 W
WAcanthochitona garnoti, the spiny chiton, is a medium-sized polyplacophoran mollusc in the family Acanthochitonidae, found on the coast of southern Africa.
 W
WAetobatus is a genus of eagle rays native to the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. It was formerly placed in Myliobatidae, but is now placed in its own family based on salient differences from myliobatids, especially the pectoral fins joining the head at the level of the eyes.
 W
WAlveopora is a genus of colonial stony corals in the family Acroporidae. Members of this genus are native to the Indo-Pacific region and are often found on reef slopes in turbid water. They are generally uncommon.
 W
WThe Amazon river dolphin, also known as the boto, bufeo or pink river dolphin, is a species of toothed whale classified in the family Iniidae. Three subspecies are currently recognized: I. g. geoffrensis, I. g. boliviensis and I. g. humboldtiana while position of Araguaian river dolphin within the clade is still unclear. The three subspecies are distributed in the Amazon basin, the upper Madeira River in Bolivia, and the Orinoco basin, respectively.
 W
WArctocyon is an extinct genus of ungulate mammals. Arctocyon was a "ground dwelling omnivore", that lived from 61.3-56.8 Ma. Synonyms of Arctocyon include Claenodon, and Neoclaenodon. Arctocyon was likely plantigrade, that is, walked like a bear.
 W
WStarfish or sea stars are star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class Asteroidea. Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to as brittle stars or basket stars. Starfish are also known as Asteroids due to being in the class Asteroidea. About 1,500 species of starfish occur on the seabed in all the world's oceans, from the tropics to frigid polar waters. They are found from the intertidal zone down to abyssal depths, 6,000 m (20,000 ft) below the surface.
 W
WThe nilgai or blue bull is the largest Asian antelope and is ubiquitous across the northern Indian subcontinent. The sole member of the genus Boselaphus, the species was described and given its binomial name by German zoologist Peter Simon Pallas in 1766. The nilgai stands 1–1.5 metres (3.3–4.9 ft) at the shoulder; males weigh 109–288 kilograms (240–635 lb), and the lighter females 100–213 kilograms (220–470 lb). A sturdy thin-legged antelope, the nilgai is characterised by a sloping back, a deep neck with a white patch on the throat, a short crest of hair along the neck terminating in a tuft, and white facial spots. A column of pendant coarse hair hangs from the dewlap ridge below the white patch. Sexual dimorphism is prominent – while females and juveniles are orange to tawny, adult males have a bluish-grey coat. Only males possess horns, 15–24 centimetres (5.9–9.4 in) long.
 W
WThe bullhead sharks are a small order of modern sharks (Neoselachii). The nine living species are placed in a single genus, Heterodontus, in the family Heterodontidae. All are relatively small, with the largest species reaching just 1.65 metres (5.5 ft) in maximum length. They are bottom feeders in tropical and subtropical waters.
 W
WThe zebra-tailed lizard is a species of phrynosomatid lizard endemic to the Southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico.
 W
WThe Cape gopher snake or Baja gopher snake is a species of nonvenomous colubrid endemic to extreme southern Baja California Sur, Mexico. They have become increasingly popular companions for people interested in the exotic pet trade, due to their extreme color variations and relatively docile behavior. It was previously considered to be a subspecies of Pituophis catenifer.
 W
WCarcharhinus is the type genus of the family Carcharhinidae, the requiem sharks. One of 12 genera in its family, it contains over half of the species therein. It contains 35 extant and eight extinct species to date, with likely more species yet to be described.
 W
WThe Caribbean reef squid, commonly called the reef squid, is a species of small, torpedo-shaped squid with undulating fins that extend nearly the entire length of the body, approximately 20 cm (8 in) in length. In 2001, marine biologist Silvia Maciá discovered that squid were able to propel themselves up out of the water about 2 m (6.6 ft) and fly approximately 10 m (33 ft) before re-entry; a discovery which led to the identification of six species of flying squid.
 W
WCarinariidae, known by the common name "heteropods" like their relatives in the Pterotracheoidea, is a taxonomic family of swimming or floating sea snails, pelagic marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Littorinimorpha.
 W
WThe basking shark is the second-largest living shark, after the whale shark, and one of three plankton-eating shark species, along with the whale shark and megamouth shark. Adults typically reach 7.9 m (26 ft) in length. It is usually greyish-brown, with mottled skin. The caudal fin has a strong lateral keel and a crescent shape.
 W
WA tuco-tuco is a neotropical rodent in the family Ctenomyidae. Tuco-tucos belong to the only living genus of the family Ctenomyidae, Ctenomys, but they include approximately 60 different species. The common name, "tuco-tuco" comes from the "tuc-tuc" sound they make while they dig their burrows.
 W
WThe leatherback sea turtle, sometimes called the lute turtle or leathery turtle or simply the luth, is the largest of all living turtles and is the fourth-heaviest modern reptile behind three crocodilians. It is the only living species in the genus Dermochelys and family Dermochelyidae. It can easily be differentiated from other modern sea turtles by its lack of a bony shell, hence the name. Instead, its carapace is covered by skin and oily flesh.
