 W
WThe anterior interosseous nerve is a branch of the median nerve that supplies the deep muscles on the anterior of the forearm, except the ulnar (medial) half of the flexor digitorum profundus. Its nerve roots come from C8 and T1.
 W
WThe axillary nerve or the circumflex nerve is a nerve of the human body, that originates from the brachial plexus at the level of the axilla (armpit) and carries nerve fibers from C5 and C6. The axillary nerve travels through the quadrangular space with the posterior circumflex humeral artery and vein to innervate the deltoid and teres minor.
 W
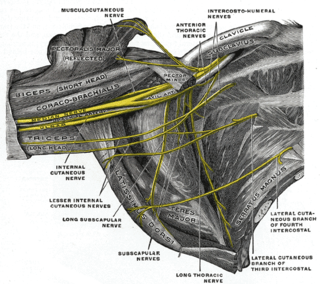
WThe brachial plexus is a network (plexus) of nerves (formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve. This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit. It supplies afferent and efferent nerve fibers to the chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand.
 W
WIn the palm of the hand the median nerve is covered by the skin and the palmar aponeurosis, and rests on the tendons of the Flexor muscles. Immediately after emerging from under the transverse carpal ligament the median nerve becomes enlarged and flattened and splits into a smaller, lateral, and a larger, medial portion.
 W
WThe common palmar digital nerves of the ulnar nerve are nerves of the hand. The nerve branches off the superficial branch of the ulnar nerve and runs toward the cleft between the ring and pinky fingers.
 W
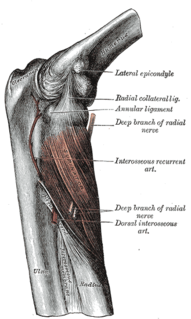
WThe radial nerve divides into a superficial (sensory) and deep (motor) branch at the cubital fossa. The deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the Supinator, and is prolonged downward between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to the middle of the forearm. The deep branch provides motor function to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm, which is mostly the extensor muscles of the hand.
 W
WThe deep branch of the ulnar nerve is a terminal, primarily motor branch of the ulnar nerve. It is accompanied by the deep palmar branch of ulnar artery.
 W
WThe dorsal branch of ulnar nerve arises about 5 cm. proximal to the wrist; it passes backward beneath the Flexor carpi ulnaris, perforates the deep fascia, and, running along the ulnar side of the back of the wrist and hand, divides into two dorsal digital branches; one supplies the ulnar side of the little finger; the other, the adjacent sides of the little and ring fingers.
 W
WDorsal digital nerves of radial nerve are branches on the dorsum of the hand.
 W
WDorsal digital nerves of ulnar nerve are branches on the dorsum of the hand. The dorsal branch of the ulnar nerve divides into two dorsal digital branches; one supplies the ulnar side of the little finger; the other, the adjacent sides of the little and ring fingers. It also sends a twig to join that given by the superficial branch of the radial nerve for the adjoining sides of the middle and ring fingers, and assists in supplying them.
 W
WThe dorsal scapular nerve arises from the brachial plexus, usually from the plexus root of the cervical nerve C5. Once the nerve leaves C5 it commonly pierces the middle scalene muscle, and continues deep to levator scapulae and the rhomboids.
 W
WThe inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm is a nerve found in humans and other animals. It is also called the inferior lateral brachial cutaneous nerve. It is a branch of the radial nerve that provides sensory and vasomotor innervation to the lower, lateral aspect of the arm.
 W
WThe lateral cord is the part of the brachial plexus formed by the anterior divisions of the upper (C5-C6) and middle trunks (C7). Its name comes from it being lateral to the axillary artery as it passes through the axilla. The other cords of the brachial plexus are the posterior cord and medial cord.
 W
WThe lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve passes behind the cephalic vein, and divides, opposite the elbow-joint, into a volar and a dorsal branch.
 W
WThe lateral pectoral nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, and through it from the C5-7.
 W
WThe lateral root of median nerve is one of the two sources of the median nerve.
 W
WThe long thoracic nerve supplies the serratus anterior muscle. This nerve characteristically arises from the anterior rami of three spinal nerve roots: the fifth, sixth, and seventh cervical nerves (C5-C7), although the root from C7 may be absent. The roots from C5 and C6 pierce through the scalenus medius, while the C7 root passes in front of the muscle.
 W
WThe lower (inferior) subscapular nerve is the third branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It innervates the inferior portion of the subscapularis and the teres major. The lower subscapular nerve contains axons from the ventral rami of the fifth (C5) and sixth (C6) cervical nerves.
 W
WThe medial cord is the part of the brachial plexus formed by of the anterior division of the lower trunk (C8-T1). Its name comes from it being medial to the axillary artery as it passes through the axilla. The other cords of the brachial plexus are the posterior cord and lateral cord.
