 W
WPrenatal care, also known as antenatal care, is a type of preventive healthcare. It is provided in the form of medical checkups, consisting of recommendations on managing a healthy lifestyle and the provision of medical information such as maternal physiological changes in pregnancy, biological changes, and prenatal nutrition including prenatal vitamins, which prevents potential health problems throughout the course of the pregnancy and promotes the mother and child's health alike. The availability of routine prenatal care, including prenatal screening and diagnosis, has played a part in reducing the frequency of maternal death, miscarriages, birth defects, low birth weight, neonatal infections and other preventable health problems.
 W
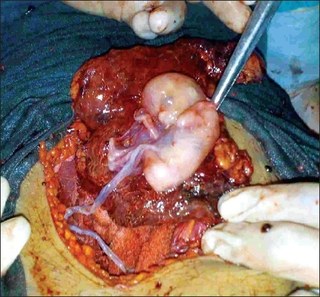
WAn abdominal pregnancy can be regarded as a form of an ectopic pregnancy where the embryo or fetus is growing and developing outside the womb in the abdomen, but not in the Fallopian tube, ovary or broad ligament.
 W
WA blighted ovum is a pregnancy in which the embryo never develops or develops and is reabsorbed. In a normal pregnancy, an embryo would be visible on an ultrasound by six weeks after the woman's last menstrual period. Anembryonic gestation is one of the causes of miscarriage of a pregnancy.
 W
WAsherman's syndrome (AS), is an acquired uterine condition that occurs when scar tissue (adhesions) form inside the uterus and/or the cervix. It is characterized by variable scarring inside the uterine cavity, where in many cases the front and back walls of the uterus stick to one another. AS can be the cause of menstrual disturbances, infertility, and placental abnormalities. Although the first case of intrauterine adhesion was published in 1894 by Heinrich Fritsch, it was only after 54 years that a full description of Asherman syndrome was carried out by Joseph Asherman. A number of other terms have been used to describe the condition and related conditions including: uterine/cervical atresia, traumatic uterine atrophy, sclerotic endometrium, and endometrial sclerosis.
 W
WCervical cerclage, also known as a cervical stitch, is a treatment for cervical weakness, when the cervix starts to shorten and open too early during a pregnancy causing either a late miscarriage or preterm birth. In women with a prior spontaneous preterm birth and who are pregnant with one baby, and have shortening of the cervical length less than 25 mm, a cerclage prevents a preterm birth and reduces death and illness in the baby.
 W
WA cervical pregnancy is an ectopic pregnancy that has implanted in the uterine endocervix. Such a pregnancy typically aborts within the first trimester, however, if it is implanted closer to the uterine cavity – a so-called cervico-isthmic pregnancy – it may continue longer. Placental removal in a cervical pregnancy may result in major hemorrhage.
 W
WA chorangioma is a non-neoplastic, hamartoma-like growth in the placenta consisting of blood vessels.
 W
WChorangiosis is a placental pathology characterized by an abundance of blood vessels within the chorionic villi.
 W
WChorionic hematoma is the pooling of blood (hematoma) between the chorion, a membrane surrounding the embryo, and the uterine wall. It occurs in about 3.1% of all pregnancies, it is the most common sonographic abnormality and the most common cause of first trimester bleeding.
 W
WA congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure.
 W
WThe effect of COVID-19 infection on pregnancy is not completely known because of the lack of reliable data. If there is increased risk to pregnant women and fetuses, so far it has not been readily detectable.
 W
WFor pregnant women with diabetes, some particular challenges exist for both mother and child. If the woman has diabetes as a pre-existing or acquired disorder, it can cause early labor, birth defects, and larger than average infants.
 W
WDiastasis recti, or rectus abdominis diastasis, is defined as a gap of about 2.7 cm or greater between the two sides of the rectus abdominis muscle. The distance between the right and left rectus abdominis muscles is created by the stretching of the linea alba, a connective collagen sheath created by the aponeurosis insertions of the transverse abdominis, internal oblique, and external oblique. This condition has no associated morbidity or mortality.
