 W
WActinia fragacea, commonly known as the strawberry anemone, is a species of sea anemone of the order Actiniaria, that occurs from Norway to Africa, including adjacent islands and the Mediterranean. It is generally found on rocks of the lower shoreline and depths up to 8–10 metres (26–33 ft).
 W
WActinothoe sphyrodeta, the sandalled anemone, is a small sea anemone in the family Sagartiidae. It is native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and is common on the north, west and south coasts of Britain. It is usually grey or whitish but may have an orange oral disc. The translucent white tentacles that grow around the edge of the oral disc can number up to 120.
 W
WAglaophenia pluma, the toothed feather hydroid or podded hydroid, is a colonial hydroid in the family Aglaopheniidae and is found worldwide. It lives from the shore to 120m under water.
 W
WAiptasia mutabilis, also known as the trumpet anemone, rock anemone, and glass anemone, is a species of anemone typically found attached to substrates in cold waters of the Atlantic Ocean. Its unique trumpet shape gives it its common name and it can grow to be 12 cm, having a column between 3 and 6 cm in size. Like many cnidarians, they rely on nematocysts for protection and to capture prey. They are not difficult to care for, and can be kept in a home aquarium, although due to their speed of reproduction, can quickly become overpopulated.
 W
WAlcyonium coralloides, commonly known as false coral, is a colonial species of soft coral in the family Alcyoniidae. It is native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. In the former location it generally grows as sheets or small lobes but in the latter it is parasitic and overgrows sea fans.
 W
WAlicia mirabilis, commonly known as the berried anemone, is a species of sea anemone in the family Aliciidae. It changes shape as night falls expanding its column and tentacles to catch its food. It can be found in the Azores, Portugal, Spain and the Mediterranean and Red Seas.
 W
WAnemonia sulcata, or Mediterranean snakelocks sea anemone, is a species of sea anemone in the family Actiniidae from the Mediterranean Sea. Whether A. sulcata should be recognized as a synonym of A. viridis remains a matter of dispute.
 W
WAntipathes dichotoma is a species of colonial coral in the order Antipatharia, the black corals, so named because their calcareous skeletons are black. It was first described by the German zoologist and botanist Peter Simon Pallas in 1766, from a single specimen he received from near Marseilles in the Mediterranean Sea.
 W
WAulactinia verrucosa, the gem anemone, is a species of sea anemone in the family Actiniidae. It is found on rocky coasts in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, North Sea and Mediterranean Sea.
 W
WAurelia is a genus of scyphozoan jellyfish, commonly called moon jellies. There are at least 13 species in the genus Aurelia including many that are still not formally described. It has been suggested that Aurelia is the best-studied group of gelatinous zooplankton, with Aurelia aurita the best-studied species in the genus; two other species, Aurelia labiata and Aurelia limbata have also been investigated. Since most previous studies of Aurelia were done without the benefit of genetic identification, one cannot positively attribute the results of most research to the species named. Species of Aurelia can be found in the Atlantic Ocean, the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, and are common to the waters off California, northern China, Japan, Korea, Australia, New Zealand, the Black Sea, Indonesia, the eastern coast of the United States as well as Europe. Aurelia undergoes alternation of generations, whereby the sexually-reproducing pelagic medusa stage is either male or female, and the benthic polyp stage reproduces asexually. Meanwhile, life cycle reversal, in which polyps are formed directly from juvenile and sexually mature medusae or their fragments, was also observed in Aurelia sp.1. The genus was first described in 1845 by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck in his book Histoire Naturelle des Animaux sans Vertebres.
 W
WAurelia aurita is a widely studied species of the genus Aurelia. All species in the genus are closely related, and it is difficult to identify Aurelia medusae without genetic sampling; most of what follows applies equally to all species of the genus. The most common method used to identify the species consists of selecting a jellyfish from a harbour using a device, usually a drinking glass and then photographing the subject. This means that they can be released in to the harbour shortly afterwards and return to their natural habitat.
 W
WBathyphysa conifera, sometimes called the flying spaghetti monster, is a bathypelagic species of siphonophore in the family Rhizophysidae.
 W
WAntipatharians, also known as black corals or thorn corals, are an order of soft deep-water corals. These corals can be recognized by their jet-black or dark brown chitin skeletons, surrounded by the polyps. Antipatharians are a cosmopolitan order, existing at nearly every location and depth, with the sole exception of brackish waters. However, they are most frequently found on continental slopes under 50 m (164 ft) deep. A black coral reproduces both sexually and asexually throughout its lifetime. Many black corals provide housing, shelter, food, and protection for other animals.
 W
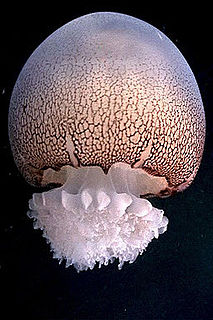
WCyanea lamarckii, also known as the blue jellyfish or bluefire jellyfish, is a species of jellyfish in the family Cyaneidae.
