 W
WWarder Clyde Allee was an American ecologist. He is recognized to be one of the great pioneers of American ecology. As an accomplished zoologist and ecologist, Allee was best known and recognized for his research on social behavior, aggregations and distributions of animals in aquatic as well as terrestrial environments. Allee attended Earlham College and upon his graduation in 1908, pursued advanced studies at the University of Chicago where he received his PhD and graduated summa cum laude in 1912. Allee’s most significant research occurred during his time at the University of Chicago and at the Marine Biological Laboratory at Woods Hole in Massachusetts. His research findings led to many publications, with the most notable being Principles of Animal Ecology and Animal Aggregations. Allee was married to author Marjorie Hill Allee and remained active in the field of biology until his death in 1955 at the age of 70.
 W
WSir (Paul) Patrick (Gordon) Bateson, was an English biologist with interests in ethology and phenotypic plasticity. Bateson was a Professor at the University of Cambridge and served as president of the Zoological Society of London from 2004 to 2014.
 W
WMarc Bekoff is an American biologist, ethologist, behavioural ecologist and writer. He is Professor Emeritus of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of Colorado, Boulder.
 W
WDaniel T. Blumstein is an ethologist and conservation biologist. He is professor at the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, as well as a professor for the Institute of the Environment and Sustainability, at the University of California, Los Angeles. He has authored or co-authored over 300 articles in peer-reviewed scientific journals. Furthermore, he authored the book The Failure of Environmental Education with Charles Saylan, which was featured in the 2011 "Summer Reading: 7 Education Books to Take to the Beach" in Time Magazine. Because of his work in conservation and education, he was invited to join the panel at the first ever United States White House conference on environmental education.
 W
WJohn Bumpass Calhoun was an American ethologist and behavioral researcher noted for his studies of population density and its effects on behavior. He claimed that the bleak effects of overpopulation on rodents were a grim model for the future of the human race. During his studies, Calhoun coined the term "behavioral sink" to describe aberrant behaviors in overcrowded population density situations and "beautiful ones" to describe passive individuals who withdrew from all social interaction. His work gained world recognition. He spoke at conferences around the world and his opinion was sought by groups as diverse as NASA and the District of Columbia's Panel on overcrowding in local jails. Calhoun's rat studies were used as a basis in the development of Edward T. Hall's 1966 proxemics theories.
 W
WMaroli Krishnayya Chandrashekaran, also known as Shekar or MKC, was an Indian zoologist, regarded as the founder of Indian chronobiology, the study of biological rhythms of organisms. He was a fellow of the Indian Academy of Sciences, and the Third World Academy of Sciences, and in 1979 received the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology. Born in Salem, Tamil Nadu, Chandrashekaran earned bachelor's and master's degrees in zoology at Presidency College, Chennai, and a PhD at the University of Madras. He served as editor of the Journal of Biosciences from 1991 to 1997 and Resonance: Journal of Science Education from 2003 to 2005.
 W
WJohn Hurrell Crook was a British ethologist who filled a pivotal role in British primatology.
 W
WWim E. Crusio is a Dutch behavioral neurogeneticist and a directeur de recherche with the French National Centre for Scientific Research in Talence, France.
 W
WBoris Cyrulnik is a French doctor, ethologist, neurologist, and psychiatrist.
 W
WCharles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist and biologist, best known for his contributions to the science of evolution. His proposition that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestors is now widely accepted, and considered a foundational concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history, and he was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey.
 W
WMarian Stamp Dawkins is a British biologist and professor of ethology at the University of Oxford. Her research interests include vision in birds, animal signalling, behavioural synchrony, animal consciousness and animal welfare.
 W
WRichard Dawkins is a British ethologist, evolutionary biologist, and author. He is an emeritus fellow of New College, Oxford, and was the University of Oxford's Professor for Public Understanding of Science from 1995 until 2008.
 W
WVladimir Dinets is a zoologist and author, known for his studies of Crocodilian behavior and of numerous rare animals in remote parts of the world, as well as for popular writings in Russian and English.
 W
WIrenäus Eibl-Eibesfeldt was an Austrian ethnologist in the field of human ethology. In authoring the book which bears that title, he applied ethology to humans by studying them in a perspective more common to volumes studying animal behavior.
