 W
WThe bárányles is a local tradition in the southern Hungarian village Hosszúhetény and around the Zengő mountain, a night pilgrimage on Easter Sunday, in which only males can take part.
 W
WThe Bussen is a mountain in southern Germany, in the region of Upper Swabia, with an elevation of 767 metres. It is also known as the Holy Mountain of Upper Swabia. It is situated on the border between the Swabian Alb and Upper Swabia proper. Being one of the most visited places of pilgrimage in Upper Swabia, it also has views as far as the Alps more than 100 kilometres (62 mi) to the south.
 W
WA calvary, also called calvary hill, Sacred Mount, or Sacred Mountain, is a type of Christian sacred place, built on the slopes of a hill, composed by a set of chapels, usually laid out in the form of a pilgrims' way. It is intended to represent the passion of Jesus Christ and its name after the Calvary, the hill in Jerusalem where, according to tradition, Jesus was crucified.
 W
WCenacle, also known as the "Upper Room" was the first Christian church according to Catholics. Other denominations believe the first church is the Church of Saint Peter. It is a room in the David's Tomb Compound in Jerusalem, and was traditionally held to be the site of the Last Supper.
 W
WChittlehampton is a village and civil parish in the North Devon district of Devon, England. The parish is surrounded clockwise from the north by the parishes of Swimbridge, Filleigh, South Molton, Satterleigh and Warkleigh, High Bickington, Atherington, and Bishop's Tawton. According to the 2001 census, the parish had a population of 820. There is an electoral ward of the same name. In the 2011 census this ward had a population of 2,255.
 W
WChristianity has a strong tradition of pilgrimages, both to sites relevant to the New Testament narrative and to sites associated with later saints or miracles.
 W
WThe Church of the Ascension is a shrine located on the Mount of Olives, in the At-Tur district of Jerusalem. Part of a larger complex consisting first of a Christian church and monastery, then an Islamic mosque, it is located on a site the faithful traditionally believed to be the earthly spot where Jesus ascended into Heaven after His Resurrection. It houses a slab of stone believed to contain one of His footprints. The Status Quo, a 250-year-old understanding between religious communities, applies to the site.
 W
WThe Church of the Holy Sepulchre is a church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem. The church contains, according to traditions dating back to at least the fourth century, the two holiest sites in Christianity: the site where Jesus was crucified, at a place known as Calvary or Golgotha, and Jesus's empty tomb, where he was buried and resurrected. The tomb is enclosed by a 19th-century shrine called the Aedicula. The Status Quo, an understanding between religious communities dating to 1757, applies to the site.
 W
WEgeria, Etheria or Aetheria was a woman, widely regarded to be the author of a detailed account of a pilgrimage to the Holy Land about 381/2–386. The long letter, dubbed Peregrinatio or Itinerarium Egeriae, is addressed to a circle of women at home. Historical details it contains set the journey in the early 380s, making it the earliest of its kind. It survives in fragmentary form in a later copy—lacking a title, date and attribution.
 W
WThe Great Žemaičių Kalvarija Festival or The Great Samogitian Calvary Festival is a Roman Catholic festival dedicated to St. Mary. The festival is held annually and takes place every July in the small town of Žemaičių Kalvarija in Samogitia, Lithuania, attracting many pilgrims and tourists.
 W
WThe Holy Blood of Wilsnack was the name given to three hosts, which survived a fire in 1383 that burned the church and village to the ground. The hosts were thus seen as miraculous. The relics became the destination of medieval religious pilgrimages to Bad Wilsnack, Germany for nearly two centuries. Revenue from the many pilgrims enabled the town to build the large St. Nicholas' Church at the site. The hosts were destroyed by reformers in 1558 during the Protestant Reformation.
 W
WHolywell is the fifth largest town and a community in Flintshire, Wales. It lies to the west of the estuary of the River Dee. The community includes Greenfield.
 W
WThe House of the Virgin Mary is a Catholic shrine located on Mt. Koressos in the vicinity of Ephesus, 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) from Selçuk in Turkey.
 W
WJerusalem's role in first-century Christianity, during the ministry of Jesus and the Apostolic Age, as recorded in the New Testament, gives it great importance.
 W
WThe Jesus Trail is a 65 km (40 mi) hiking and pilgrimage route in the Galilee region of Israel that traces the route Jesus may have walked, connecting many sites from his life and ministry. The main part of the trail begins in Nazareth and passes through Sepphoris, Cana, the Horns of Hattin, Mount Arbel Cliffs, the Sea of Galilee, Capernaum, Tabgha, and the Mount of Beatitudes. An alternate return route passes by Tiberias, the Jordan River, Mount Tabor, and Mount Precipice.
 W
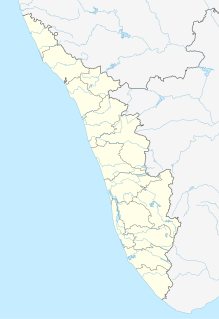
WSt. Thomas is believed to have landed in Kerala at Kodungallur (Cranganore) in AD 50 and was engaged in evangelical activity. AD 62 St Thomas returns to Malankara coast via Malayatur where he establishes ‘the half Church’.
