 W
WMusculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are injuries or pain in the human musculoskeletal system, including the joints, ligaments, muscles, nerves, tendons, and structures that support limbs, neck and back. MSDs can arise from a sudden exertion, or they can arise from making the same motions repeatedly repetitive strain, or from repeated exposure to force, vibration, or awkward posture. Injuries and pain in the musculoskeletal system caused by acute traumatic events like a car accident or fall are not considered musculoskeletal disorders. MSDs can affect many different parts of the body including upper and lower back, neck, shoulders and extremities. Examples of MSDs include carpal tunnel syndrome, epicondylitis, tendinitis, back pain, tension neck syndrome, and hand-arm vibration syndrome.
 W
WMusculoskeletal injury refers to damage of muscular or skeletal systems, which is usually due to a strenuous activity. In one study, roughly 25% of approximately 6300 adults received a musculoskeletal injury of some sort within 12 months—of which 83% were activity-related. Musculoskeletal injury spans into a large variety of medical specialties including orthopedic surgery, sports medicine, emergency medicine and rheumatology.
 W
WAchard syndrome is a syndrome consisting of arachnodactyly, receding lower jaw, and joint laxity limited to the hands and feet. Hypermobility and subluxations of the joints, increased lateral excursion of the patellas and other findings reflect the increased ligament laxity. It is clinically similar to Marfan syndrome.
 W
WAcropachy refers to a dermopathy associated with Graves' disease. It is characterized by soft-tissue swelling of the hands and clubbing of the fingers. Radiographic imaging of affected extremities typically demonstrates periostitis, most commonly the metacarpal bones. The exact cause is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by stimulating auto-antibodies that are implicated in the pathophysiology of Graves' thyrotoxicosis. There is no effective treatment for acropachy.
 W
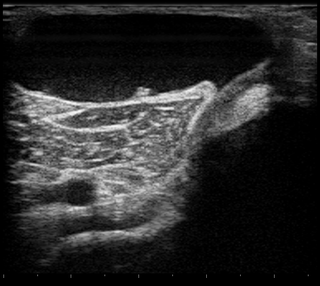
WAttenuated patella alta is an extremely rare condition affecting mobility and leg strength. It is characterized by an unusually small knee cap (patella) that develops out of and above the joint. Normally, as the knee cap sits in the joint, it is stimulated to growth by abrasion from the opposing bones. When not situated properly in the joint, the knee cap does not experience such stimulation and remains small and undeveloped. Note that the cartilage under and around the kneecap is eight times smoother than ice, so "abrasion" may not be the best term.
 W
WA Baker's cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a type of fluid collection behind the knee. Often there are no symptoms. If symptoms do occur these may include swelling and pain behind the knee, or knee stiffness. If the cyst breaks open, pain may significantly increase with swelling of the calf. Rarely complications such as deep vein thrombosis, peripheral neuropathy, ischemia, or compartment syndrome may occur.
 W
WA bone cyst or geode is a cyst that forms in bone.
 W
WCalcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) crystal deposition disease, also known as pseudogout and pyrophosphate arthropathy, is a rheumatologic disease which is thought to be secondary to abnormal accumulation of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals within joint soft tissues. The knee joint is most commonly affected.
 W
WCervical spinal stenosis is a bone disease involving the narrowing of the spinal canal at the level of the neck. It is frequently due to chronic degeneration, but may also be congenital. Treatment is frequently surgical.
 W
WCervical spine disorders are illnesses that affect the cervical spine, which is made up of the upper first seven vertebrae, encasing and shielding the spinal cord. This fragment of the spine starts from the region above the shoulder blades and ends by supporting and connecting the skull.