 W
WEchinorhinus is the only extant genus in the family Echinorhinidae.
 W
WThe cornetfishes or flutemouths are a small family, the Fistulariidae, of extremely elongated fishes in the order Syngnathiformes. The family consists of a single genus, Fistularia, with four species, found worldwide in tropical and subtropical marine environments.
 W
WThe four-horned antelope, or chousingha, is a small antelope found in India and Nepal. This antelope has four horns, which distinguish it from most other bovids, which have two horns. The sole member of the genus Tetracerus, the species was first described by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1816. Three subspecies are recognised. The four-horned antelope stands nearly 55–64 centimetres (22–25 in) at the shoulder and weighs nearly 17–22 kilograms (37–49 lb). Slender with thin legs and a short tail, the four-horned antelope has a yellowish brown to reddish coat. One pair of horns is located between the ears, and the other on the forehead. The posterior horns are always longer than the anterior horns, which might be mere fur-covered studs. While the posterior horns measure 8–12 centimetres (3.1–4.7 in), the anterior ones are 2–5 centimetres (0.79–1.97 in) long.
 W
WThe school shark is a houndshark of the family Triakidae, and the only member of the genus Galeorhinus. Common names also include tope shark, snapper shark, and soupfin shark. It is found worldwide in temperate seas at depths down to about 800 m (2,600 ft). It can grow to nearly 2 m long. It feeds both in midwater and near the seabed, and its reproduction is ovoviviparous. This shark is caught in fisheries for its flesh, its fins, and its liver, which has a very high vitamin A content. The IUCN has classified this species as critically endangered in its Red List of Threatened Species.
 W
WA gazelle is any of many antelope species in the genus Gazella. This article also deals with the six species included in two further genera, Eudorcas and Nanger, which were formerly considered subgenera of Gazella. A third former subgenus, Procapra, includes three living species of Asian gazelles.
 W
WA gazelle is any of many antelope species in the genus Gazella. This article also deals with the six species included in two further genera, Eudorcas and Nanger, which were formerly considered subgenera of Gazella. A third former subgenus, Procapra, includes three living species of Asian gazelles.
 W
WGoniopora, often called flowerpot coral, is a genus of colonial stony coral found in lagoons and turbid water conditions. Goniopora have numerous daisy-like polyps that extend outward from the base, each tipped with 24 stinging tentacles which surrounds a mouth.
 W
WThe bullhead sharks are a small order of modern sharks (Neoselachii). The nine living species are placed in a single genus, Heterodontus, in the family Heterodontidae. All are relatively small, with the largest species reaching just 1.65 metres (5.5 ft) in maximum length. They are bottom feeders in tropical and subtropical waters.
 W
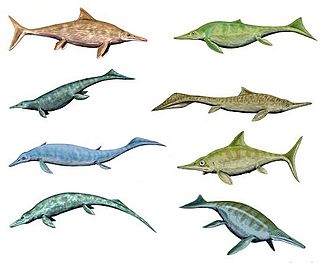
WIchthyosaurs are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia. Ichthyosaurs lived during the time of the dinosaurs, but formed a separate group from the dinosaurs and may not have been closely related to them.
 W
WIchthyosaurs are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia. Ichthyosaurs lived during the time of the dinosaurs, but formed a separate group from the dinosaurs and may not have been closely related to them.
 W
WThe leopard seal, also referred to as the sea leopard, is the second largest species of seal in the Antarctic. Its only natural predator is the killer whale. It feeds on a wide range of prey including cephalopods, other pinnipeds, krill, birds and fish. It is the only species in the genus Hydrurga. Its closest relatives are the Ross seal, the crabeater seal and the Weddell seal, which together are known as the tribe of Lobodontini seals. The name hydrurga means "water worker" and leptonyx is the Greek for "small clawed".
 W
WLobophyllia, commonly called lobed brain coral or lobo coral, is a genus of large polyp stony corals. Members of this genus are sometimes found in reef aquariums.
 W
WMillipedes are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name being derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from the Latin for "thousand feet", no known species has 1,000; the record of 750 legs belongs to Illacme plenipes. There are approximately 12,000 named species classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures.
 W
WOryx is a genus consisting of four large antelope species called oryxes. Three of them are native to arid parts of Africa, and the fourth to the Arabian Peninsula. Their fur is pale with contrasting dark markings in the face and on the legs, and their long horns are almost straight. The exception is the scimitar oryx, which lacks dark markings on the legs, only has faint dark markings on the head, has an ochre neck, and horns that are clearly decurved.
 W
WThe muskox, also spelled musk ox and musk-ox, is an Arctic hoofed mammal of the family Bovidae, noted for its thick coat and for the strong odor emitted by males during the seasonal rut, from which its name derives. This musky odor is used to attract females during mating season. Its Inuktitut name "umingmak" translates to "the bearded one". Its Woods Cree names "mâthi-môs" and "mâthi-mostos" translate to "ugly moose" and "ugly bison", respectively. Muskoxen primarily live in Greenland and the Canadian Arctic of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, with introduced populations in the American state of Alaska, the Canadian territory of Yukon, the Scandinavian Peninsula, and Siberia.