 W
WDian Fossey was an American primatologist and conservationist known for undertaking an extensive study of mountain gorilla groups from 1966 until her 1985 murder. She studied them daily in the mountain forests of Rwanda, initially encouraged to work there by paleoanthropologist Louis Leakey. Gorillas in the Mist, a book published two years before her death, is Fossey's account of her scientific study of the gorillas at Karisoke Research Center and prior career. It was adapted into a 1988 film of the same name.
 W
WKarl Ritter von Frisch, was a German-Austrian ethologist who received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1973, along with Nikolaas Tinbergen and Konrad Lorenz.
 W
WBirutė Marija Filomena Galdikas, OC, is a Lithuanian-Canadian anthropologist, primatologist, conservationist, ethologist, and author. She is a Professor at Simon Fraser University. In the field of primatology, Galdikas is recognized as a leading authority on orangutans. Prior to her field study of orangutans, scientists knew little about the species.
 W
WDame Jane Morris Goodall, formerly Baroness Jane van Lawick-Goodall, is an English primatologist and anthropologist. Considered to be the world's foremost expert on chimpanzees, Goodall is best known for her 60-year study of social and family interactions of wild chimpanzees since she first went to Gombe Stream National Park in Tanzania in 1960.
 W
WMary Temple Grandin is a prominent proponent for the humane treatment of livestock for slaughter and author of more than 60 scientific papers on animal behavior. She is a consultant to the livestock industry on animal behavior, and an autism spokesperson. She is one of the first individuals on the autism spectrum to document the insights she gained from her personal experience of autism. She is currently a faculty member with Animal Sciences in the College of Agricultural Sciences at Colorado State University.
 W
WJudith L. Hand is an American evolutionary biologist, animal behaviorist (ethologist) and a novelist. She writes on a variety of topics related to the science of animal and human behavior, including the biological and evolutionary roots of war, gender differences in conflict resolution, the empowerment of women, and the steps for ending war.
 W
WMaarten 't Hart is a Dutch writer. Trained as a biologist in zoology and ethology at the University of Leiden, he taught that subject before becoming a full-time writer in the 1980s, having made his debut as a novelist in 1971 under the name Martin Hart with Stenen voor een ransuil.
 W
WOskar Heinroth was a German biologist who was one of the first to apply the methods of comparative morphology to animal behavior, and was thus one of the founders of ethology. He worked, largely isolated from most other scientists of the period, at the Berlin Aquarium where he took care of fishes, reptiles and birds, especially waterfowl.
 W
WBernard Hollander was a London psychiatrist and one of the main proponents of the new interest in phrenology in the early 20th century.
 W
WSir Julian Sorell Huxley was an English evolutionary biologist, eugenicist, and internationalist. He was a proponent of natural selection, and a leading figure in the mid-twentieth century modern synthesis. He was secretary of the Zoological Society of London (1935–1942), the first Director of UNESCO, a founding member of the World Wildlife Fund and the first President of the British Humanist Association.
 W
WWilliam Tinsley Keeton was an American zoologist known internationally for his work on animal behavior, especially bird migration, and for his work on millipede taxonomy. He was a well-liked professor of biology at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York and author of a widely used introductory textbook, Biological Science.
 W
WProf. Dr. Adriaan Kortlandt was a Dutch ethologist.
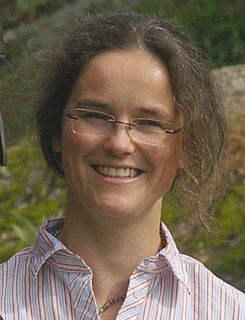 W
WKonstanze Krüger is a German zoologist and behaviour researcher. She is Professor of Horse Management at Nürtingen-Geislingen University of Applied Science, and her special field of research is the social system of horses.
 W
WEniko Kubinyi is a Hungarian biologist. She completed her Ph.D. degree in animal behaviour from the Eotvos Lorand University, where she is the principal investigator of the Senior Family Dog Project and the Canine Brain and Tissue Bank.
 W
WRonald Douglas Lawrence was a Canadian naturalist and wildlife author. He was an expert on the wildlife of Canada, on which he wrote more than thirty books, which have been published in 14 languages.