 W
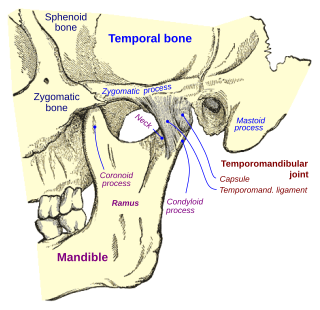
WCondylar resorption, also called idiopathic condylar resorption, ICR, and condylysis, is a temporomandibular joint disorder in which one or both of the mandibular condyles are broken down in a bone resorption process. This disorder is nine times more likely to be present in females than males, and is more common among teenagers.
 W
WCostochondritis, also known as chest wall pain, costosternal syndrome, or costosternal chondrodynia is an acute and often temporary inflammation of the costal cartilage, the structure that connects each rib to the sternum at the costosternal joint. The condition is a common cause of chest pain. Though costochondritis often resolves on its own, it can be a recurring condition that has little or no signs of onset.
 W
WDiffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a condition characterized by abnormal calcification/bone formation ("hyperostosis") of the soft tissues surrounding the joints of the spine, and also the peripheral or appendicular skeleton. In the spine, there is bone formation along the anterior longitudinal ligament and sometimes the posterior longitudinal ligament, which may lead to partial or complete fusion of adjacent spinal levels. The facet and sacroiliac joints tend to be uninvolved. The thoracic spine is the most common level involved. In the peripheral skeleton, DISH manifests as a calcific enthesopathy, with pathologic bone formation at sites where ligaments and tendons attach to bone.
 W
WEmacs or EMACS is a family of text editors that are characterized by their extensibility. The manual for the most widely used variant, GNU Emacs, describes it as "the extensible, customizable, self-documenting, real-time display editor". Development of the first Emacs began in the mid-1970s, and work on its direct descendant, GNU Emacs, continues actively as of 2020.
 W
WAn enthesopathy refers to a disorder involving the attachment of a tendon or ligament to a bone. This site of attachment is known as the enthesis . If the condition is known to be inflammatory, it can more precisely be called an enthesitis.
 W
WEnthesophytes are abnormal bony projections at the attachment of a tendon or ligament. They are not to be confused with osteophytes, which are abnormal bony projections in joint spaces. Enthesophytes and osteophytes are bone responses for stress.
 W
WFoot drop is a gait abnormality in which the dropping of the forefoot happens due to weakness, irritation or damage to the common fibular nerve including the sciatic nerve, or paralysis of the muscles in the anterior portion of the lower leg. It is usually a symptom of a greater problem, not a disease in itself. Foot drop is characterized by inability or impaired ability to raise the toes or raise the foot from the ankle (dorsiflexion). Foot drop may be temporary or permanent, depending on the extent of muscle weakness or paralysis and it can occur in one or both feet. In walking, the raised leg is slightly bent at the knee to prevent the foot from dragging along the ground.
 W
WGenu recurvatum is a deformity in the knee joint, so that the knee bends backwards. In this deformity, excessive extension occurs in the tibiofemoral joint. Genu recurvatum is also called knee hyperextension and back knee. This deformity is more common in women and people with familial ligamentous laxity. Hyperextension of the knee may be mild, moderate or severe.
 W
WTenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) is a group of rare, typically non-malignant tumors of the joints. TGCT tumors often develop from the lining of joints.
 W
WA Hill–Sachs lesion, or Hill–Sachs fracture, is a cortical depression in the posterolateral head of the humerus. It results from forceful impaction of the humeral head against the anteroinferior glenoid rim when the shoulder is dislocated anteriorly.
 W
WA joint effusion is the presence of increased intra-articular fluid. It may affect any joint. Commonly it involves the knee.
 W
WKnee effusion occurs when excess synovial fluid accumulates in or around the knee joint. It has many common causes, including arthritis, injury to the ligaments or meniscus, or fluid collecting in the bursa, a condition known as prepatellar bursitis.
 W
WKnee pain is pain in or around the knee.
 W
WLumbar disc disease is the drying out of the spongy interior matrix of an intervertebral disc in the spine. Many physicians and patients use the term lumbar disc disease to encompass several different causes of back pain or sciatica. In this article, the term is used to describe a lumbar herniated disc. It is thought that lumbar disc disease causes about one-third of all back pain.
