 W
WLike humans and other animals, fish suffer from diseases and parasites. Fish defences against disease are specific and non-specific. Non-specific defences include skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps microorganisms and inhibits their growth. If pathogens breach these defences, fish can develop inflammatory responses that increase the flow of blood to infected areas and deliver white blood cells that attempt to destroy the pathogens.
 W
WAllogastrocotyle is a genus within the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea. The only species in this genus is parasitic upon fish.
 W
WAllogastrocotyle bivaginalis is a species of monogenean flatworm, which is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae.
 W
WAllopseudaxine is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; all its species are parasites of fish.
 W
WAllopseudaxine katsuwonis is a species of monogenean flatworm, which is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Axinidae.
 W
WAllopseudaxine macrova is a species of monogenean flatworm, which is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Axinidae.
 W
WAllopseudaxine yaito is a species of monogenean flatworm, which is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Axinidae.
 W
WAllopseudaxinoides is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; all its species are parasites of fish. It was created by Yamaguti in 1965, to include Allopseudaxinoides euthynni.
 W
WAscarophis is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Ascarophis are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of marine and estuarine fishes.
 W
WC. oestroides is a crustacean isopod, obligate ectoparasite of marine fish that dwells in the buccal cavity. It is the causative agent of various pathologies including tissue damage at the parasitisation site (tongue), growth defects, decrease in mean host weight and size and increases mortalities in farmed and wild fish populations. It has been recorded in six different fish families: Sparidae, Carangidae, Clupeidae, Maenidae, Scorpenidae, and Mugilidae.
 W
WCryptobia is a genus of kinetoplastids. Several species are known for being fish pathogens. They can be found in other animals, as well. The name Trypanoplasma is occasionally used for some of these.
 W
WDiplozoidae is a family of monogeneans in the order Mazocraeidea. In all species of this family, the bodies of the two hermaphroditic members of a couple are permanently fused for life. These monogeneans are parasitic on the gills of freshwater fish.
 W
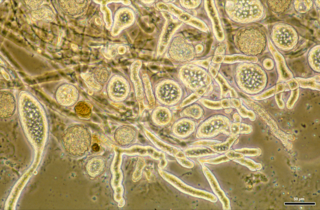
WIchthyophonus is a genus of unicellular eukaryotic parasites of fish. They were once considered to be fungi, but phylogenetic evidence suggests they are protists related to both fungi and animals.
 W
WIchthyophonus hoferi is a single-celled protist that occupies a key phylogenetic position to understand the origin of animals. It has chitin cell wall, hyphae, and an amoeboid stage. It is a common parasite of marine and freshwater fishes.
 W
WLamellodiscus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae; all species of Lamellodiscus are small worms, parasitic on the gills of teleost fish.
 W
WLaticola is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. All known species are parasitic on the gills of marine fish, including members of Lates (Latidae) and Epinephelus (Serranidae).
 W
WLepotrema acanthochromidis is a species of lepocreadiid digenean parasitic in the intestine of marine fish. It was described in 2018.
 W
WLepotrema amansis is a species of lepocreadiid digenean parasitic in the intestine of marine fish. It was described in 2018.
 W
WLepotrema amblyglyphidodonis is a species of lepocreadiid digenean parasitic in the intestine of marine fish. It was described in 2018.
 W
WLepotrema hemitaurichthydis is a species of lepocreadiid digenean parasitic in the intestine of marine fish. It was described in 2018.
 W
WLepotrema justinei is a species of lepocreadiid digenean parasitic in the intestine of marine fish. It was described in 2018. This species was not characterised by molecular means but was distinguished from other species of the genus Lepotrema by morphological characteristics. It is the only species with more or less symmetrical testes, and, probably as a result, it tends to be broader than the other species.
 W
WThe common thresher can harbor a number of internal and external parasites:
 W
WThe Mesomycetozoea are a small group of Opisthokonta in Eukaryota, mostly parasites of fish and other animals.
 W
WMicrocotyle aigoi is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMicrocotyle algeriensis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMicrocotyle angelichthys is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMicrocotyle archosargi is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. It was first described by MacCallum in 1913 based on ten specimens. Hargis (1956) pointed out that the description and figures given by MacCallum were poor in details.
 W
WMicrocotyle centropristis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMicrocotyle donavini is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMicrocotyle elegans is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
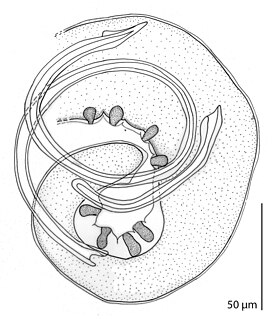
WMicrocotyle fusiformis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish, described by Seitarō Gotōin 1894. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. This species was first.
 W
WMicrocotyle pempheri is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMicrocotyle pomacanthi is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMicrocotyle pomatomi is a species of monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMicrocotyle sebastis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMicrocotyle visa is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
 W
WMoravecnema is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Moravecnema are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the genus currently (2019) includes a single species, Moravecnema segonzaci, which is a parasite in a deep-sea fish.
 W
WNeodiplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. According to Mizelle & Blatz (1941), the genus Neodiplectanum "differs from Diplectanum Diesing, 1858, its closest relative, by the presence of two, instead of three, cuticular bars on the haptor". Oliver (1987) thought that the two genera were synonyms, but Neodiplectanum was resurrected later.
 W
WPhilasterides dicentrarchi is a marine protozoan ciliate that was first identified in 1995 after being isolated from infected European sea bass reared in France. The species was also identified as the causative agent of outbreaks of scuticociliatosis that occurred between summer 1999 and spring 2000 in turbot cultivated in the Atlantic Ocean. Infections caused by P. dicentrarchi have since been observed in turbot reared in both open flow and recirculating production systems. In addition, the ciliate has also been reported to cause infections in other flatfishes, such as the olive flounder in Korea and the fine flounder in Peru, as well as in seadragons, seahorses, and several species of sharks in other parts of the world.
 W
WPseudaxine is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; all its species are parasites of fish.
 W
WPseudaxine trachuri is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae.
 W
WSibitrema is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; the only species included in this genus is parasite of fish.
 W
WSibitrema poonui is a species of monogenean flatworm, which is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae.
 W
WSparicotyle chrysophrii is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of the marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. Its type-host is the gilt-head seabream.
 W
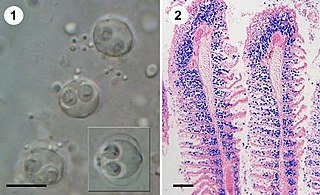
WSphaerospora molnari is a microscopic endoparasite of carp in pond cultures and natural freshwater habitats in Central and Eastern Europe. In natural infections, S. molnari invades the epithelia of gills and surrounding skin regions. It then forms spores in between epithelial cells, causing sphaerosporosis, a pathological condition of the skin and gill tissues. Affected tissues show marked dystrophic changes and necrosis, causing secondary bacterial infections and resulting in osmoregulatory and respiratory failure. Mortalities can reach 100% but little is known about the overall distribution of the parasite species in European carp ponds or its economic impact on carp aquaculture.
 W
WTrichodina is a genus of ciliate alveolates that is ectocommensal or parasitic on aquatic animals, particularly fish. They are characterised by the presence of a ring of interlocking cytoskeletal denticles, which provide support for the cell and allow for adhesion to surfaces including fish tissue.