 W
WThe Pacific gopher snake is a subspecies of large non-venomous colubrid snake native to the western coast of the United States.
 W
WPhascolarctos is a genus of marsupials containing only one extant species, the koala (P. cinereus). The genus was named by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1816.
 W
WPituophis catenifer is a species of nonvenomous colubrid snake endemic to North America. Nine subspecies are currently recognized, including the nominotypical subspecies, Pituophis catenifer catenifer, described here. This snake is often mistaken for the prairie rattlesnake, but can be easily distinguished from a rattlesnake by the lack of black and white banding on its tail and by the shape of its head, which is narrower than a rattlesnake's.
 W
WThe Pacific gopher snake is a subspecies of large non-venomous colubrid snake native to the western coast of the United States.
 W
WThe Cape gopher snake or Baja gopher snake is a species of nonvenomous colubrid endemic to extreme southern Baja California Sur, Mexico. They have become increasingly popular companions for people interested in the exotic pet trade, due to their extreme color variations and relatively docile behavior. It was previously considered to be a subspecies of Pituophis catenifer.
 W
WThe Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.
 W
WPristigenys is an extinct genus of fish in the family Priacanthidae. Fossils of the only species, P. substriata, have been found in the Eocene of Mount Bolca, Italy. The closely related extant genus Pseudopriacanthus was previously synonymized with Pristigenys, but has been recently revalidated based on numerous differences in the cranial region and the fins.
 W
WQuaternates is an obsolete order of mammals created by Henri-Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1839, imitating Linnean nomenclature (Primates). It included the suborders Gravigrada, Pachydermata, and Ruminantia.
 W
WRupicapra is a genus of goat-antelope called the chamois. They belong to the bovine family of hoofed mammals, the Bovidae.
 W
WScyliorhinus is a genus of catsharks in the family Scyliorhinidae. This genus is known in the fossil records from the Cretaceous period, late Albian age to the Pliocene epoch.
 W
WSecundates is an obsolete order of mammals created by Henri-Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1839, imitating Linnean nomenclature (Primates). It included the suborders Chiroptera, Insectivora and Carnivora.
 W
WSepia elegans, the elegant cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish in the family Sepiidae from the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is an important species for fisheries in some parts of the Mediterranean where its population may have suffered from overfishing.
 W
WStarfish or sea stars are star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class Asteroidea. Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to as brittle stars or basket stars. Starfish are also known as Asteroids due to being in the class Asteroidea. About 1,500 species of starfish occur on the seabed in all the world's oceans, from the tropics to frigid polar waters. They are found from the intertidal zone down to abyssal depths, 6,000 m (20,000 ft) below the surface.
 W
WTertiates is an obsolete order of mammals created by Henri-Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1839, imitating Linnean nomenclature (Primates). It included the suborder Glires.
 W
WThe four-horned antelope, or chousingha, is a small antelope found in India and Nepal. This antelope has four horns, which distinguish it from most other bovids, which have two horns. The sole member of the genus Tetracerus, the species was first described by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1816. Three subspecies are recognised. The four-horned antelope stands nearly 55–64 centimetres (22–25 in) at the shoulder and weighs nearly 17–22 kilograms (37–49 lb). Slender with thin legs and a short tail, the four-horned antelope has a yellowish brown to reddish coat. One pair of horns is located between the ears, and the other on the forehead. The posterior horns are always longer than the anterior horns, which might be mere fur-covered studs. While the posterior horns measure 8–12 centimetres (3.1–4.7 in), the anterior ones are 2–5 centimetres (0.79–1.97 in) long.
 W
WThracia is a genus of bivalve mollusc in the family Thraciidae.
 W
WTragelaphus is a genus of medium- to large-sized spiral-horned antelopes. It contains several species of bovine, all of which are relatively antelope-like. Species in this genus tend to be large sized, lightly built, have long necks and considerable sexual dimorphism. Elands, including the common eland, are embedded within this genus meaning that Taurotragus must be subsumed into Tragelaphus to avoid paraphyly. Alternatively, Taurotragus could be maintained as a separate genus, if the nyala and the lesser kudu are relocated to their own monospecific genera: respectively, Nyala and Ammelaphus. Other generic synonyms include Strepsiceros and Boocercus. The name "Tragelaphus" comes from the mythical tragelaph.
 W
WA tuco-tuco is a neotropical rodent in the family Ctenomyidae. Tuco-tucos belong to the only living genus of the family Ctenomyidae, Ctenomys, but they include approximately 60 different species. The common name, "tuco-tuco" comes from the "tuc-tuc" sound they make while they dig their burrows.
 W
WThe zebra-tailed lizard is a species of phrynosomatid lizard endemic to the Southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico.