 W
WThe anterior cervical lymph nodes are a group of nodes found on the anterior part of the neck, in front of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. These can be grouped into a deep and superficial group.
 W
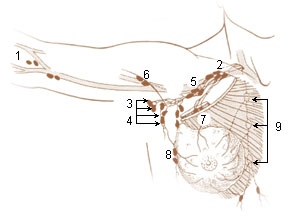
WAn apical group of six to twelve glands is situated partly posterior to the upper portion of the Pectoralis minor and partly above the upper border of this muscle.
 W
WThe efferent vessels of the tracheobronchial lymph nodes ascend upon the trachea and unite with efferents of the internal mammary and anterior mediastinal glands to form the right and left bronchomediastinal trunks.
 W
WThe buccinator lymph node or nodes are one or more lymph nodes placed on the Buccinator opposite the angle of the mouth.
 W
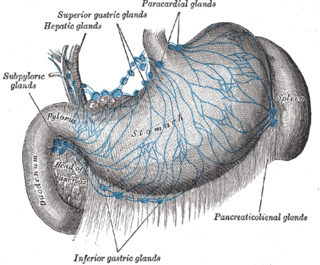
WThe celiac lymph nodes are associated with the branches of the celiac artery. Other lymph nodes in the abdomen are associated with the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries. The celiac lymph nodes are grouped into three sets: the gastric, hepatic and splenic lymph nodes.
 W
WA central or intermediate group of three or four large glands is imbedded in the adipose tissue near the base of the axilla.
 W
WA centrocyte generally refers to a B cell with a cleaved nucleus, as may appear in e.g. follicular lymphoma.
 W
WThe common iliac lymph nodes, four to six in number, are grouped behind and on the sides of the common iliac artery, one or two being placed below the bifurcation of the aorta, in front of the fifth lumbar vertebra.
 W
WThe deep anterior cervical lymph nodes are found near the middle cricothyroid ligament and the trachea.
 W
WThe deep lateral cervical lymph nodes are found near the upper part of the internal jugular vein in the neck, lateral or posterior to the carotid sheath.
 W
WThe deep parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found below the parotid gland.
 W
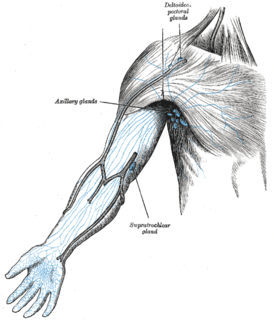
WOne or two deltopectoral lymph nodes are found beside the cephalic vein, between the pectoralis major and deltoideus, immediately below the clavicle.
 W
WThe external iliac lymph nodes are lymph nodes, from eight to ten in number, that lie along the external iliac vessels.
 W
WThe inferior deep cervical lymph nodes extend beyond the posterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid muscle into the subclavian triangle, where they are closely related to the brachial plexus and subclavian vein.
 W
WThe infra-auricular deep parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found underneath the ear.
 W
WThe Intraglandular deep parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found inside the parotid gland.
 W
WThe jugular trunk is a lymphatic vessel in the neck. It is formed by vessels that emerge from the superior deep cervical lymph nodes and unite to efferents of the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes.
 W
WThe juguloomohyoid lymph node is related to the intermediate tendon of the omohyoid muscle. It is designated as one of the deep cervical lymph nodes. As it is associated with the lymph drainage of the tongue if enlarged, it can be a sign of a tongue carcinoma.
 W
WThe jugulodigastric lymph nodes are large lymph nodes of the neck.
 W
WThe lateral cervical lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found in the lateral side of the neck.
 W
WThe lumbar trunks are formed by the union of the efferent vessels from the lateral aortic lymph nodes.
 W
WA lymph duct is a great lymphatic vessel that empties lymph into one of the subclavian veins. There are two lymph ducts in the body—the right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct. The right lymphatic duct drains lymph from the right upper limb, right side of thorax and right halves of head and neck. The thoracic duct drains lymph into the circulatory system at the left brachiocephalic vein between the left subclavian and left internal jugular veins.
 W
WThe mandibular lymph node is a lymph node found near the jaw.
 W
WThe mastoid lymph nodes are a small group of lymph nodes, usually two in number, located just beneath the ear, on the mastoid insertion of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, beneath the posterior auricular muscle.
 W
WThe nasolabial lymph node is a facial node found near the nose and upper lip.
 W
WThe occipital lymph nodes, one to three in number, are located on the back of the head close to the margin of the trapezius and resting on the insertion of the semispinalis capitis.
