 W
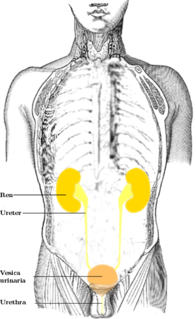
WThe kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about 12 centimetres in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder.
 W
WCalcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalate with the chemical formula CaC2O4·(H2O)x, where x varies from 0 to 3. All forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The rarer dihydrate (mineral: weddellite) and trihydrate (mineral: caoxite) are also recognized. Calcium oxalates are a major constituent of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries.
 W
WCostovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness is pain that results from touching the region inside of the costovertebral angle. The CVA is formed by the 12th rib and the spine. Assessing for CVA tenderness is part of the abdominal exam, and CVA tenderness indicates kidney pathology.
 W
WMadin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells are a model mammalian cell line used in biomedical research. MDCK cells are used for a wide variety of cell biology studies including cell polarity, cell-cell adhesions, collective cell motility, as well as responses to growth factors. It is one of few cell culture models that is suited for 3D cell culture and multicellular rearrangements known as branching morphogenesis.
 W
WThe mesonephros is one of three excretory organs that develop in vertebrates. It serves as the main excretory organ of aquatic vertebrates and as a temporary kidney in reptiles, birds, and mammals. The mesonephros is included in the Wolffian body after Caspar Friedrich Wolff who described it in 1759.
 W
WThe opisthonephros is the functional adult kidney in lampreys (cyclostomes), most fishes, and amphibians. It is formed from the extended mesonephros along with tubules from the posterior nephric ridge. The functional embryonic kidney in anamniotes is the pronephros.
 W
WThe renal plexus is formed by filaments from the celiac ganglia and plexus, aorticorenal ganglia, lower thoracic splanchnic nerves and first lumbar splanchnic nerve and aortic plexus.
 W
WThe ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the human adult, the ureters are usually 20–30 cm (8–12 in) long and around 3–4 mm (0.12–0.16 in) in diameter. The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epithelium, and has an additional smooth muscle layer in third closest to the bladder that assists with peristalsis.