 W
WKonrad Zacharias Lorenz was an Austrian zoologist, ethologist, and ornithologist. He shared the 1973 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Nikolaas Tinbergen and Karl von Frisch. He is often regarded as one of the founders of modern ethology, the study of animal behavior. He developed an approach that began with an earlier generation, including his teacher Oskar Heinroth.
 W
WÁdám Miklósi is a Hungarian ethologist, expert on dog cognition and behavior. He holds the position of professor and the head of the Ethology Department at the Eötvös Loránd University in Budapest, Hungary. In 2016 he was elected as a corresponding member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. He is the co-founder and leader of the Family Dog Project, which aims to study human-dog interaction from an ethological perspective. In 2014 he published the 2nd edition of an academic volume entitled Dog Behaviour, Evolution, and Cognition by Oxford University Press
 W
WConwy Lloyd Morgan, FRS was a British ethologist and psychologist. He is remembered for his theory of emergent evolution, and for the experimental approach to animal psychology now known as Morgan's Canon, a principle that played a major role in behaviourism, insisting that higher mental faculties should only be considered as explanations if lower faculties could not explain a behaviour.
 W
WDesmond John Morris FLS hon. caus. is an English zoologist, ethologist and surrealist painter, as well as a popular author in human sociobiology. He is known for his 1967 book The Naked Ape, and for his television programmes such as Zoo Time.
 W
WMartin Humphrey Moynihan was a behavioral evolutionary biologist and ornithologist who studied under Ernst Mayr and Niko Tinbergen, and was a contemporary of Desmond Morris. He was the founding director of the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) in Panama.
 W
WDonald H. Owings was a professor of psychology and faculty member of the Animal Behavior Graduate Group at the University of California, Davis. His research focused on ground squirrels, in particular, their interactions with predators such as rattlesnakes; and, more generally, on concepts of communication within and between species. In 1994, he was elected as a fellow of the animal behavior society and in 2010 he received the Exemplar Award for mentoring graduate students.
 W
WRobert E. Page Jr. is one of the foremost honey bee geneticists in the world and a Foundation Chair of Life Sciences of Arizona State University. An author of more than 250 research papers and articles, his work on the self-organizing regulatory networks of honey bees has been outlined in his book, "The Spirit of the Hive: The Mechanisms of Social Evolution," published by Harvard University Press in 2013. Page currently holds the titles of Arizona State University Provost Emeritus and Regents Professor Emeritus. He is also Chair and Professor Emeritus at the University of California-Davis and an External Professor at the Santa Fe Institute.
 W
WIvan Petrovich Pavlov was a Russian physiologist known primarily for his work in classical conditioning.
 W
WGeorge Williams Peckham and Elizabeth Maria Gifford Peckham were a married couple who were early American teachers, taxonomists, ethologists, arachnologists, and entomologists, specializing in animal behavior and in the study of jumping spiders and wasps.
 W
WOlwen Anne Elisabeth Rasa is a British Ethologist, who rendered outstanding services to the knowledge of the social behavior of Dwarf mongoose.
 W
WLouis Robinson (1857–1928) was a 19th-century English physician, paediatrician and author. An ardent evolutionist, he helped pioneer modern child medicine during the later Victorian era, writing prolifically in journals on the emerging science of paediatrics. Active in scientific debate, Robinson was critiqued in some parts of the press for his outspoken evolutionary views in the wider debate between scientific theories of human origin and the religious view.
 W
WGeorge John Romanes FRS was a Canadian-Scots evolutionary biologist and physiologist who laid the foundation of what he called comparative psychology, postulating a similarity of cognitive processes and mechanisms between humans and other animals.
 W
WGeorge Beals Schaller is a German-born American mammalogist, biologist, conservationist and author. Schaller is recognized by many as the world's preeminent field biologist, studying wildlife throughout Africa, Asia and South America. Born in Berlin, Schaller grew up in Germany, but moved to Missouri as a teen. He is vice president of Panthera Corporation and serves as chairman of their Cat Advisory Council. Schaller is also a senior conservationist at the Bronx Zoo-based Wildlife Conservation Society.
 W
WMargret Else Schleidt was a German human ethologist. She worked at the Max-Planck-Institut für Verhaltensphysiologie, which has now become the Max-Planck Institute for Ornithology.
 W
WChristopher M. Sherwin was an English veterinary scientist and senior research fellow at the University of Bristol Veterinary School in Lower Langford, Somerset. He specialised in applied ethology, the study of the behaviour of animals in the context of their interactions with humans, and of how to balance the animals' needs with the demands placed on them by humans.
