 W
WA barbiturate is a drug that acts as a central nervous system depressant. Barbiturates are effective as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as well as overdose potential among other possible adverse effects. They have largely been replaced by benzodiazepines and nonbenzodiazepines ("Z-drugs") in routine medical practice, particularly in the treatment of anxiety and insomnia, due to the significantly lower risk of addiction and overdose and the lack of an antidote for barbiturate overdose. Despite this, barbiturates are still in use for various purposes: in general anesthesia, epilepsy, treatment of acute migraines or cluster headaches, acute tension headaches, euthanasia, capital punishment, and assisted suicide.
 W
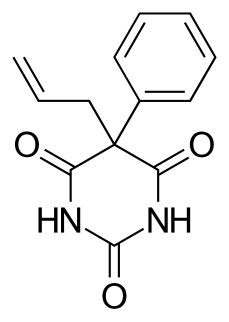
WAllobarbital, also known as allobarbitone and branded as Dial, Cibalgine, or Dial-Ciba, is a barbiturate derivative invented in 1912 by Ernst Preiswerk and Ernst Grether working for CIBA. It was used primarily as an anticonvulsant although it has now largely been replaced by newer drugs with improved safety profiles. Other uses for allobarbital included as an adjutant to boost the activity of analgesic drugs, and use in the treatment of insomnia and anxiety.
 W
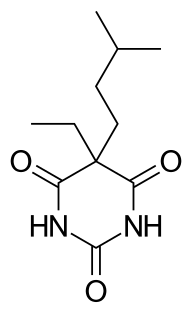
WAlphenal, also known as 5-allyl-5-phenylbarbituric acid, is a barbiturate derivative developed in the 1920s. It has primarily anticonvulsant properties, and was used occasionally for the treatment of epilepsy or convulsions, although not as commonly as better known barbiturates such as phenobarbital.
 W
WAmobarbital is a drug that is a barbiturate derivative. It has sedative-hypnotic properties. It is a white crystalline powder with no odor and a slightly bitter taste. It was first synthesized in Germany in 1923. It is considered an intermediate acting barbiturate. If amobarbital is taken for extended periods of time, physical and psychological dependence can develop. Amobarbital withdrawal mimics delirium tremens and may be life-threatening. Amobarbital was once manufactured by Eli Lilly and Company in the US under the brand name Amytal in bright blue bullet shaped capsule form containing either 50 or 100 mg of the drug. It was widely abused, known as "blue heavens" on the streets, and was discontinued by Eli Lilly in the early 1980s.
 W
WAprobarbital, sold as Oramon, Somnifaine, and Allonal, is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1920s by Ernst Preiswerk. It has sedative, hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily for the treatment of insomnia. Aprobarbital was never as widely used as more common barbiturate derivatives such as phenobarbital and is now rarely prescribed as it has been replaced by newer drugs with a better safety margin.
 W
WBarbexaclone (Maliasin) is a salt compound of phenobarbital and levopropylhexedrine. It was introduced in 1983. It has been reported to be as effective as phenobarbital but better tolerated; however, as of 2004, these "promising results" had not yet been confirmed nor denied in controlled trials.
 W
WBarbital, marketed under the brand names Veronal for the pure acid and Medinal for the sodium salt, was the first commercially available barbiturate. It was used as a sleeping aid (hypnotic) from 1903 until the mid-1950s. The chemical names for barbital are diethylmalonyl urea or diethylbarbituric acid; hence, the sodium salt is known also as sodium diethylbarbiturate.
 W
WBarbiturate overdose is poisoning due to excessive doses of barbiturates. Symptoms typically include difficulty thinking, poor coordination, decreased level of consciousness, and a decreased effort to breathe. Complications of overdose can include noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. If death occurs this is typically due to a lack of breathing.
 W
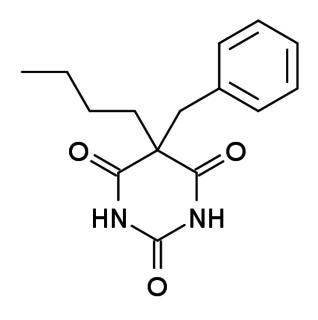
WBenzobarbital (Benzonal) is a barbiturate derivative. It has anticonvulsant effects and has been used for the treatment of epilepsy.