 W
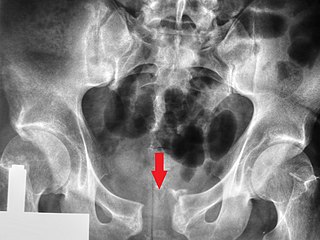
WDiastasis symphysis pubis is the separation of normally joined pubic bones, as in the dislocation of the bones, without a fracture. Separation of the symphysis pubis can occur spontaneously in at least 1 in 800 vaginal deliveries. It is usually noticed after delivery and has been associated with forceps delivery, rapid second stage of labour or severe abduction of the thighs during delivery. Common signs and symptoms include symphyseal pain aggravated by weight bearing and walking, a waddling gait, pubic tenderness, and a palpable interpubic gap
 W
WEctopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare exceptions the fetus is unable to survive.
 W
WEisenmenger's syndrome is defined as the process in which a long-standing left-to-right cardiac shunt caused by a congenital heart defect causes pulmonary hypertension and eventual reversal of the shunt into a cyanotic right-to-left shunt. Because of the advent of fetal screening with echocardiography early in life, the incidence of heart defects progressing to Eisenmenger's has decreased.
 W
WFetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) are a group of conditions that can occur in a person whose mother drank alcohol during pregnancy. Symptoms can include an abnormal appearance, short height, low body weight, small head size, poor coordination, low intelligence, behavior problems, learning difficulties and problems with hearing or sight. Those affected are more likely to have trouble in school, legal problems, participate in high-risk activities and have problems with alcohol or other drugs. The most severe form of the condition is known as fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). Other types include partial fetal alcohol syndrome (pFAS), alcohol-related neurodevelopmental disorder (ARND) and alcohol-related birth defects (ARBD). Some accept only FAS as a diagnosis, seeing the evidence as inconclusive with respect to other types.
 W
WFetal thrombotic vasculopathy is a chronic disorder characterized by thrombosis in the fetus leading to vascular obliteration and hypoperfusion.
 W
WFoetal cerebral redistribution or 'brain-sparing' is a diagnosis in foetal medicine. It is characterised by preferential flow of blood towards the brain at the expense of the other vital organs, and it occurs as a haemodynamic adaptation in foetuses which have placental insufficiency. The underlying mechanism is thought to be vasodilation of the cerebral arteries. Cerebral redistribution is defined by the presence of a low middle cerebral artery pulsatility index (MCA-PI). Ultrasound of the middle cerebral artery to examine the Doppler waveform is used to establish this. Although cerebral redistribution represents an effort to preserve brain development in the face of hypoxic stress, it is nonetheless associated with adverse neurodevelopmental outcome. The presence of cerebral redistribution will be one factor taken into consideration when deciding whether to artificially deliver a baby with placental insufficiency via induction of labour or caesarian section.
 W
WGestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it does increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and requiring a Caesarean section. Babies born to mothers with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at increased risk of being too large, having low blood sugar after birth, and jaundice. If untreated, it can also result in a stillbirth. Long term, children are at higher risk of being overweight and developing type 2 diabetes.
 W
WGestational hypertension or pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is the development of new hypertension in a pregnant woman after 20 weeks' gestation without the presence of protein in the urine or other signs of pre-eclampsia. Gestational hypertension is defined as having a blood pressure greater than 140/90 on two separate occasions at least 6 hours apart.
 W
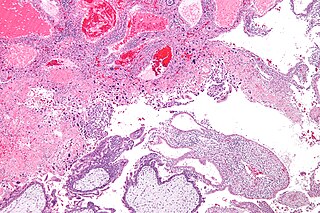
WGestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is a term used for a group of pregnancy-related tumours. These tumours are rare, and they appear when cells in the womb start to proliferate uncontrollably. The cells that form gestational trophoblastic tumours are called trophoblasts and come from tissue that grows to form the placenta during pregnancy.
 W
WGroup B streptococcal infection, also known as Group B streptococcal disease or just Group B strep, is the infection caused by the bacterium Streptococcus agalactiae. GBS infection can cause serious illness and sometimes death, especially in newborns, the elderly, and people with compromised immune systems.
 W
WGroup B streptococcal infection, also known as Group B streptococcal disease or just Group B strep, is the infection caused by the bacterium Streptococcus agalactiae. GBS infection can cause serious illness and sometimes death, especially in newborns, the elderly, and people with compromised immune systems.
 W
WA heterotopic pregnancy is a rare complication of pregnancy in which both extra-uterine and intrauterine pregnancy occur simultaneously. It may also be referred to as a combined ectopic pregnancy, multiple‑sited pregnancy, or coincident pregnancy.