 W
WA mallet finger, also known as hammer finger or PLF finger, is an extensor tendon injury at the farthest away finger joint. This results in the inability to extend the finger tip without pushing it. There is generally pain and bruising at the back side of the farthest away finger joint.
 W
WMelorheostosis is a medical developmental disorder and mesenchymal dysplasia in which the bony cortex widens and becomes hyperdense in a sclerotomal distribution. The condition begins in childhood and is characterized by thickening of the bones. Pain is a frequent symptom and the bone can have the appearance of dripping candle wax.
 W
WMicrotrauma is any of many possible small injuries to the body.
 W
WThe neuromechanics of idiopathic scoliosis is about the changes in the bones, muscles and joints in cases of spinal deformity consisting of a lateral curvature scoliosis and a rotation of the vertebrae within the curve, that is not explained by either congenital vertebral abnormalities, or neuromuscular disorders such as muscular dystrophy. The idiopathic scoliosis accounts for 80–90% of scoliosis cases. Its pathogenesis is unknown. However, changes in the vestibular system, a lateral shift of the hand representation and abnormal variability of erector spinae motor map location in the motor cortex may be involved in this disease. A short spinal cord and associated nerve tensions has been proposed as a cause and model for idiopathic scoliosis. Besides idiopathic scoliosis being more frequent in certain families, it is suspected to be transmitted via autosomal dominant inheritance. Estrogens could also play a crucial part in the progression of idiopathic scoliosis through their roles in bone formation, growth, maturation and turnover. Finally, collagen, intervertebral disc and muscle abnormalities have been suggested as the cause in idiopathic scoliosis, although these are perhaps results rather than causes.
 W
WPeroneal nerve paralysis is a paralysis on common fibular nerve that affects patient’s ability to lift the foot at the ankle. The condition was named after Friedrich Albert von Zenker. Peroneal nerve paralysis usually leads to neuromuscular disorder, peroneal nerve injury, or foot drop which can be symptoms of more serious disorders such as nerve compression. The origin of peroneal nerve palsy has been reported to be associated with musculoskeletal injury or isolated nerve traction and compression. Also it has been reported to be mass lesions and metabolic syndromes. Peroneal nerve is most commonly interrupted at the knee and possibly at the joint of hip and ankle. Most studies reported that about 30% of peroneal nerve palsy is followed from knee dislocations.
 W
WTenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) is a group of rare, typically non-malignant tumors of the joints. TGCT tumors often develop from the lining of joints.
 W
WPiriformis syndrome is a condition which is believed to result from compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle. Symptoms may include pain and numbness in the buttocks and down the leg. Often symptoms are worsened with sitting or running.
 W
WPotassium-aggravated myotonia is a rare genetic disorder that affects skeletal muscle. Beginning in childhood or adolescence, people with this condition experience bouts of sustained muscle tensing (myotonia) that prevent muscles from relaxing normally. Myotonia causes muscle stiffness, often painful, that worsens after exercise and may be aggravated by eating potassium-rich foods such as bananas and potatoes. Stiffness occurs in skeletal muscles throughout the body. Potassium-aggravated myotonia ranges in severity from mild episodes of muscle stiffness to severe, disabling disease with frequent attacks. Potassium-aggravated myotonia may, in some cases, also cause paradoxical myotonia, in which myotonia becomes more severe at the time of movement instead of after movement has ceased. Unlike some other forms of myotonia, potassium-aggravated myotonia is not associated with episodes of muscle weakness.
 W
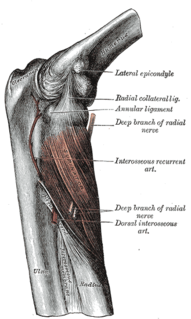
WRadial tunnel syndrome (RTS) is caused by increased pressure on the radial nerve as it travels from the upper arm to the hand and wrist.