 W
WBenzylbutylbarbiturate is a rare example of a barbiturate designer drug, possibly the only such compound encountered in recent years.
 W
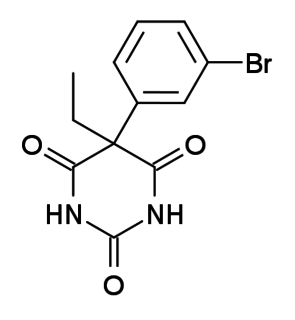
WBrallobarbital was a barbiturate developed in the 1920s. It has sedative and hypnotic properties, and was used for the treatment of insomnia. Brallobarbital was primarily sold as part of a combination product called Vesparax, composed of 150 mg secobarbital, 50 mg brallobarbital and 50 mg hydroxyzine. The long half-life of this combination of drugs tended to cause a hangover effect the next day, and Vesparax fell into disuse once newer drugs with lesser side effects had been developed. Vesparax reportedly was the drug that musician Jimi Hendrix supposedly overdosed on and led to his untimely death. It is no longer made.
 W
WBrophebarbital is a barbiturate derivative. It has sedative and hypnotic effects and is considered to have a moderate abuse potential.
 W
WBucolome (Paramidine) is a barbiturate derivative. Unlike most barbiturates it does not have any significant sedative or hypnotic effects, but instead acts as an analgesic and antiinflammatory. It also acts as a CYP2C9 inhibitor and reduces the metabolism of several commonly used drugs, which makes it useful for potentiating or extending the duration of action of those drugs, or reducing the production of unwanted metabolites.
 W
WButabarbital is a prescription barbiturate sleep aid and anxiety medication. Butabarbital has a particularly fast onset of effects and short duration of action compared to other barbiturates, which makes it useful for certain applications such as treating severe insomnia, relieving general anxiety and relieving anxiety before surgical procedures; however it is also relatively dangerous particularly when combined with alcohol, and so is now rarely used, although it is still prescribed in some Eastern European and South American countries. Its intermediate duration of action gives butabarbital an abuse potential slightly lower than secobarbital. Butabarbital can be hydrolyzed to Valnoctamide.
 W
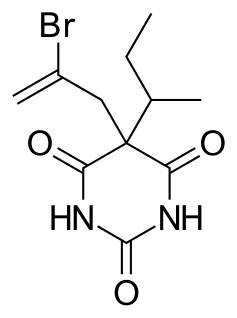
WButalbital is a barbiturate with an intermediate duration of action. Butalbital is often combined with other medications, such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) or aspirin, for the treatment of pain and headache. The various formulations combined with codeine are FDA-approved for the treatment of tension headaches. Butalbital has the same chemical formula as talbutal but a different structure—one that presents as 5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid. Its use for headaches is discouraged due to its toxicity and the availability of safer agents.
 W
WButallylonal is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1920s. It has sedative properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine. Butallylonal is considered similar in effects to pentobarbital but is longer in action, being considered an intermediate-acting barbiturate rather than short-acting.
 W
WButobarbital, also called butobarbitone or butethal, Soneryl, and Neonal, is a hypnotic drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It was developed by Poulenc Brothers in 1921.
 W
WCarbubarb is a carbamate-substituted barbiturate derivative, which has sedative effects.
 W
WCorvalol is a tranquilizer based on the herb valerian root and the barbiturate phenobarbital, popular in Eastern Europe and the former Soviet Union as a heart medication. It is available as a transparent liquid with a characteristic strong aroma, and as white bi-concave scored tablets. While not available for sale in the Western countries, Corvalol is sometimes brought over from Eastern Europe for self-administration to other countries of residence. Corvalol contains documented amounts of psychoactive chemicals, and may interact with other prescription medications that a person is taking.
 W
WCrotylbarbital, also known as crotarbital, is a barbiturate derivative developed by Eli Lilly in the 1930s It has sedative and hypnotic effects, and was used for the treatment of insomnia until it was replaced by newer alternative drugs with less side effects and lower risk of overdose.