 W
WIn pathology, hypertrophic decidual vasculopathy, abbreviated HDV, is the histomorphologic correlate of gestational hypertension, as may be seen in intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and HELLP syndrome.
 W
WAn interstitial pregnancy is a uterine but ectopic pregnancy; the pregnancy is located outside the uterine cavity in that part of the fallopian tube that penetrates the muscular layer of the uterus. The term cornual pregnancy is sometimes used as a synonym, but remains ambiguous as it is also applied to indicate the presence of a pregnancy located within the cavity in one of the two upper "horns" of a bicornuate uterus. Interstitial pregnancies have a higher mortality than ectopics in general.
 W
WKegel exercise, also known as pelvic-floor exercise, involves repeatedly contracting and relaxing the muscles that form part of the pelvic floor, now sometimes colloquially referred to as the "Kegel muscles". The exercise can be performed multiple times each day, for several minutes at a time, but takes one to three months to begin to have an effect.
 W
WPhenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated, PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also result in a musty smell and lighter skin. A baby born to a mother who has poorly treated PKU may have heart problems, a small head, and low birth weight.
 W
WMaternal physiological changes in pregnancy are the adaptations during pregnancy that the pregnant woman's body undergoes to accommodate the growing embryo or fetus. These physiologic changes are entirely normal, and include behavioral (brain), cardiovascular, hematologic (blood), metabolic, renal (kidney), posture, and respiratory (breathing) changes. Increases in blood sugar, breathing, and cardiac output are all expected changes that allow a pregnant woman's body to facilitate the proper growth and development of the embryo or fetus during the pregnancy. The pregnant woman and the placenta also produce many other hormones that have a broad range of effects during the pregnancy.
 W
WMaternal–fetal medicine (MFM), also known as perinatology, is a branch of medicine that focuses on managing health concerns of the mother and fetus prior to, during, and shortly after pregnancy.
 W
WMeconium peritonitis refers to rupture of the bowel prior to birth, resulting in fetal stool (meconium) escaping into the surrounding space (peritoneum) leading to inflammation (peritonitis). Despite the bowel rupture, many infants born after meconium peritonitis in utero have normal bowels and have no further issues.
 W
WNutrition and pregnancy refers to the nutrient intake, and dietary planning that is undertaken before, during and after pregnancy. Nutrition of the fetus begins at conception. For this reason, the nutrition of the mother is important from before conception as well as throughout pregnancy and breast feeding. An ever-increasing number of studies have shown that the nutrition of the mother will have an effect on the child, up to and including the risk for cancer, cardiovascular disease, hypertension and diabetes throughout life.
 W
WPlacenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in an abnormal position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated with pain. Complications may include placenta accreta, dangerously low blood pressure, or bleeding after delivery. Complications for the baby may include fetal growth restriction.
 W
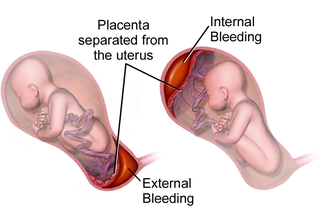
WPlacental abruption is when the placenta separates early from the uterus, in other words separates before childbirth. It occurs most commonly around 25 weeks of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, and dangerously low blood pressure. Complications for the mother can include disseminated intravascular coagulopathy and kidney failure. Complications for the baby can include fetal distress, low birthweight, preterm delivery, and stillbirth.
 W
WA placental site nodule (PSN) is benign remnant from a previous pregnancy.
 W
WPlacental site trophoblastic tumor is a form of gestational trophoblastic disease, which is thought to arise from intermediate trophoblast.
 W
WPlacental villous immaturity is chorionic villous development that is inappropriate for the gestational age.
 W
WPre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet count, impaired liver function, kidney dysfunction, swelling, shortness of breath due to fluid in the lungs, or visual disturbances. Pre-eclampsia increases the risk of poor outcomes for both the mother and the baby. If left untreated, it may result in seizures at which point it is known as eclampsia.
 W
WThe Pregnancy Outcome Prediction (POP) Study is a prospective cohort study of 4,512 women that have never given birth recruited at the Rosie Hospital between January 2008 and July 2012.
 W
WPrelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature rupture of membranes, is breakage of the amniotic sac before the onset of labor. Women usually experience a painless gush or a steady leakage of fluid from the vagina. Complications in the baby may include premature birth, cord compression, and infection. Complications in the mother may include placental abruption and postpartum endometritis.
