 W
WClione limacina, known as the naked sea butterfly, sea angel, and common clione, is a sea angel found from the surface to greater than 500 m (1,600 ft) depth. It lives in the Arctic Ocean and cold regions of the North Atlantic Ocean. It was first described by Friderich Martens in 1676 and became the first gymnosomatous "pteropod" to be described.
 W
WThe ivory gull is a small gull, the only species in the genus Pagophila. It breeds in the high Arctic and has a circumpolar distribution through Greenland, northernmost North America, and Eurasia.
 W
WLimacina helicina is a species of small swimming planktonic sea snail in the family Limacinidae, which belong to the group commonly known as sea butterflies (Thecosomata).
 W
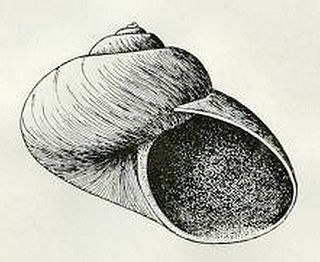
WMargarites helicinus, common name the helicina margarite or spiral margarite, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae.
 W
WThe ivory gull is a small gull, the only species in the genus Pagophila. It breeds in the high Arctic and has a circumpolar distribution through Greenland, northernmost North America, and Eurasia.
 W
WThe polar bear is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear species, as well as the largest extant land carnivore. A boar weighs around 350–700 kg (770–1,540 lb), while a sow is about half that size. Although it is the sister species of the brown bear, it has evolved to occupy a narrower ecological niche, with many body characteristics adapted for cold temperatures, for moving across snow, ice and open water, and for hunting seals, which make up most of its diet. Although most polar bears are born on land, they spend most of their time on the sea ice. Their scientific name means "maritime bear" and derives from this fact. Polar bears hunt their preferred food of seals from the edge of sea ice, often living off fat reserves when no sea ice is present. Because of their dependence on the sea ice, polar bears are classified as marine mammals.
 W
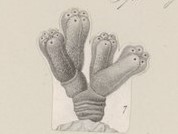
WSynoicum is a genus of colonial sea squirts, tunicates in the family Polyclinidae.
 W
WThe polar bear is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear species, as well as the largest extant land carnivore. A boar weighs around 350–700 kg (770–1,540 lb), while a sow is about half that size. Although it is the sister species of the brown bear, it has evolved to occupy a narrower ecological niche, with many body characteristics adapted for cold temperatures, for moving across snow, ice and open water, and for hunting seals, which make up most of its diet. Although most polar bears are born on land, they spend most of their time on the sea ice. Their scientific name means "maritime bear" and derives from this fact. Polar bears hunt their preferred food of seals from the edge of sea ice, often living off fat reserves when no sea ice is present. Because of their dependence on the sea ice, polar bears are classified as marine mammals.