 W
WCyclobarbital, also known as cyclobarbitol or cyclobarbitone, is a drug that is a barbiturate derivative. It was available in Russia as a fixed-dose combination with diazepam for the treatment of insomnia but was discontinued in 2019.
 W
WCyclopentobarbital sodium is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1940s. It has sedative and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine. Cyclopal is considered similar in effects to phenobarbital but lasts almost three times as long, and is considered a long-acting barbiturate with a fairly slow onset of action.
 W
WDarusentan is an endothelin receptor antagonist. Gilead Colorado, a subsidiary of Gilead Sciences, under license from Abbott Laboratories, is developing darusentan for the potential treatment of uncontrolled hypertension.
 W
WDifebarbamate (INN) is a tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe as a component of a combination drug formulation referred to as tetrabamate.
 W
WEnallylpropymal (Narconumal) is a barbiturate derivative developed by Hoffman la Roche in the 1930s. It has sedative and hypnotic effects and is considered to have a moderate abuse potential.
 W
WEterobarb (Antilon) is a barbiturate derivative. It has mainly anticonvulsant action with less sedative effects than the closely related compound phenobarbital. It saw reasonable success in clinical trials, but is not in widespread medical use.
 W
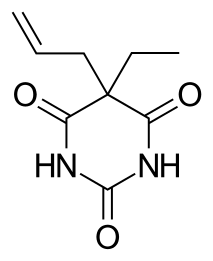
WEthallobarbital, also known as ethallymal and 5-allyl-5-ethylbarbituric acid, is an allyl-substituted barbiturate described as a sedative/hypnotic. It was first synthesized in 1927.
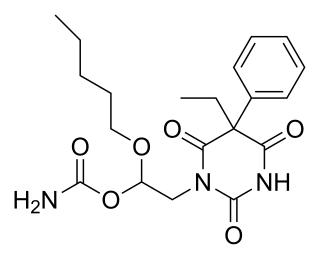 W
WFebarbamate, also known as phenobamate, is an anxiolytic and tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe by itself and as part of a combination drug formulation called tetrabamate.
 W
WHeptabarb, also known as heptabarbitone (BAN) or heptabarbital, is a sedative and hypnotic drug of the barbiturate family. It was used in Europe for the treatment of insomnia from the 1950s onwards, but has since been discontinued.
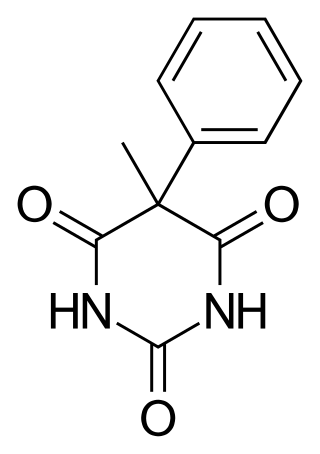 W
WHeptobarbital (Rutonal), also known as phenylmethylbarbituric acid is a barbiturate derivative. It has often been confused with methylphenobarbital because both drugs contain a methylphenyl moiety and are overall very similar in structure.
 W
WHexethal (Ortal) is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1940s. It has sedative, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine.
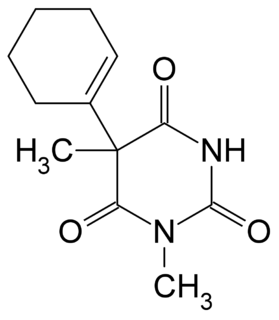 W
WHexobarbital or hexobarbitone, sold both in acid and sodium salt forms as Citopan, Evipan, and Tobinal, is a barbiturate derivative having hypnotic and sedative effects. It was used in the 1940s and 1950s as an agent for inducing anesthesia for surgery, as well as a rapid-acting, short-lasting hypnotic for general use, and has a relatively fast onset of effects and short duration of action. It was also used to murder women prisoners at Ravensbrück concentration camp. Modern barbiturates have largely supplanted the use of hexobarbital as an anesthetic, as they allow for better control of the depth of anesthesia. Hexobarbital is still used in some scientific research.