 W
WPrenatal nutrition addresses nutrient recommendations before and during pregnancy. Nutrition and weight management before and during pregnancy has a profound effect on the development of infants. This is a rather critical time for healthy development since infants rely heavily on maternal stores and nutrient for optimal growth and health outcome later in life.
 W
WTobacco smoking during pregnancy causes many detrimental effects on health and reproduction, in addition to the general health effects of tobacco. A number of studies have shown that tobacco use is a significant factor in miscarriages among pregnant smokers, and that it contributes to a number of other threats to the health of the foetus.
 W
WStreptococcus agalactiae is a gram-positive coccus with a tendency to form chains. It is a beta-hemolytic, catalase-negative, and facultative anaerobe.
 W
WStretch marks, also known as Striae or Striae distensae, are a form of scarring on the skin with an off-color hue. Over time they may diminish, but will not disappear completely. Stretch marks are caused by tearing of the dermis during periods of rapid growth of the body, such as during puberty or pregnancy. In pregnancy they usually form during the last trimester, and usually on the belly, but also commonly occur on the breasts, thighs, hips, lower back and buttocks; these are known as striae gravidarum. Stretch marks may also be influenced by the hormonal changes associated with puberty, pregnancy, bodybuilding, or hormone replacement therapy. There is no evidence that creams used during pregnancy prevent stretch marks. Once they have formed there is no clearly effective treatment, though various methods have been attempted and studied.
 W
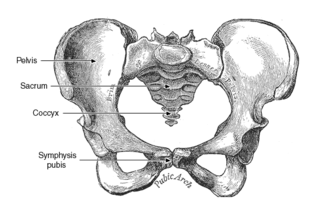
WSymphysis pubis dysfunction (SPD) is a condition that causes excessive movement of the pubic symphysis, either anterior or lateral, as well as associated pain, possibly because of a misalignment of the pelvis. Most commonly associated with pregnancy and childbirth, it is diagnosed in approximately 1 in 300 pregnancies, although some estimates of incidence are as high as 1 in 50.
 W
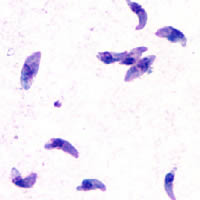
WToxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii. Infections with toxoplasmosis usually cause no obvious symptoms in adults. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes. In a small number of people, eye problems may develop. In those with a weak immune system, severe symptoms such as seizures and poor coordination may occur. If infected during pregnancy, a condition known as congenital toxoplasmosis may affect the child.
 W
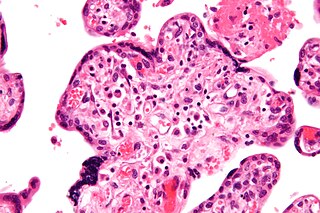
WVillitis of unknown etiology (VUE), also known as chronic villitis, is a placental injury. VUE is an inflammatory condition involving the chorionic villi. VUE is a recurrent condition and can be associated with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). IUGR involves the poor growth of the foetus, stillbirth, miscarriage, and premature delivery. VUE recurs in about 1/3 of subsequent pregnancies.
 W
WPrenatal vitamins, also known as prenatal supplements, are vitamin and mineral supplements intended to be taken before and during pregnancy and during postnatal lactation. Although not intended to replace a healthy diet, prenatal vitamins provide women of childbearing age with nutrients recognized by the various health organizations including the American Dietetic Association as helpful for a healthy pregnancy outcome. It may be appropriate to start taking prenatal vitamins once the woman enters childbearing age. Prenatal vitamins are similar to other multivitamins but do contain different amounts of specific nutrients to better suit the needs of an expecting mother.
 W
WWorld Prematurity Day is observed on 17 November each year to raise awareness of preterm birth and the concerns of preterm babies and their families worldwide. Approximately 15 million babies are born preterm each year, accounting for about one in 10 of all babies born worldwide. Premature birth is the leading cause of death in children under the age of five worldwide. Urgent action is always requested to address preterm birth given that the first country-level estimates show that globally 15 million babies are born too soon and rates are increasing in most countries with reliable time trend data. Preterm birth is critical for progress on Millennium Development Goal 4 (MDG) for child survival by 2015 and beyond, and gives added value to maternal health investments also linking to non-communicable diseases. For preterm babies who survive, the additional burden of prematurity-related disability may affect families and health systems.