 W
WHyblaeidae are the "teak moths", a family of insects in the Lepidopteran order. The two genera with about 18 species make up one of the two families of the Hyblaeoidea superfamily, which in the past has been included in the Pyraloidea. Recent phylogenetic studies find varying relationships of Hyblaeoidea among Ditrysian Lepidoptera: Mutanen et al. (2010) find the superfamily to group either with Pyraloidea, or – more often – with Thyridoidea or butterflies. The results of Wahlberg et al. (2013) and Heikilä et al. (2015) indicate a sister-group relationship with Pyraloidea.
 W
WHyblaea is a genus of moths of the family Hyblaeidae first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1793.
 W
WHyblaea constellata is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found in India, Sri Lanka, south-east Asia, including China, Japan, Taiwan, Myanmar and Thailand. It is also found in Queensland, Australia.
 W
WHyblaea firmamentum is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by Achille Guenée in 1852.
 W
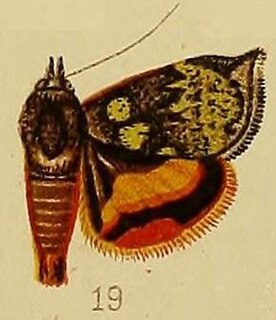
WHyblaea flavifasciata is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by George Hampson in 1910.
 W
WHyblaea flavipicta is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by George Hampson in 1910.
 W
WHyblaea ibidias is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae. It is found in New South Wales, Australia.
 W
WHyblaea puera, the teak defoliator, is a moth and cryptic species complex native to South Asia and South-east Asia. It was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1777. The species has also been recently reported to be present in Central America and Africa. The caterpillar feeds on teak and other trees. It is considered to be one of the major teak pests around the world.
Hyblaea xanthia is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by George Hampson in 1910. It is found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Katanga), the Seychelles (Aldabra), South Africa and Zambia.