 W
WIn human anatomy, the accessory obturator nerve is an accessory nerve in the lumbar region present in about 29% of cases.
 W
WThe anococcygeal nerve is a nerve in the pelvis which provides sensory innervation to the skin over the coccyx.
 W
WThe anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve consist of the following nerves: intermediate cutaneous nerve and medial cutaneous nerve.
 W
WThe anterior scrotal nerves are branches of the ilioinguinal nerve. The nerves innervates the scrotum in males. The equivalent nerves in the female are the anterior labial nerves.
 W
WThe coccygeal plexus is a plexus of nerves near the coccyx bone.
 W
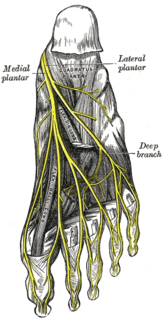
WThe common plantar digital nerves of lateral plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. The common digital nerve communicates with the third common digital branch of the medial plantar nerve and divides into two proper digital nerves which supply the adjoining sides of the fourth and fifth toes.
 W
WThe common plantar digital nerves of medial plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. The three common digital nerves pass between the divisions of the plantar aponeurosis, and each splits into two proper digital nerves:Those of the first common digital nerve supply the adjacent sides of the great and second toes; Those of the second, the adjacent sides of the second and third toes; and those of the third, the adjacent sides of the third and fourth toes. The third common digital nerve receives a communicating branch from the lateral plantar nerve; the first gives a twig to the first Lumbricalis.
 W
WThe deep branch of lateral plantar nerve accompanies the lateral plantar artery on the deep surface of the tendons of the Flexor muscles and the Adductor hallucis, and supplies all the Interossei, the second, third, and fourth Lumbricales.
 W
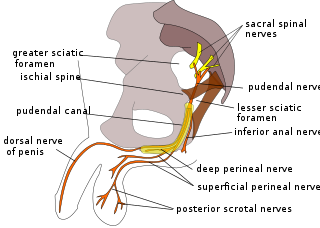
WThe deep branch of the perineal nerve are distributed to the muscles of the perineum. These include the superficial transverse perineal muscle, bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus, and Sphincter urethræ.
 W
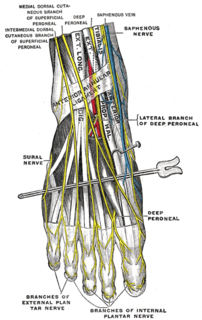
WThe deep peroneal nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common peroneal nerve between the fibula and upper part of the peroneus longus, passes infero-medially, deep to extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.
 W
WDorsal digital nerves of foot are branches of the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, sural nerve and deep fibular nerve. There are 10 total dorsal digital branches.
 W
WThe dorsal nerve of the clitoris is a nerve in females that branches off the pudendal nerve to innervate the clitoris.
 W
WThe dorsal nerve of the penis is the deepest division of the pudendal nerve; it accompanies the internal pudendal artery along the ramus of the ischium; it then runs forward along the margin of the inferior ramus of the pubis, between the superior and inferior layers of the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm.
 W
WThe femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee.
 W
WThe genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, also known as the external spermatic nerve in males, is a nerve in the abdomen that arises from the genitofemoral nerve. The genital branch supplies the cremaster muscle and anterior scrotal skin in males, and the skin of the mons pubis and labia majora in females.
 W
WThe genitofemoral nerve refers to a nerve that is found in the abdomen. Its branches, the genital branch and femoral branch supply sensation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. The femoral branch is different from the femoral nerve, which also arises from the lumbar plexus.
 W
WThe iliohypogastric nerve is a nerve that originates from the lumbar plexus that supplies sensation to skin over the lateral gluteal and hypogastric regions and motor to the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles.
 W
WThe ilioinguinal nerve is a branch of the first lumbar nerve (L1). It separates from the first lumbar nerve along with the larger iliohypogastric nerve. It emerges from the lateral border of the psoas major just inferior to the iliohypogastric, and passes obliquely across the quadratus lumborum and iliacus. The ilioinguinal nerve then perforates the transversus abdominis near the anterior part of the iliac crest, and communicates with the iliohypogastric nerve between the transversus and the internal oblique muscle.
 W
WThe Inferior rectal nerves usually branch from the pudendal nerve but occasionally arises directly from the sacral plexus; they cross the ischiorectal fossa along with the inferior rectal artery and veins, toward the anal canal and the lower end of the rectum, and is distributed to the Sphincter ani externus and to the integument (skin) around the anus.
 W
WThe inferior clunial nerves innervate the skin of the lower part of the buttocks. They arise as branches of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh.
 W
WThe inferior gluteal nerve is the main motor neuron that innervates the gluteus maximus muscle. It is responsible for the movement of the gluteus maximus in activities requiring the hip to extend the thigh, such as climbing stairs. Injury to this nerve is rare but often occurs as a complication of posterior approach to the hip during hip replacement. When damaged, one would develop gluteus maximus lurch, which is a gait abnormality which causes the individual to 'lurch' backwards to compensate lack in hip extension.
 W
WThe infrapatellar branch of saphenous nerve is a nerve of the lower limb.
 W
WThe intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, the smaller, passes along the lateral part of the dorsum of the foot, and divides into dorsal digital branches, which supply the contiguous sides of the third and fourth, and of the fourth and fifth toes.
 W
WThe lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a cutaneous nerve that innervates the skin on the lateral part of the thigh.