 W
WA repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury to part of the musculoskeletal or nervous system caused by repetitive use, vibrations, compression or long periods in a fixed position. Other common names include repetitive stress disorders, cumulative trauma disorders (CTDs), and overuse syndrome.
 W
WSacroiliac joint dysfunction generally refers to pain in the sacroiliac joint region that is caused by abnormal motion in the sacroiliac joint, either too much motion or too little motion. It typically results in inflammation of the sacroiliac joint, and can be debilitating.
 W
WSever's Disease, otherwise known as apophysitis of the calcaneus, is an inflammation of the growth plate in the heel of growing children. The condition presents as pain in the heel and is caused by repetitive stress to the heel and is thus particularly common in active children. It usually resolves when the bone has completed growth or activity is lessened. The pain can be eased through stretching.
 W
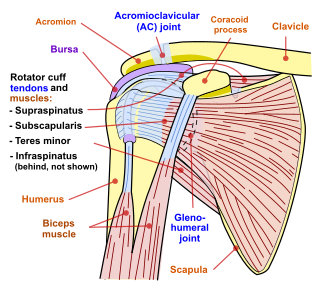
WShoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.
 W
WSnapping hip syndrome, also referred to as dancer's hip, is a medical condition characterized by a snapping sensation felt when the hip is flexed and extended. This may be accompanied by a snapping or popping noise and pain or discomfort. Pain often decreases with rest and diminished activity. Snapping hip syndrome is commonly classified by the location of the snapping as either extra- articular or intra-articular.
 W
WSpinal decompression is a surgical procedure intended to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or on one or more compressed nerve roots passing through or exiting the spinal column. Decompression of the spinal neural elements is a key component in treating spinal radiculopathy, myelopathy and claudication.
 W
WSubungual exostoses are bony projections which arise from the dorsal surface of the distal phalanx, most commonly of the hallux.
 W
WA synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer which occurs primarily in the extremities of the arms or legs, often in proximity to joint capsules and tendon sheaths. It is a type of soft tissue sarcoma.
 W
WTemporomandibular joint dysfunction is an umbrella term covering pain and dysfunction of the muscles of mastication and the temporomandibular joints. The most important feature is pain, followed by restricted mandibular movement, and noises from the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) during jaw movement. Although TMD is not life-threatening, it can be detrimental to quality of life; this is because the symptoms can become chronic and difficult to manage.
 W
WTenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) is a group of rare, typically non-malignant tumors of the joints. TGCT tumors often develop from the lining of joints.
 W
WUlnar nerve entrapment is a condition where the ulnar nerve becomes physically trapped or pinched, resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness, primarily affecting the little finger and ring finger of the hand. Entrapment may occur at any point from the spine at cervical vertebra C7 to the wrist; the most common point of entrapment is in the elbow. Prevention is mostly through correct posture and avoiding repetitive or constant strain. Treatment is usually conservative, including medication, activity modification and exercise, but may sometimes include surgery. Prognosis is generally good, with mild to moderate symptoms often resolving spontaneously.
 W
WUlnar tunnel syndrome, also known as Guyon's canal syndrome or Handlebar palsy, is caused by entrapment of the ulnar nerve in the Guyon canal as it passes through the wrist. Symptoms usually begin with a feeling of pins and needles in the ring and little fingers before progressing to a loss of sensation and/or impaired motor function of the intrinsic muscles of the hand which are innervated by the ulnar nerve. Ulnar tunnel syndrome is commonly seen in regular cyclists due to prolonged pressure of the Guyon's canal against bicycle handlebars. Another very common cause of sensory loss in the ring and pink finger is due to ulnar nerve entrapment at the cubital tunnel near the elbow, which is known as cubital tunnel syndrome.
 W
WUnequal leg length is where the legs are either different lengths or appear to be different lengths because of misalignment. The condition has been estimated to affect between 40% and 70% of the population, with at least 0.1% having a difference greater than 20 mm.
 W
WA winged scapula is a skeletal medical condition in which the shoulder blade protrudes from a person's back in an abnormal position.