 W
WThe cannonball jellyfish, also known as the cabbagehead jellyfish, is a species of jellyfish in the family Stomolophidae. Its common name derives from its similarity to a cannonball in shape and size. Its dome-shaped bell can reach 25 cm (10 in) in diameter and, in the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico, the rim is sometimes colored with brown pigment. In the Pacific, this jellyfish can also have a blue pigment. Underneath the body is a cluster of oral arms that extend out around the mouth. These arms function in propulsion and as an aid in catching prey. Cannonballs are prominent from North America's eastern seaboard all the way to Brazil, but are also found in parts of the Pacific.
 W
WCassiopea xamachana, commonly known as the upside-down jellyfish, is a species of jellyfish in the family Cassiopeidae. It is found in warm parts of the western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico. It was first described by the American marine biologist Henry Bryant Bigelow in 1892.
 W
WCereus pedunculatus or the daisy anemone is a species of sea anemone in the family Sagartiidae. It is found in shallow parts of the northeast Atlantic Ocean and in the North Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. It is an omnivore, predator and scavenger.
 W
WChiropsalmus quadrumanus, commonly known as the four-handed box jellyfish, is a species of box jellyfish found in the western Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. The sting is venomous and dangerous to humans, especially children.
 W
WClytia hemisphaerica is a small hydrozoan-group cnidarian, about 1 cm in diameter, that is found in the Mediterranean Sea and the North-East Atlantic Ocean. Clytia has the free-swimming jellyfish form typical of the Hydrozoa, as well as vegetatively propagating polyps.
 W
WCorynactis annulata, or the strawberry anemone, is a bright pink colonial anthozoan similar in body form to sea anemones and scleractinian stony corals. This species is a solitary animal of the order Corallimorpharia.
 W
WCorynactis viridis, the jewel anemone, is a brightly coloured anthozoan similar in body form to a sea anemone or a scleractinian coral polyp, but in the order Corallimorpharia. It is found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea and was first described by the Irish naturalist George Allman in 1846.
 W
WCotylorhiza tuberculata is a species of jellyfish, of the phylum Cnidaria, also known as the Mediterranean jellyfish, Mediterranean jelly or fried egg jellyfish. It is commonly found in the Mediterranean Sea, Aegean Sea, and Adriatic Sea.
 W
WThe dahlia anemone is a sea anemone found in the north Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Its colour is variable, from deep red to brown or purplish, with green spots and darker tentacles. Dahlia anemones live attached to rock on the seabed from the lower tidal limit down to a depth of 100 m and also attached to other organisms. Their diet comprises small fish and crustaceans, which they immobilize by firing groups of stinging cells (cnidae) into them. Dahlia anemones are closely related to mottled anemones, and both species are usually referred to as northern red anemones.
 W
WDiadumene cincta is a small and delicate, usually orange, sea anemone. It has a smooth slender column and up to 200 long tentacles, and normally grows to a length of up to 35 mm (1.4 in), with a base of 10 mm (0.4 in), but specimens twice this size have been recorded. Diadumene cincta is found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean.
 W
WEdwardsia claparedii is a species of sea anemone in the family Edwardsiidae.
 W
WIvell's sea anemone is a species of sea anemone in the family Edwardsiidae. It is endemic to a single location, Widewater Lagoon in West Sussex, England, where it was first discovered by Richard Ivell. It has been listed as Data Deficient by the IUCN since 1996.
 W
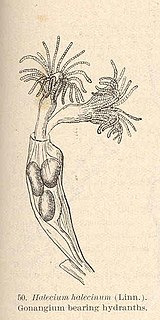
WHalecium halecinum, commonly known as the herring-bone hydroid, is a species of hydrozoan in the family Haleciidae. It is native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean, the western Atlantic Ocean and the eastern Pacific Ocean.
 W
WIsophyllia sinuosa, the sinuous cactus coral, is a species of stony coral in the family Mussidae. It is found in shallow water in the tropical western Atlantic and the Caribbean Sea.
 W
WIvell's sea anemone is a species of sea anemone in the family Edwardsiidae. It is endemic to a single location, Widewater Lagoon in West Sussex, England, where it was first discovered by Richard Ivell. It has been listed as Data Deficient by the IUCN since 1996.
 W
WLebrunia neglecta is a species of sea anemone in the family Aliciidae. It is found in the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico.
 W
WThe lion's mane jellyfish, also known as the giant jellyfish, arctic red jellyfish, or the hair jelly, is one of the largest known species of jellyfish. Its range is confined to cold, boreal waters of the Arctic, northern Atlantic, and northern Pacific Oceans. It is common in the English Channel, Irish Sea, North Sea, and in western Scandinavian waters south to Kattegat and Øresund. It may also drift into the southwestern part of the Baltic Sea. Similar jellyfish – which may be the same species – are known to inhabit seas near Australia and New Zealand. The largest recorded specimen was measured by Alexander Agassiz off the coast of Massachusetts in 1865 and had a bell with a diameter of 210 centimetres and tentacles around 36.6 m (120 ft) long. Lion's mane jellyfish have been observed below 42°N latitude for some time in the larger bays of the east coast of the United States.
 W
WMesacmaea mitchellii is a species of sea anemone in the family Haloclavidae. It is found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea where it burrows in soft sediment.
 W
WMetridium dianthus is a species of sea anemone in the family Metridiidae. It is found in the northern Atlantic Ocean and in the northeast Pacific Ocean. There is also a record from South Africa, possible resulting from an introduction.
 W
WMillepora alcicornis, or sea ginger, is a species of colonial fire coral with a calcareous skeleton. It is found on shallow water coral reefs in the tropical west Atlantic Ocean. It shows a variety of different morphologies depending on its location. It feeds on plankton and derives part of its energy requirements from microalgae found within its tissues. It is an important member of the reef building community and subject to the same threats as other corals. It can cause painful stings to unwary divers.
 W
WParamuricea clavata, the violescent sea-whip, is a species of colonial soft coral in the family Plexauridae. It is found in shallow seas of the north-eastern Atlantic Ocean and the north-western Mediterranean Sea as well as Ionian Sea. This species was first described by the French naturalist Antoine Risso in 1826.
 W
WParanthus rapiformis, the onion anemone, is a species of sea anemone in the family Actinostolidae. It was first described by the French naturalist Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1817 and is native to the northwestern Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.
 W
WPlumapathes is a genus of black coral in the order Antipatharia.
 W
WPlumapathes pennacea is a species of black coral in the order Antipatharia. It is found in the tropical Indian, Pacific and Atlantic Oceans in deep reef habitats where it forms part of a biologically diverse community.
 W
WPorites astreoides, commonly known as mustard hill coral or yellow porites, is a colonial species of stony coral in the family Poritidae.
 W
WPorites furcata, commonly known as hump coral, thin finger coral or branched finger coral, is a species of stony coral in the genus Porites. It is found in the Caribbean Sea and western Atlantic Ocean.
 W
WPorites porites, commonly known as hump coral or finger coral, is a species of stony coral in the genus Porites. It is found in the Caribbean Sea and western Atlantic Ocean and also along the coast of West Africa.
 W
WThe Portuguese man o' war, also known as the man-of-war, bluebottle, or floating terror is a marine hydrozoan found in the Atlantic Ocean and Indian Oceans. It is considered to be the same species as the Pacific man o' war, which is found mainly in the Pacific Ocean.
 W
WThe Praya dubia, or giant siphonophore, is an invertebrate which lives in the deep sea at 700 m (2,300 ft) to 1,000 m (3,300 ft) below sea level. It has been found off the coasts around the world, from Iceland in the North Atlantic, to Chile in the South Pacific.
 W
WSagartia elegans, the elegant anemone, is a species of sea anemone in the family Sagartiidae. It is found in coastal areas of northwest Europe at depths down to 50 metres.
 W
WSagartia ichthystoma is a species of sea anemone in the family Sagartiidae, also known as the fish-mouth anemone. The species name refers to the short pointed tentacles round the edge of the disc which resemble the sharp teeth of certain fish.
 W
WSagartia troglodytes is a species of sea anemone in the family Sagartiidae, also known as the mud sagartia or the cave-dwelling anemone.
 W
WSavalia savaglia, commonly known as gold coral, is a species of colonial false black coral in the family Parazoanthidae. It is native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea where it often grows in association with a gorgonian. It is extremely long-lived, with a lifespan of 2,700 years, and develops into a large tree-like colony.
 W
WThe snakelocks anemone is a sea anemone found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. The latter population is however sometimes considered a separate species, the Mediterranean snakelocks anemone.
 W
WSolenosmilia variabilis is a species of colonial coral in the family Caryophylliidae. It is a deep water, azooxanthellate coral with a semi-cosmopolitan distribution.
 W
WThe starlet sea anemone is a species of small sea anemone in the family Edwardsiidae native to the east coast of the United States, with introduced populations along the coast of southeast England and the west coast of the United States. Populations have also been located in Nova Scotia, Canada. This sea anemone is found in the shallow brackish water of coastal lagoons and salt marshes where its slender column is usually buried in the mud and its tentacles exposed. Its genome has been sequenced and it is cultivated in the laboratory as a model organism, but the IUCN has listed it as being a "Vulnerable species" in the wild.
 W
WStomphia coccinea is a small reddish, orange or brownish sea anemone in the family Actinostolidae from the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic Ocean. It can swim away when necessary in order to escape a predator.