 W
WMariánská Týnice is a former pilgrimage destination in Bohemia, now the Czech Republic, with the Baroque Church of the Annunciation and the Cistercian Provost Office built by Jan Santini Aichel in the 18th century.
 W
WThe Monastery of the Mother of God at the Spring or simply Zoödochos Pege is an Eastern Orthodox sanctuary in Istanbul, Turkey. The present church, built in 1835, bears the same dedication as the shrine erected in this place between the end of the fifth and the beginning of the sixth century. After several renovations, this building was destroyed in the first half of the fifteenth century by the Ottomans. The complex got its name from a nearby holy spring, reputed to have healing properties. For almost fifteen hundred years, this sanctuary has been one of the most important pilgrimage sites of Greek Orthodoxy.
 W
WThe Monza ampullae form the largest collection of a specific type of Early Medieval pilgrimage ampullae or small flasks designed to hold holy oil from pilgrimage sites in the Holy Land related to the life of Jesus. They were made in Palestine, probably in the fifth to early seventh centuries, and have been in the Treasury of Monza Cathedral north of Milan in Italy since they were donated by Theodelinda, queen of the Lombards,. Since the great majority of surviving examples of such flasks are those in the Monza group, the term may be used to cover this type of object in general.
 W
WMughni is a village in the Aragatsotn Province of Armenia. It is located just to the north of Ashtarak town and belongs to its municipality. Until the Russian conquest, it was the southernmost town in the district of Aparan. Mughni is home to the 14th-century Saint Gevork Monastery, which was formerly a popular pilgrimage site and the seat of an archbishop. The dome of the church was rebuilt in the 1660s.
 W
WThe Nabi Yahya Mosque is a mosque containing the traditional Tomb of John the Baptist as well as the Tomb of Elisha and the Tomb of Obadiah.
 W
WNidaros Cathedral is a cathedral of the Church of Norway located in the city of Trondheim in Trøndelag county. It is built over the burial site of King Olav II, who became the patron saint of the nation, and is the traditional location for the consecration of new kings of Norway. It was built over a 230 year period, from 1070 to 1300 when it was substantially completed. However additional work, additions and renovations have continued intermittently since then; the most recent changes were completed in 2001. Nidaros was designated as the cathedral for the Diocese of Nidaros in 1152. After experiencing the turmoil and controversies of the Protestant Reformation of the 16th century, it was taken from the Catholic Church by the newly established state Church of Norway in 1537, which adopted the teachings and reforms of Martin Luther, Phillip Melanchthon and others, becoming an Evangelical Lutheran church. Nidaros is the northernmost medieval cathedral in the world.
 W
WThe Chartres pilgrimage, also known in French as the pèlerinage de Chrétienté, is an annual pilgrimage from Notre-Dame de Paris to Notre-Dame de Chartres occurring around the Christian feast of Pentecost, organized by Notre-Dame de Chrétienté, a Catholic lay non-profit organization based in Versailles, France. Although the pilgrimage has existed since 1983, the organisation was not founded until 2000.
 W
WPilgrim badges are decorations worn by some of those who undertake a Christian pilgrimage to a place considered holy by the Church. They became very popular among Catholics in the later medieval period. Typically made of lead alloy, they were sold as souvenirs at sites of Christian pilgrimage and bear imagery relating to the saint venerated there. The production of pilgrim badges flourished in the Middle Ages in Europe, particularly in the 14th and 15th centuries, but declined after the Protestant Reformation of the mid-16th century. Tens of thousands have been found since the mid-19th century, predominantly in rivers. Together they form the largest corpus of medieval art objects to survive to us today.
 W
WThe Pilgrim's Route, (Pilegrimsleden) also known as St. Olav's Way or the Old Kings' Road, was a pilgrimage route to the Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim, Norway, the site of the medieval tomb of St. Olav. The main route is approximately 640 kilometres (400 mi) long. It starts in the ancient part of Oslo and heads north along the lake Mjøsa, up the Gudbrandsdal valley, over the Dovrefjell mountains, and down the Oppdal and Gauldalen valleys to end at the Nidaros Cathedral.
 W
WQasr al-Yahud is the official name of a baptism site in the Jordan River Valley in the West Bank. After the Six-Day War in 1967, it has been placed under Israeli control, and the site and facilities are administered by the Israeli Civil Administration and the Israeli Ministry of Tourism as part of a national park.
 W
WReek Sunday or Garland Sunday is an annual day of pilgrimage in Ireland. On the last Sunday in July, pilgrims climb Ireland's holiest mountain, Croagh Patrick in County Mayo. It is held in honour of Saint Patrick who, in the year 441, spent 40 days fasting on the mountain. Masses are held at the summit, where there is a small chapel. Some climb the mountain barefoot, as an act of penance, and some carry out 'rounding rituals', which were formerly a key part of the pilgrimage. This involves praying while walking sunwise around features on the mountain. They walk seven times around the cairn of Leacht Benáin, fifteen times around the circular perimeter of the summit, seven times around Leaba Phádraig, and then seven times around three ancient cairns known as Reilig Mhuire.
 W
WChristianity has a strong tradition of pilgrimages, both to sites relevant to the New Testament narrative and to sites associated with later saints or miracles.
 W
WThe Romería de la Bajada de la Virgen del Socorro, is a romeria of popular character that is held in September in the town of Güímar in Tenerife. This festival also declared Regional Tourist Interest. It is considered the oldest romeria of Canary Islands is also one of the most popular.
 W
WRomería Regional de San Benito Abad it is a popular romeria that is held the second Sunday of July in the city of San Cristóbal de La Laguna. It is held in honor of St. Benedict of Nursia, the patron saint of farmers of Tenerife.
 W
WSaintes-Maries-de-la-Mer is the capital of the Camargue in the south of France. It is a commune in the Bouches-du-Rhône department by the Mediterranean Sea. Its 2012 population was 2,495, though it can swell to 500,000 during the summer holidays. It covers the second-largest area of all communes in Metropolitan France, smaller only than that of neighbouring Arles.
 W
WThe Hohe Salve is a well-known mountain located between Kufstein, Wörgl and Kitzbühel in the Austrian state of Tyrol. It is part of the Kitzbühel Alps and is also nicknamed the Rigi of the Tyrol. Its summit is 1,828 m above sea level (AA) high, and in fine weather has a good view of the High Tauern and Zillertal Alps, as well as the Wilder Kaiser, which lies immediately to the north of the Hohe Salve. From the top the Großglockner and Großvenediger can also be made out.
 W
WSt. Olavsleden, is a pilgrim's way between Selånger outside Sundsvall in Sweden and Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim in Norway, commemorating Saint Olaf who was King of Norway from 1015 to 1028. St. Olavsleden was one of the Pilgrim's Routes. From the 1970s until 2012, it was called the Mittnordenleden.
 W
WThe Status Quo is an understanding among religious communities with respect to nine shared religious sites in Jerusalem and Bethlehem. Other Holy Places in Israel and Palestine were not deemed subject to the Status Quo because the authorities of one religion or of one community within a religion are in recognized or effective possession.
 W
WTaizé is a commune in the Saône-et-Loire department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France. The commune lies 33 km (21 mi) northwest of Mâcon, the capital of Saône-et-Loire, and 9 km (5.6 mi) north of the town of Cluny.
 W
WThe Umayyad Mosque, also known as the Great Mosque of Damascus, located in the old city of Damascus, is one of the largest and oldest mosques in the world. The mosque is also important in Islam because of its historical and eschatological reports and events associated with the mosque.
 W
WThe Via Dolorosa is a processional route in the Old City of Jerusalem, believed to be the path that Jesus walked on the way to his crucifixion. The winding route from the former Antonia Fortress to the Church of the Holy Sepulchre — a distance of about 600 metres — is a celebrated place of Christian pilgrimage. The current route has been established since the 18th century, replacing various earlier versions. It is today marked by nine Stations of the Cross; there have been fourteen stations since the late 15th century, with the remaining five stations being inside the Church of the Holy Sepulchre.
 W
WThe Via Francigena is the common name of an ancient road and pilgrim route running from France to Rome and Apulia, where there were the ports of embarkation for the Holy Land, though it is usually considered to have its starting point on the other side of the English Channel, in the cathedral city of Canterbury. As such, the route passes through England, France, Switzerland and Italy. The route was known in Italy as the "Via Francigena" or the "Via Romea Francigena". In medieval times it was an important road and pilgrimage route for those wishing to visit the Holy See and the tombs of the apostles Peter and Paul.
 W
WWalsingham is a village in North Norfolk, England, famous for its religious shrines in honour of the Virgin Mary. It also contains the ruins of two medieval monastic houses. Walsingham is 27 miles (43 km) northwest of Norwich.
 W
WThe Basilica of Our Lady of Walsingham, informally known as the Slipper Chapel or the Chapel of Saint Catherine of Alexandria, is a Roman Catholic basilica located in Houghton Saint Giles, Norfolk, England. Built in 1340, it was the last chapel on the pilgrim route to Walsingham.
 W
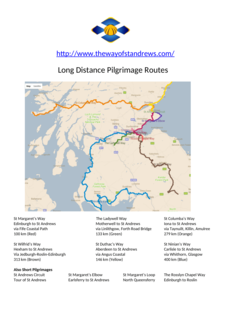
WThe Way of St Andrews is a Christian pilgrimage to St Andrews Cathedral in Fife, on the east coast of Scotland, UK, where the relics of the apostle, Saint Andrew, were once kept. A group started a revival in 2012 introducing new routes.
 W
WWhitekirk is a small settlement in East Lothian, Scotland. Together with the nearby settlement of Tyninghame, it gives its name to the parish of Whitekirk and Tyninghame.
 W
WWrocław Walking Pilgrimage – an annual walking pilgrimage from Wrocław to Jasna Góra held in August. It leaves Wrocław on August 2 and after nine days of walking approximately 230 kilometers enters Częstochowa.