 W
WThe pararectal lymph nodes are in contact with the muscular coat of the rectum. They drain the descending iliac and sigmoid parts of the colon and the upper part of the rectum; their efferents pass to the preaortic glands.
 W
WThe parasternal lymph nodes are placed at the anterior ends of the intercostal spaces, by the side of the internal thoracic artery.
 W
WThe right and left paratracheal lymph nodes are groups of lymph nodes located in the throat.
 W
WParotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found near the parotid gland in the immune system.
 W
WAn anterior or pectoral group consists of four or five glands along the lower border of the Pectoralis minor, in relation with the lateral thoracic artery.
 W
WThe preaortic lymph nodes lie in front of the aorta, and may be divided into celiac lymph nodes, superior mesenteric lymph nodes, and inferior mesenteric lymph nodes groups, arranged around the origins of the corresponding arteries.
 W
WThe preauricular deep parotid lymph nodes, from one to three in number, lie immediately in front of the tragus.
 W
WPrelaryngeal lymph nodes are lymph nodes located anterior to the larynx.
 W
WThe pretracheal lymph nodes are lymph nodes located anterior to the trachea.
 W
WThe retroaortic lymph nodes are placed below the cisterna chyli, on the bodies of the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae.
 W
WThe sacral lymph nodes are placed in the concavity of the sacrum, in relation to the middle and lateral sacral arteries; they receive lymphatics from the rectum and posterior wall of the pelvis.
 W
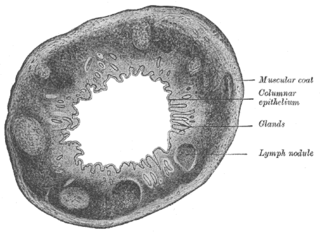
WThe Solitary lymphatic nodules are structures found in the small intestine and large intestine.
 W
WThe splenic lymph nodes are found at the splenic hilum and in relation to the tail of the pancreas.
 W
WThe efferent vessels of the subclavicular group unite to form the subclavian trunk, which opens either directly into the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins or into the jugular lymphatic trunk; on the left side it may end in the thoracic duct.
 W
WThe submandibular lymph nodes, three to six in number, are lymph nodes beneath the body of the mandible in the submandibular triangle, and rest on the superficial surface of the submandibular gland.
 W
WThe submental glands are situated between the anterior bellies of the digastric muscle and the hyoid bone.
 W
WA posterior or subscapular group of six or seven glands is placed along the lower margin of the posterior wall of the axilla in the course of the subscapular artery.
 W
WThe superficial anterior cervical lymph nodes are found in proximity to the anterior jugular vein.
 W
WThe superficial cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes that lie near the surface of the neck.
 W
WThe superficial lateral cervical lymph nodes are found along the course of the external jugular vein, between the inferior aspect of the parotid gland and the supraclavicular nodes. The nodes are intercalated along the course of the vessels draining the parotid nodes and the infraauricular nodes. These nodes drain into the supraclavicular nodes, and on to the jugular trunk, followed by the thoracic duct on the left or the right lymphatic duct.
 W
WThe superficial parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes anterior to the ear.
 W
WThe superior deep cervical lymph nodes lie under the sternocleidomastoid muscle in close relation with the accessory nerve and the internal jugular vein.
 W
WThe superior mesenteric lymph nodes may be divided into three principal groups:mesenteric lymph nodes ileocolic lymph nodes mesocolic lymph nodes
 W
WOne or two supratrochlear lymph nodes are placed above the medial epicondyle of the humerus, medial to the basilic vein.
 W
WThe lymph glands of the thorax may be divided into parietal and visceral — the former being situated in the thoracic wall, the latter in relation to the viscera.
 W
WThe thyroid lymph nodes are deep anterior cervical lymph nodes found near the thyroid gland on the neck.
 W
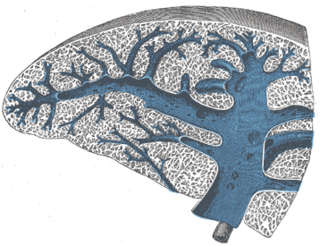
WThe fibroelastic coat of the spleen invests the organ, and at the hilum is reflected inward upon the vessels in the form of sheaths. From these sheaths, as well as from the inner surface of the fibroelastic coat, numerous small fibrous bands, the trabeculae of the spleen, emerge from all directions; these uniting, constitute the frame-work of the spleen.
 W
WThe tracheobronchial lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are located around the division of trachea and main bronchi.
 W
WWhite pulp is a histological designation for regions of the spleen, that encompasses approximately 25% of splenic tissue. White pulp consists entirely of lymphoid tissue.