 W
WThe medial brachial cutaneous nerve is distributed to the skin on the medial brachial side of the arm.
 W
WThe medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm branches from the medial cord of the brachial plexus. It contains axons from the ventral rami of the eighth cervical (C8) and first thoracic (T1) nerves.
 W
WThe medial pectoral nerve arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus, and through it from the eighth cervical and first thoracic roots.
 W
WThe medial root of median nerve is one of the two sources of the median nerve.
 W
WThe median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
 W
WThe muscular branches of the radial nerve supply the Triceps brachii, Anconæus, Brachioradialis, and Extensor carpi radialis longus, and are grouped as medial, posterior, and lateral.
 W
WThe musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, opposite the lower border of the pectoralis major, its fibers being derived from C5, C6 and C7.
 W
WCutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific nerve.
 W
WThe palmar branch of the median nerve is a branch of the median nerve which arises at the distal part of the forearm.
 W
WThe palmar branch of the ulnar nerve arises about five cm proximal to the wrist from where the ulnar nerve splits into palmar and dorsal branches. It supplies sensory innervation to a small area in the palmar surface of the wrist.
 W
WThe posterior cord is a part of the brachial plexus. It consists of contributions from all of the roots of the brachial plexus.
 W
WThe posterior cutaneous nerve of arm is a branch of the radial nerve that provides sensory innervation for much of the skin on the back of the arm. It arises in the axilla.
 W
WThe posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm is a nerve found in humans and other animals. It is also known as the dorsal antebrachial cutaneous nerve, the external cutaneous branch of the musculospiral nerve, and the posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve. It is a cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
 W
WThe posterior interosseous nerve is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared to the deep branch of the radial nerve. The nerve fibers originate from cervical segments C7 and C8.
 W
WIn the palm of the hand the median nerve is covered by the skin and the palmar aponeurosis, and rests on the tendons of the flexor muscles. Immediately after emerging from under the transverse carpal ligament the median nerve becomes enlarged and flattened and splits into a smaller, lateral, and a larger, medial portion.
 W
WThe proper palmar digital nerves of the ulnar nerve are nerves of the hand.
 W
WThe radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.
 W
WRadial nerve dysfunction is a problem associated with the radial nerve resulting from injury consisting of acute trauma to the radial nerve. The damage has sensory consequences, as it interferes with the radial nerve's innervation of the skin of the posterior forearm, lateral three digits, and the dorsal surface of the lateral side of the palm. The damage also has motor consequences, as it interferes with the radial nerve's innervation of the muscles associated with the extension at the elbow, wrist, and fingers, as well the supination of the forearm. This type of injury can be difficult to localize, but relatively common, as many ordinary occurrences can lead to the injury and resulting mononeuropathy. One out of every ten patients suffering from radial nerve dysfunction do so because of a fractured humerus.
 W
WThe recurrent branch of the median nerve is the branch of the median nerve which supplies the thenar muscles. It is also occasionally referred to as the thenar branch, or the thenar muscular branch, of the median nerve. In the thenar eminence it provides motor innervation to:opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, and superficial part of flexor pollicis brevis.
 W
WThe subclavian nerve or nerve to the subclavius is small branch of the upper trunk of the brachial plexus where C5 and C6 join. It contains axons derived from the ventral rami of the fifth (C5) and sixth (C6) cervical nerves. The subclavian nerve provides motor innervation to the subclavius muscle.
 W
WSubscapular nerves can refer to:Upper subscapular nerve Lower subscapular nerve Thoracodorsal nerve
 W
WThe superficial branch of the radial nerve passes along the front of the radial side of the forearm to the commencement of its lower third. It is a sensory nerve.
 W
WThe superficial branch of the ulnar nerve is a terminal branch of the ulnar nerve. It supplies the palmaris brevis and the skin on the ulnar side of the hand, and divides into a common palmar digital nerve and a proper palmar digital nerve.
 W
WThe superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm is the continuation of the posterior cord of the axillary nerve, after it pierces the deep fascia. It contains axons from C5-C6.
 W
WThe suprascapular nerve is a nerve that branches from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It is responsible for the innervation of two of the muscles that originate from the scapula, namely the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles.
 W
WThe thoracodorsal nerve is a nerve present in humans and other animals, also known as the middle subscapular nerve or the long subscapular nerve. It supplies the latissimus dorsi muscle.
 W
WIn human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.
 W
WThe upper (superior) subscapular nerve is the first branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It innervates the superior portion of the subscapularis. The inferior portion of the subscapularis is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve. The upper subscapular nerve contains axons from the ventral rami of the fifth (C5) and sixth (C6) cervical nerves.