 W
WAmantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended due to drug resistance. It acts as a nicotinic antagonist and noncompetitive NMDA antagonist. The antiviral mechanism of action is antagonism of the influenzavirus A M2 proton channel, which prevents endosomal escape.
 W
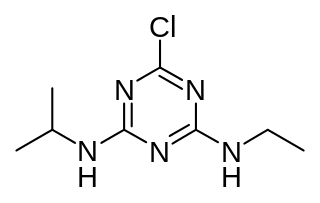
WAtrazine is a herbicide of the triazine class. It is used to prevent pre-emergence broadleaf weeds in crops such as maize (corn) and sugarcane and on turf, such as golf courses and residential lawns. Atrazine's primary manufacturer is Syngenta and it is one of the most widely used herbicides in US and Australian agriculture.
 W
WCyanazine is a herbicide that belongs to the group of triazines. Cyanazine inhibits photosynthesis and is therefore used as a herbicide.
 W
WDepleted uranium is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope U-235 than natural uranium. Natural uranium contains about 0.72% U-235, while the DU used by the U.S. Department of Defense contains 0.3% U-235 or less. The less radioactive and non-fissile uranium-238 constitutes the main component of depleted uranium. Uses of DU take advantage of its very high density of 19.1 g/cm3.
 W
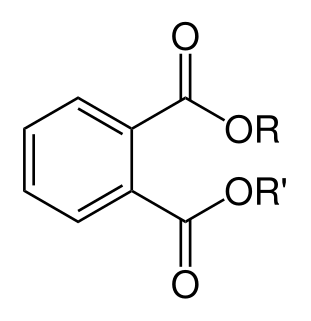
WPhthalates, or phthalate esters, are esters of phthalic anhydride. They are mainly used as plasticizers, i.e., substances added to plastics to increase their flexibility, transparency, durability, and longevity. They are used primarily to soften polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
 W
WRimantadine is an orally administered antiviral drug used to treat, and in rare cases prevent, influenzavirus A infection. When taken within one to two days of developing symptoms, rimantadine can shorten the duration and moderate the severity of influenza. Both rimantadine and the similar drug amantadine are derivates of adamantane. Rimantadine was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1994.
 W
WYtterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. However, like the other lanthanides, its most common oxidation state is +3, as in its oxide, halides, and other compounds. In aqueous solution, like compounds of other late lanthanides, soluble ytterbium compounds form complexes with nine water molecules. Because of its closed-shell electron configuration, its density and melting and boiling points differ significantly from those of most other lanthanides.