 W
WMetharbital was patented in 1905 by Emil Fischer working for Merck. It was marketed as Gemonil by Abbott Laboratories. It is a barbiturate anticonvulsant, used in the treatment of epilepsy. It has similar properties to phenobarbital.
 W
WMethohexital or methohexitone is a drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It is classified as short-acting, and has a rapid onset of action. It is similar in its effects to sodium thiopental, a drug with which it competed in the market for anaesthetics.
 W
WPhenobarbital, also known as phenobarbitone or phenobarb, or by the trade name Luminal, is a medication of the barbiturate type. It is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the treatment of certain types of epilepsy in developing countries. In the developed world, it is commonly used to treat seizures in young children, while other medications are generally used in older children and adults. It may be used intravenously, injected into a muscle, or taken by mouth. The injectable form may be used to treat status epilepticus. Phenobarbital is occasionally used to treat trouble sleeping, anxiety, and drug withdrawal and to help with surgery. It usually begins working within five minutes when used intravenously and half an hour when administered by mouth. Its effects last for between four hours and two days.
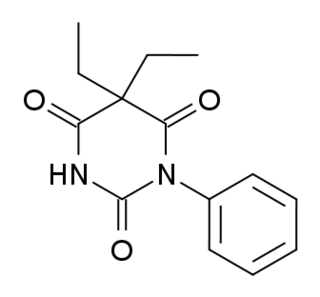 W
WPhetharbital (phenetharbital) is a barbiturate derivative. It has anticonvulsant effects and relatively weak sedative action, and is considered to have a low abuse potential.
 W
WPrazitone (AGN-511) is a barbiturate derivative developed in the 1970s. Unlike most barbiturates, it has little or no sedative effects, instead acting as a non-sedating anxiolytic and antidepressant. The dosage range in humans is around 200–600 mg, although higher doses have been used in trials for the treatment of depression associated with Parkinson's disease.
 W
WProbarbital is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1920s. It has sedative, hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties.
 W
WPropylbarbital, also known as 5,5-dipropylbarbituric acid, is a barbiturate derivative used as a hypnotic drug.
 W
WProxibarbital (Ipronal) is a barbiturate derivative synthesized in 1956. It has anti-anxiety properties and in contrast to most barbiturates almost without hypnotic action.
 W
WReposal is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1960s in Denmark. It has sedative, hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily for the treatment of insomnia.
 W
WSecobarbital sodium is a short-acting barbiturate derivative drug that was patented in 1934 in the United States. It possesses anaesthetic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, sedative, and hypnotic properties. In the United Kingdom, it was known as quinalbarbitone. It is the most frequently used drug in physician-assisted suicide within the United States. Secobarbital is considered to be an obsolete sedative-hypnotic, and as a result, it has largely been replaced by the benzodiazepine family. Seconal was widely abused, known on the street as "red devils" or "reds".
 W
WSigmodal (Rectidon) is a barbiturate derivative. It has sedative, hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties, and was used in surgical anaesthesia in the 1950s, and frequently appeared in drug mixtures in the 60's.
 W
WSpirobarbital is a barbiturate derivative developed by Eli Lilly in the 1940s. It has hypnotic and sedative effects, and has a moderate potential for abuse.
 W
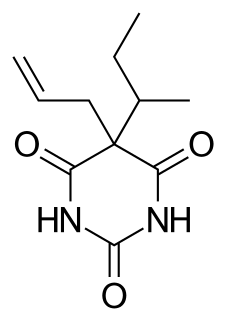
WTalbutal (Lotusate) is a barbiturate with a short to intermediate duration of action. It is a structural isomer of butalbital. Talbutal is a schedule III drug in the U.S.
 W
WTetrabarbital is a barbiturate derivative used as a hypnotic.
 W
WTuinal was the brand name of a discontinued combination drug composed of two barbiturate salts in equal proportions.
 W
WVinylbital, also known as butylvinal, is a sedative hypnotic drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It was developed by Aktieboleget Pharmacia in the 1950s.
 W
WZoliflodacin is an experimental antibiotic that is being studied for the treatment of infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea). It has a novel mechanism of action which involves inhibition of bacterial type II topoisomerases. It is being developed by Entasis Therapeutics and is in Phase III clinical trials.