 W
WBurrhus Frederic Skinner was an American psychologist, behaviorist, author, inventor, and social philosopher. He was a professor of psychology at Harvard University from 1958 until his retirement in 1974.
 W
WEdward Lee Thorndike was an American psychologist who spent nearly his entire career at Teachers College, Columbia University. His work on comparative psychology and the learning process led to the theory of connectionism and helped lay the scientific foundation for educational psychology. He also worked on solving industrial problems, such as employee exams and testing. He was a member of the board of the Psychological Corporation and served as president of the American Psychological Association in 1912. A Review of General Psychology survey, published in 2002, ranked Thorndike as the ninth-most cited psychologist of the 20th century. Edward Thorndike had a powerful impact on reinforcement theory and behavior analysis, providing the basic framework for empirical laws in behavior psychology with his law of effect. Through his contributions to the behavioral psychology field came his major impacts on education, where the law of effect has great influence in the classroom.
 W
WWilliam Homan Thorpe FRS was Professor of Animal Ethology at the University of Cambridge, and a significant British zoologist, ethologist and ornithologist. Together with Nikolaas Tinbergen, Patrick Bateson and Robert Hinde, Thorpe contributed to the growth and acceptance of behavioural biology in Great Britain.
 W
WNikolaas "Niko" Tinbergen was a Dutch biologist and ornithologist who shared the 1973 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Karl von Frisch and Konrad Lorenz for their discoveries concerning organization and elicitation of individual and social behavior patterns in animals. He is regarded as one of the founders of modern ethology, the study of animal behavior.
 W
WJakob Johann Freiherr von Uexküll was a Baltic German biologist who worked in the fields of muscular physiology, animal behaviour studies, and the cybernetics of life. However, his most notable contribution is the notion of Umwelt, used by semiotician Thomas Sebeok and philosopher Martin Heidegger. His works established biosemiotics as a field of research.
 W
WProf. Zdeněk Veselovský was one of the most important Czech zoologists of the 20th century, founder of Czech ethology, very successful director of the Prague Zoo (1959-1988) and the president of the International Union of Directors of Zoological Gardens (1971-1975)
 W
WFranciscus Bernardus Maria "Frans" de Waal is a Dutch primatologist and ethologist. He is the Charles Howard Candler Professor of Primate Behavior in the Department of Psychology at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, director of the Living Links Center at the Yerkes National Primate Research Center at Emory, and author of numerous books including Chimpanzee Politics (1982) and Our Inner Ape (2005). His research centers on primate social behavior, including conflict resolution, cooperation, inequity aversion, and food-sharing. He is a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences and the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
 W
WLyall Watson was a South African botanist, zoologist, biologist, anthropologist, ethologist, and author of many books, among the most popular of which is the best seller Supernature. Lyall Watson tried to make sense of natural and supernatural phenomena in biological terms. He is credited with coining the "hundredth monkey" effect in his 1979 book, Lifetide; later, in The Whole Earth Review, he conceded this was "a metaphor of my own making".
 W
WWilliam Morton Wheeler was an American entomologist, myrmecologist and Harvard professor.
 W
WWolfgang Wickler is a German zoologist, behavioral researcher and author. He led the ethological department of the Max Planck Institute for Behavioral Physiology from 1974, and he took over as director of the institute in 1975. Even after he was given emeritus status, he remained closely associated to the institute in Seewiesen and ensured its smooth transition under the newly created Max Planck Institute for Ornithology.
 W
WEdward Osborne Wilson, usually cited as E. O. Wilson, is an American biologist, naturalist, and writer. His biological specialty is myrmecology, the study of ants, on which he has been called the world's leading expert.
 W
WBenjamin DeKalbe Wood was an American educator, researcher, and director / professor at Columbia University. He was a pioneer in learning technologies and automated testing methods. Wood is the creator of the multiple choice test, which was the state-of-the-art way of measuring a teacher's understanding of certain subjects that in the long run influenced their salaries. He helped in the design of the multiple choice form of the pencil-in bubbles used in the 20th-century and the scoring machine that automatically read these forms, saving many hours in manual clerk labor. His concepts of intelligence tests were expanded to the accounting fields.