 W
WAmerila astreus is a moth of subfamily Arctiinae described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found from the Oriental region to New Guinea. The species is found in primary and secondary habitats ranging from lowlands to montane regions.
 W
WAmesia sanguiflua is a moth of the family Zygaenidae. It is found in northern India, Myanmar, Indochina, Malay Peninsular, Sumatra, Java, and Taiwan.
 W
WAnisota virginiensis, the pink-striped oakworm moth, is a species of silk moth of the family Saturniidae.
 W
WAntheraea mylitta is a species of moth in the family Saturniidae known commonly as the tasar silkworm and vanya silkworm. It is actually one of a number of tasar silkworms, species that produce Tussar silk, a kind of wild silk that is made from the products of saturniid silkworms instead of the domesticated silkworm. This species is native to India.
 W
WAntheua servula is a species of moth of the family Notodontidae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Madras. It is also found in other parts of India, Sri Lanka and on Sumatra.
 W
WApantesis nais, the Nais tiger moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773.
 W
WAre is a monotypic moth genus in the subfamily Arctiinae erected by Francis Walker in 1855. The type species is Are druryi, which is found on Jamaica. This species was described by Dru Drury in 1773 under the name Phalaena marginata, but this name is preoccupied by Phalaena marginata Linnaeus, 1758 and a new specific epithet, honouring Drury, was assigned in 1986.
 W
WArgyrostrotis anilis, the short-lined chocolate, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in North America from Quebec and Ontario, down through the eastern United States to Florida and Texas. It is listed as a species of special concern in the state of Connecticut.
 W
WAsota speciosa, the specious tiger, formerly Aganais speciosa, is a moth of the subfamily Aganainae, now regarded as being within the family Erebidae. Formerly it was regarded variously as a member of the Arctiidae, the Hypsidae, and subsequently the family Aganaidae, which was formerly regarded as a family by some authorities. The species is found in Sierra Leone, Mozambique, South Africa and Togo.
 W
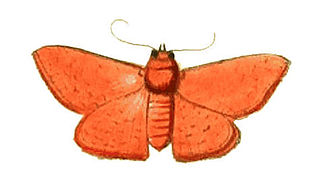
WBanisia myrtaea is a species of moth of the family Thyrididae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Madras.
 W
WThe buck moth is a common insect found in oak forests, stretching in the United States from peninsular Florida to New England, and as far west as Texas and Kansas. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. The larvae typically emerge in a single generation in the spring. The larvae are covered in hollow spines that are attached to a poison sac. The poison can cause symptoms ranging from stinging, itching and burning sensations to nausea. Subspecies Hemileuca maia maia is listed as endangered in the US state of Connecticut.
 W
WCallosamia promethea, commonly known as the promethea silkmoth, is a member of the family Saturniidae, which contains approximately 1,300 species. It is also known as the spicebush silkmoth, which refers to is one of the promethea silkmoth's common host plants, spicebush. C. promethea is classified as a silk moth, which stems from its ability to produce silk, which it does in the formation of its cocoon. C. promethea lives in forests in the eastern U.S. and does not damage the trees on which it lives. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773.
 W
WCastrica phalaenoides is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in Mexico, Guatemala, Panama, Honduras, Costa Rica, Brazil, French Guiana, Peru, Venezuela, Ecuador and Trinidad.
 W
WCatocala epione, the Epione underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in North America from Quebec and Ontario south through Connecticut to Florida and west to Texas and Oklahoma.
 W
WChrysiridia rhipheus, the Madagascan sunset moth, is a species of day-flying moth of the family Uraniidae. It is considered one of the most impressive and appealing-looking lepidopterans. Famous worldwide, it is featured in most coffee table books on Lepidoptera and is much sought after by collectors, though many older sources misspell the species name as "ripheus". It is very colourful, though the iridescent parts of the wings do not have pigment; rather the colours originate from optical interference. Adults have a wingspan of 7–9 cm (2.8–3.5 in).
 W
WCingilia is a monotypic moth genus in the family Geometridae erected by Francis Walker in 1862. Its only species, Cingilia catenaria, the chain-dotted geometer, chain dot geometer, chainspotted geometer or chain-spotted geometer, was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in North America from Nova Scotia south to Maryland and west to Kansas and Alberta.
