial arteries extend through the upper arm. The pulse of the brachial artery is palpable on the anterior aspect of the elbow, medial to the tendon of the biceps, and, with the use of a stethoscope and sphygmomanometer often used to measure the blood pressure.
 W
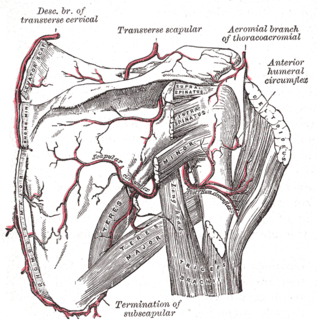
WThe circumflex scapular artery is a branch of the subscapular artery and part of the scapular anastomoses.
 W
WThe common interosseous artery, about 1 cm. in length, arises immediately below the tuberosity of the radius from the ulnar artery.
 W
WThree common palmar digital arteries arise from the convexity of the superficial palmar arch and proceed distally on the second, third, and fourth lumbricales muscles.
 W
WThe deep artery of arm is a large vessel which arises from the lateral and posterior part of the brachial artery, just below the lower border of the teres major.
 W
WThe deep palmar arch is an arterial network found in the palm. It is usually formed mainly from the terminal part of the radial artery, with the ulnar artery contributing via its deep palmar branch, by an anastomosis. This is in contrast to the superficial palmar arch, which is formed predominantly by the ulnar artery.
 W
WThe deep palmar branch of ulnar artery passes between the Abductor digiti minimi and Flexor digiti minimi brevis and through the origin of the Opponens digiti minimi; it anastomoses with the radial artery, and completes the deep volar arch.
 W
WThe dorsal carpal arch is an anatomical term for the combination (anastomosis) of dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery and the dorsal carpal branch of the ulnar artery near the back of the wrist.
 W
WThe dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery is a small vessel which arises beneath the extensor tendons of the thumb; crossing the carpus transversely toward the medial border of the hand, it anastomoses with the dorsal carpal branch of the ulnar artery.
 W
WThe dorsal carpal branch of the ulnar artery arises from the ulnar artery immediately above the pisiform bone, and winds backward beneath the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris; it passes across the dorsal surface of the carpus beneath the extensor tendons, to anastomose with a corresponding branch of the radial artery.
 W
WMost of the dorsal metacarpal arteries arise from the dorsal carpal arch and run downward on the second, third, and fourth dorsal interossei of the hand and bifurcate into the dorsal digital arteries. Near their origin, they anastomose with the deep palmar arch by perforating arteries. They also anastomose with common palmar digital arteries, also via perforating arteries.
 W
WThe inferior ulnar collateral artery is an artery in the arm. It arises about 5 cm. above the elbow from the brachial artery.
 W
WThe interosseous recurrent artery is an artery of the forearm which arises from the posterior interosseous artery near its origin. It ascends to the interval between the lateral epicondyle and olecranon, on or through the fibers of the supinator but beneath the anconeus. It anastomoses with the middle collateral artery.
 W
WIn human anatomy, the lateral thoracic artery is a blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the lateral structures of the thorax and breast.
 W
WThe medial collateral artery is a branch of profunda brachii artery that descends in the middle head of the triceps brachii and assists in forming the anastomosis with the interosseous recurrent artery above the olecranon of the ulna near the elbow.
 W
WThe palmar carpal arch is the combination (anastomosis) of two arteries: the Palmar carpal branch of radial artery and the palmar carpal branch of ulnar artery.
 W
WThe palmar carpal branch of the radial artery is a small branch of the radial artery which arises near the lower border of the pronator quadratus, and, running across the front of the carpus, anastomoses with the palmar carpal branch of the ulnar artery.
 W
WThe palmar carpal branch of ulnar artery is a small vessel which crosses the front of the carpus beneath the tendons of the Flexor digitorum profundus, and anastomoses with the corresponding branch of the radial artery.
 W
WThe palmar metacarpal arteries, three or four in number, arise from the convexity of the deep volar arch.
 W
WThe posterior humeral circumflex artery arises from the third part of axillary artery at the lower border of the subscapularis, and runs posteriorly with the axillary nerve through the quadrangular space.
 W
WThe posterior interosseous artery is an artery of the forearm.
 W
WThe posterior ulnar recurrent artery is an artery in the forearm. It is one of two recurrent arteries that arises from the ulnar artery, the other being the anterior ulnar recurrent artery. The posterior ulnar recurrent artery being much larger than the anterior and also arises somewhat lower than it.
 W
WThe princeps pollicis artery, or principal artery of the thumb, arises from the radial artery just as it turns medially towards the deep part of the hand; it descends between the first dorsal interosseous muscle and the oblique head of the adductor pollicis, along the medial side of the first metacarpal bone to the base of the proximal phalanx, where it lies beneath the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus muscle and divides into two branches.
 W
WThe proper palmar digital arteries travel along the sides of the phalanges, each artery lying just below its corresponding digital nerve.
 W
WIn human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
 W
WThe radialis indicis artery is a branch of the radial artery that provides blood to the index finger.
 W
WThe radial collateral artery is a branch of the deep brachial artery. It arises in the arm proper and anastomoses with the radial recurrent artery near the elbow.
 W
WThe radial recurrent artery arises from the radial artery immediately below the elbow.
 W
WThe scapular anastomosis is a system connecting certain subclavian artery and their corresponding axillary artery, forming a circulatory anastomosis around the scapula. It allows blood to flow past the joint in case of occlusion, damage, or pinching of the following scapular arteries:Transverse cervical artery Dorsal scapular artery Suprascapular artery Branches of subscapular artery Branches of thoracic aorta
 W
WThe subscapular artery, the largest branch of the axillary artery, arises from the third part of the axillary artery at the lower border of the subscapularis muscle, which it follows to the inferior angle of the scapula, where it anastomoses with the lateral thoracic and intercostal arteries, and with the descending branch of the dorsal scapular artery, and ends in the neighboring muscles.
 W
WThe superficial palmar arch is formed predominantly by the ulnar artery, with a contribution from the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery. However, in some individuals the contribution from the radial artery might be absent, and instead anastomoses with either the princeps pollicis artery, the radialis indicis artery, or the median artery, the former two of which are branches from the radial artery.
 W
WThe superficial palmar branch of the radial artery arises from the radial artery, just where this vessel is about to wind around the lateral side of the wrist.
 W
WThe superior thoracic artery is a small artery located near the armpit in humans. It normally arises from the first division of the axillary artery, but may arise from the thoracoacromial artery, itself a branch of the second division of the axillary artery.
 W
WThe superior ulnar collateral artery, of small size, arises from the brachial artery a little below the middle of the arm; it frequently springs from the upper part of the a. profunda brachii.
 W
WThe thoracoacromial artery is a short trunk that arises from the second part of the axillary artery, its origin being generally overlapped by the upper edge of the pectoralis minor.
 W
WThe thoracodorsal artery is a branch of the subscapular artery. It travels inferiorly with the thoracodorsal nerve and supplies the latissimus dorsi.
 W
WThe ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.