 W
WThe lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve is a cutaneous branch of the foot. This is a separate branch from the Lateral sural cutaneous nerve which is located on the back of the leg. This turns into a dorsal digital nerve and supplies the lateral side of the fifth toe. The course of this nerve influences the surgical approach to fixation of fractures of the fifth metatarsal, as the most direct surgical approach is at risk of damaging it.
 W
WThe lateral plantar nerve is a branch of the tibial nerve, in turn a branch of the sciatic nerve and supplies the skin of the fifth toe and lateral half of the fourth, as well as most of the deep muscles, its distribution being similar to that of the ulnar nerve in the hand.
 W
WThe lateral sural cutaneous nerve supplies the skin on the posterior and lateral surfaces of the leg. The lateral sural cutaneous nerve originates from the common peroneal nerve.
 W
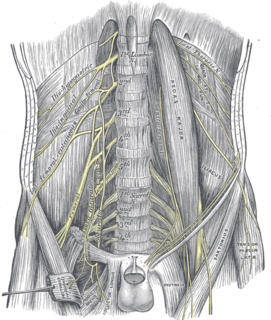
WThe lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.
 W
WThe lumboinguinal nerve, also known as the femoral or crural branch of genitofemoral, is a nerve in the abdomen. The lumboinguinal nerve is a branch of the genitofemoral nerve. The "femoral" part supplies skin to the femoral triangle area.
 W
WThe anterior divisions of the lumbar nerves, sacral nerves, and coccygeal nerve form the lumbosacral plexus, the first lumbar nerve being frequently joined by a branch from the twelfth thoracic. For descriptive purposes this plexus is usually divided into three parts:lumbar plexus sacral plexus pudendal plexus
 W
WThe medial calcaneal branches of the tibial nerve perforate the laciniate ligament, and supply the skin of the heel and medial side of the sole of the foot.
 W
WThe medial crural cutaneous branches of saphenous nerve provide cutaneous innervation to the medial leg.
 W
WThe medial dorsal cutaneous nerve passes in front of the ankle-joint, and divides into two dorsal digital branches, one of which supplies the medial side of the great toe, the other, the adjacent side of the second and third toes.
 W
WThe medial plantar nerve is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve, which accompanies the medial plantar artery.
 W
WThe medial sural cutaneous nerve originates from the tibial nerve of the sciatic, descends between the two heads of the Gastrocnemius, and, about the middle of the back of the leg, pierces the deep fascia, and unites with the anastomotic ramus of the common peroneal to form the sural nerve.
 W
WCutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific nerve.
 W
WThe nerve to quadratus femoris is a nerve that provides innervation to the quadratus femoris and gemellus inferior muscles.
 W
WThe nerve to obturator internus is a nerve that innervates the obturator internus and gemellus superior muscles.
 W
WThe obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.
 W
WIt is a plexus of fine nerves situated in front of the patella, the ligamentum patellae and the upper end of the tibia. It is formed by contribution from the following:
 W
WThe perforating cutaneous nerve is a cutaneous nerve that supplies skin over the gluteus maximus muscle.
 W
WThe perineal branches of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve are distributed to the skin at the upper and medial side of the thigh.
 W
WThe perineal nerve is a nerve arising from the pudendal nerve that supplies the perineum.
 W
WThe nerve to piriformis is the peripheral nerve that innervates the piriformis muscle.
 W
WThe posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh provides innervation to the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh and leg, as well as to the skin of the perineum.
 W
WThe posterior scrotal branches or posterior labial branches are two in number, medial and lateral. They are branches of the perineal nerve, which is itself a branch of the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve arises from spinal roots S2 through S4, travels through the pudendal canal on the fascia of the obturator internus muscle, and gives off the perineal nerve in the perineum. The major branch of the perineal nerve is the posterior scrotal/posterior labial.
 W
WThe proper plantar digital nerves of lateral plantar nerve are nerves of the foot that arise from the superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve. The superficial branch splits into a proper digital nerve and a common digital nerve:the proper digital nerve supplies the lateral side of the little toe, the common digital nerve communicates with the third common digital branch of the medial plantar nerve to help supply the adjacent sides of the third and fourth digits, and divides into two proper digital nerves which supply the adjoining sides of the fourth and fifth toes.
 W
WThe proper plantar digital nerves of medial plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. They primarily arise from the medial plantar nerve's superficial and deep branches. The superficial branch of the medial plantar nerve turns into a proper digital nerve and is responsible for supplies the medial side of the great toe.
 W
WThe pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, lesions may cause sensory loss or fecal incontinence. The nerve may be temporarily blocked as part of an anaesthetic procedure.
 W
WIn human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar vertebrae and sacral vertebrae (L4-S4). A sacral plexopathy is a disorder affecting the nerves of the sacral plexus, usually caused by trauma, nerve compression, vascular disease, or infection. Symptoms may include pain, loss of motor control, and sensory deficits.
 W
WThe sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.
 W
WThe superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into a proper and a common plantar digital nerve:the lateral proper plantar digital nerve supplies the lateral side of the 5th digit and a branch for innervation of the Flexor digiti quinti brevis the 4th common plantar digital nerve communicates with the third common plantar digital branch of the medial plantar nerve and divides into two proper digital nerves, which supply the adjoining sides of the fourth and fifth toes. The 4th common plantar digital nerve also has a branch that supplies the interosseus muscles of the 4th intermetatarsal space.
 W
WThe superficial peroneal nerve innervates the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis muscles and the skin over the antero-lateral aspect of the leg along with the greater part of the dorsum of the foot.
 W
WThe superior gluteal nerve is a nerve that originates in the pelvis and supplies the gluteus medius, the gluteus minimus, the tensor fasciae latae and the piriformis muscles.
 W
WThe tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.