 W
WCocytius antaeus, the giant sphinx, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773.
 W
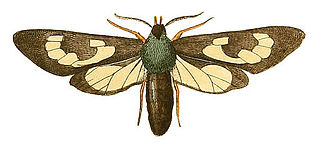
WCosmosoma fenestrata is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found on Jamaica and Cuba.
 W
WCrameria is a monotypic moth genus in the family Noctuidae erected by Jacob Hübner in 1819. Its only species, Crameria amabilis, was first described by Dru Drury in 1773.
 W
WCyana puella is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in the north-western Himalayas, Nepal, India, Sri Lanka, Madagascar, Kenya and Eritrea.
 W
WCyclosia papilionaris, Drury's jewel, is a moth in the family Zygaenidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found from Thailand to southern China. It is also found in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. The habitat consists of rainforests and humid deciduous forests at altitudes up to 1,000 meters.
 W
WCyligramma fluctuosa is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in most parts of Africa, from Sénégal in the West to Kenya in the East, and Egypt in the North to South Africa, including the Indian Ocean islands
 W
WDatana ministra, the yellownecked caterpillar, is a moth of the family Notodontidae. It is found in southern Canada and the United States east of the Rocky Mountains, in the south-west it ranges to California.
 W
WDolba is a monotypic moth genus in the family Sphingidae erected by Francis Walker in 1856. Its only species, Dolba hyloeus, the pawpaw sphinx, was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It ranges throughout the eastern United States from Maine south to Florida, and west to Wisconsin, eastern Oklahoma, and southern Texas.
 W
WEacles imperialis, the imperial moth, is a Nearctic member of the family Saturniidae and subfamily Ceratocampinae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773.
 W
WEphyriades arcas, the Caribbean duskywing, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Central America and the Caribbean, the type specimen being described from Saint Kitts.
 W
WEpimecis scolopaiae is a species of moth in the family Geometridae, subfamily Ennominae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Jamaica.
 W
WErebus hieroglyphica is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found from the Oriental tropical countries such as India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Japan, China, Taiwan, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, Philippines, Malaysia, Singapore, and Korea. The habitat consist of lowland forests.
 W
WEstigmene acrea, the salt marsh moth or acrea moth, is a moth in the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in North America, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Colombia and Mexico.
 W
WEuchaetes egle, the milkweed tiger moth or milkweed tussock moth, is a moth in the family Erebidae and the tribe Arctiini, the tiger moths. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is a common mid- through late-summer feeder on milkweeds and dogbane. Like most species in this family, it has chemical defenses it acquires from its host plants, in this case, cardiac glycosides. These are retained in adults and deter bats, and presumably other predators, from feeding on them. Only very high cardiac glycoside concentrations deterred bats, however. Adults indicate their unpalatability with clicks from their tymbal organs.
 W
WEuglyphis rivulosa is a species of moth in the family Lasiocampidae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Suriname.
 W
WEumorpha achemon, the Achemon sphinx, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773.
 W
WThe fall webworm is a moth in the family Erebidae known principally for its larval stage, which creates the characteristic webbed nests on the tree limbs of a wide variety of hardwoods in the late summer and fall. It is considered a pest but although unsightly, does not harm otherwise healthy trees. It is well known to commercial tree services and arboriculturists.
 W
WGrammia arge, the arge moth or arge tiger moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in North America from Quebec and Maine to Florida, West to New Mexico, North to North Dakota and Ontario.
 W
WGrammia figurata, the figured tiger moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in North America from southern Ontario and New Hampshire south to Georgia and west to Colorado and Texas.
 W
WGrammia phyllira, the phyllira tiger moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in North America from Quebec and New England south to Florida and west to Texas, Colorado and Alberta. The habitat consists of dry, open woodland and grassland. The species is listed as endangered in Connecticut.
 W
WHorama plumipes is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in southern Texas, Mexico, Honduras, Belize, Guatemala and Nicaragua.
 W
WHyalurga vinosa is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found on Saint Kitts, Antigua, Jamaica and the Dominican Republic.
