 W
WAnkarapithecus is a genus of extinct ape. It was probably frugivorous, and would have weighed about 27 kilograms (60 lb). Its remains were found close to Ankara in central Turkey beginning in the 1950s. It lived during the Late Miocene and was similar to Sivapithecus.
 W
WGibbons are apes in the family Hylobatidae. The family historically contained one genus, but now is split into four extant genera and 18 species. Gibbons live in subtropical and tropical rainforest from eastern Bangladesh to Northeast India to southern China and Indonesia.
 W
WKhoratpithecus is an extinct genus of pongin primates that lived during the late Miocene in Myanmar and Thailand.
 W
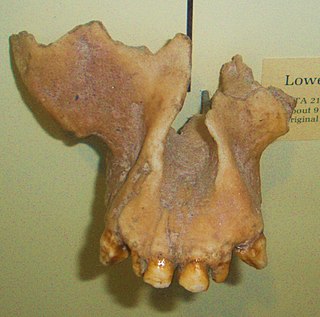
WLufengpithecus lufengensis is a prehistoric species of hominoid from the Late Miocene found in China, named after the Lufeng site and dated around 6.2 Ma. It is the latest Miocene fossil ape that has been discovered in the entire world. Some researchers believe that genus Lufengpithecus could be an ancestor to African apes and hominids.
 W
WMesopithecus is an extinct genus of Old World monkey that lived in Europe and Asia 7 to 5 million years ago. Mesopithecus resembled a modern macaque, with a body length of about 40 centimetres (16 in). It was adapted to both walking and climbing, possessing a slender body with long, muscular limbs and flexible fingers. Its teeth suggest that it primarily ate soft leaves and fruit. It was once thought that these extinct monkeys might be an ancestor of the grey langur, but a more recent study suggests that they are more closely related to the snub-nosed monkeys and doucs.
 W
WOuranopithecus is a genus of extinct Eurasian great ape represented by two species, Ouranopithecus macedoniensis, a late Miocene hominoid from Greece and Ouranopithecus turkae, also from the late Miocene of Turkey.
 W
WSivapithecus is a genus of extinct apes. Fossil remains of animals now assigned to this genus, dated from 12.2 million years old in the Miocene, have been found since the 19th century in the Siwalik Hills of the Indian subcontinent as well as in Kutch. Any one of the species in this genus may have been the ancestor to the modern orangutans.