 W
WMotion sickness occurs due to a difference between actual and expected motion. Symptoms commonly include nausea, vomiting, cold sweat, headache, sleepiness, yawning, loss of appetite, and increased salivation. Complications may rarely include dehydration, electrolyte problems, or a lower esophageal tear.
 W
WA sickness bag is a small bag commonly provided to passengers on board airplanes and boats to collect and contain vomit in the event of motion sickness. Hovercraft-ferry operators and even train companies have also been known to furnish bags. People who know they are prone to motion sickness will sometimes bring their own bags.
 W
WThe Barany chair or Bárány chair, named for Hungarian physiologist Robert Bárány, is a device used for aerospace physiology training, particularly for student pilots.
 W
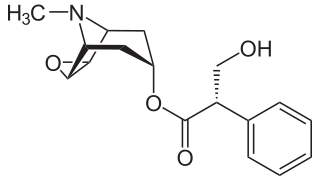
WDimenhydrinate, marketed as Draminate, Dramamine and Gravol among others, is an over-the-counter drug used to treat motion sickness and nausea. Dimenhydrinate is a combination drug of diphenhydramine and 8-Chlorotheophylline.
 W
WHyoscine, also known as scopolamine, is a medication used to treat motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. It is also sometimes used before surgery to decrease saliva. When used by injection, effects begin after about 20 minutes and last for up to 8 hours. It may also be used by mouth and as a transdermal patch.
 W
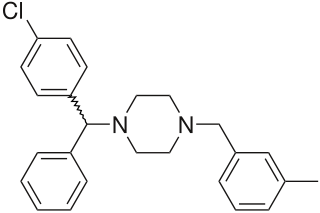
WMeclizine, sold under the brand names Bonine among others, is an antihistamine used to treat motion sickness and the feeling like the world is spinning (vertigo). It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin in an hour and last for up to a day.
 W
WSpace adaptation syndrome (SAS) or space sickness is a condition experienced by as many as half of all space travelers during their adaptation to weightlessness once in orbit. It is the opposite of terrestrial motion sickness since it occurs when the environment and the person appear visually to be in motion relative to one another even though there is no corresponding sensation of bodily movement originating from the vestibular system.