 W
WHypocrita pylotis is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in Honduras.
 W
WImbrasia epimethea is a species of moth belonging to the family Saturniidae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from the Calabar coast.
 W
WLetis hercyna is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Jamaica.
 W
WLycomorpha pholus, the black-and-yellow lichen moth, is a moth in the family Erebidae. It is found in North America from Nova Scotia to North Carolina, west to South Dakota and Texas. The habitat consists of short-grass prairie.
 W
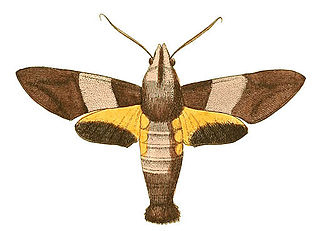
WMacroglossum passalus, the black-based hummingbird hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is known from Sri Lanka, India, Thailand, south-eastern China, Taiwan, southern Japan, Indonesia and the Philippines.
 W
WManduca brontes is a species of moth in the family Sphingidae first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is known from Jamaica, Cuba, Haiti, Puerto Rico, the Cayman Islands, the Dominican Republic and Suriname.
 W
WPachypasa otus is a moth of the family Lasiocampidae first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in southern Europe, Asia Minor, Armenia, Iraq, Iran and Israel.
 W
WPaonias astylus, the huckleberry sphinx, is a moth in the family Sphingidae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in eastern North America, from Maine south to Florida, west to Missouri and Mississippi.
 W
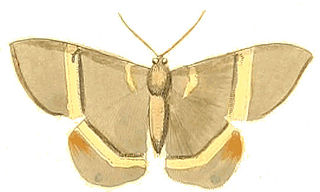
WPhrygionis argentata is a species of moth in the family Geometridae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Jamaica.
 W
WPidorus glaucopis is a moth of the family Zygaenidae. It is found in Nepal, northern India, Indochina, the Malay Peninsula, Korea and Japan.
 W
WPitthea famula is a species of moth in the family Geometridae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Calabar, in what is now Nigeria. It is found in Angola, Benin, Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea (Bioko), Nigeria, Sierra Leone and Zambia.
 W
WSamia cynthia, the ailanthus silkmoth, is a saturniid moth, used to produce silk fabric but not as domesticated as the silkworm, Bombyx mori. The moth has very large wings of 113–125 mm (4.4–4.9 in), with a quarter-moon shaped spot on both the upper and lower wings, whitish and yellow stripes and brown background. There are eyespots on the outer forewings. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773.
 W
WStemorrhages sericea, the large emerald pearl, is a moth of the subfamily of Spilomelinae within the family Crambidae. It lives throughout Africa south of the Sahara, and the Indian Ocean islands of Réunion, Madagascar, Mauritius and the Comoros.
 W
WTheretra clotho, the common hunter hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It is found from Sri Lanka, India, Nepal and Myanmar, east through China to Taiwan, South Korea and Japan, and then south-east through South East Asia as far as the Lesser Sunda Islands and Timor in Indonesia. An uncommon migrant may be found up to northern China. The habitat consists of open forests, forest edges, orchards, plantations, wooded scrubs, suburban gardens and city parks.
 W
WTheretra nessus, the yam hawk moth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773.
 W
WTifama is a monotypic moth genus in the family Notodontidae erected by Francis Walker in 1855. Its only species, Tifama chera, was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. The species is known from Suriname and Brazil.
 W
WTrichura coarctata is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in Brazil.
 W
WUrola nivalis, the snowy urola moth, is a moth of the family Crambidae. It is found from southern Canada and Maine, south to Florida and west to Illinois and Texas.
 W
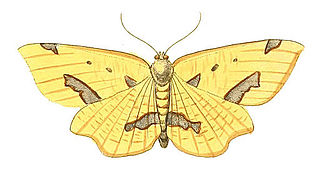
WXanthotype sospeta, the crocus geometer, is a species of moth in the family Geometridae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Jamaica. It is also found in North America, where it has been recorded from Nova Scotia to southern British Columbia, south to Colorado and Georgia. The habitat consists of deciduous and mixedwood forests.
 W
WZale undularis, the black zale moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in the eastern United States and southern Ontario.