 W
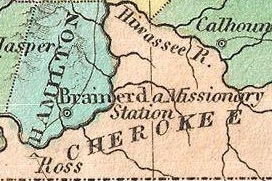
WCherokee removal, part of the Trail of Tears, refers to the forced relocation between 1836 and 1839 of an estimated 16,000 members of the Cherokee Nation and 1,000-2,000 of their slaves; from their lands in Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Alabama to the Indian Territory in the then Western United States, and the resultant deaths along the way and at the end of the movement of an estimated 4,000 Cherokee and unknown number of slaves.
 W
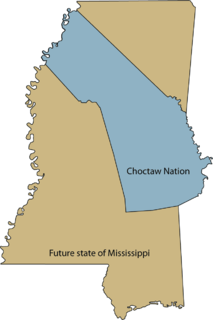
WThe Choctaw Trail of Tears was the attempted ethnic cleansing and relocation by the United States government of the Choctaw Nation from their country, referred to now as the Deep South, to lands west of the Mississippi River in Indian Territory in the 1830s by the United States government. A Choctaw miko (chief) was quoted by the Arkansas Gazette as saying that the removal was a "trail of tears and death." Since removal, the Choctaw have developed since the 20th century as three federally recognized tribes: the largest, the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma; the Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, and the Jena Band of Choctaw Indians in Louisiana.
 W
WIndian removal was a forced migration in the 19th century whereby Native Americans were forced by the United States government to leave their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi River, specifically to a designated Indian Territory. The Indian Removal Act, the key law that forced the removal of the Indians, was signed by Andrew Jackson in 1830. Jackson took a hard line on Indian removal, but the law was put into effect primarily under the Martin van Buren administration.
 W
WThe Native American Removal Act was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States President Andrew Jackson. The law authorized the president to negotiate with southern Native American tribes for their removal to federal territory west of the Mississippi River in exchange for white settlement of their ancestral lands. The act has been referred to as a unitary act of systematic genocide, because it discriminated against an ethnic group in so far as to make certain the death of vast numbers of its population. The Act was signed by Andrew Jackson and it was strongly enforced under his administration and that of Martin Van Buren, which extended until 1841.
 W
WIndian removals in Indiana followed a series of the land cession treaties made between 1795 and 1846 that led to the removal of most of the native tribes from Indiana. Some of the removals occurred prior to 1830, but most took place between 1830 and 1846. The Lenape (Delaware), Piankashaw, Kickapoo, Wea, and Shawnee were removed in the 1820s and 1830s, but the Potawatomi and Miami removals in the 1830s and 1840s were more gradual and incomplete, and not all of Indiana's Native Americans voluntarily left the state. The most well-known resistance effort in Indiana was the forced removal of Chief Menominee and his Yellow River band of Potawatomi in what became known as the Potawatomi Trail of Death in 1838, in which 859 Potawatomi were removed to Kansas and at least forty died on the journey west. The Miami were the last to be removed from Indiana, but tribal leaders delayed the process until 1846. Many of the Miami were permitted to remain on land allotments guaranteed to them under the Treaty of St. Mary's (1818) and subsequent treaties.
 W
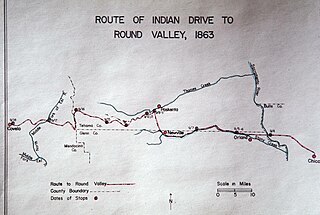
WThe Nome Cult Trail is a northern Californian historic trail located in present-day Mendocino National Forest which goes along Round Valley Road and through Rocky Ridge and the Sacramento Valley. It is also known as the Konkow Trail of Tears. On 28 August 1863 all Konkow Maidu were to be at the Bidwell Ranch in Chico to be taken to the Round Valley Reservation at Covelo in Mendocino County. Any Indians remaining in the area were to be shot. 435 Maidu were rounded up and marched under guard west out of the Sacramento Valley and through to the Coastal Range. 461 Native Americans started the trek, 277 finished. They reached Round Valley on 18 September 1863.
 W
WThe Long Walk of the Navajo, also called the Long Walk to Bosque Redondo, refers to the 1864 deportation and attempted ethnic cleansing of the Navajo people by the United States federal government. Navajos were forced to walk from their land in what is now Arizona to eastern New Mexico. Some 53 different forced marches occurred between August 1864 and the end of 1866. Some anthropologists claim that the "collective trauma of the Long Walk...is critical to contemporary Navajos' sense of identity as a people".
 W
WThe Nome Cult Trail is a northern Californian historic trail located in present-day Mendocino National Forest which goes along Round Valley Road and through Rocky Ridge and the Sacramento Valley. It is also known as the Konkow Trail of Tears. On 28 August 1863 all Konkow Maidu were to be at the Bidwell Ranch in Chico to be taken to the Round Valley Reservation at Covelo in Mendocino County. Any Indians remaining in the area were to be shot. 435 Maidu were rounded up and marched under guard west out of the Sacramento Valley and through to the Coastal Range. 461 Native Americans started the trek, 277 finished. They reached Round Valley on 18 September 1863.
 W
WThe Potawatomi Trail of Death was the forced removal by militia in 1838 of some 859 members of the Potawatomi nation from Indiana to reservation lands in what is now eastern Kansas. The march began at Twin Lakes, Indiana on September 4, 1838, and ended on November 4, 1838, along the western bank of the Osage River, near present-day Osawatomie, Kansas. During the journey of approximately 660 miles (1,060 km) over 61 days, more than 40 persons died, most of them children. It marked the single largest Indian removal in Indiana history.
 W
WThe Trail of Tears was part of a series of forced relocations of approximately 100,000 Native Americans between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government known as the Indian removal. Members of the Cherokee, Muscogee (Creek), Seminole, Chickasaw, and Choctaw nations were forcibly removed from their ancestral homelands in the Southeastern United States to areas to the west of the Mississippi River that had been designated 'Indian Territory'. The forced relocations were carried out by government authorities after the passage of the Indian Removal Act in 1830. The Cherokee removal in 1838 was brought on by the discovery of gold near Dahlonega, Georgia in 1828, resulting in the Georgia Gold Rush.
 W
WThe Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek was a treaty signed on September 27, 1830, and proclaimed on February 24, 1831, between the Choctaw American Indian tribe and the United States Government. This was the first removal treaty carried into effect under the Indian Removal Act. The treaty ceded about 11 million acres (45,000 km2) of the Choctaw Nation in what is now Mississippi in exchange for about 15 million acres (61,000 km2) in the Indian territory, now the state of Oklahoma. The principal Choctaw negotiators were Chief Greenwood LeFlore, Musholatubbee, and Nittucachee; the U.S. negotiators were Colonel John Coffee and Secretary of War John Eaton.
 W
WThe Yavapai Wars, or the Tonto Wars, were a series of armed conflicts between the Yavapai and Tonto tribes against the United States in Arizona. The period began no later than 1861, with the arrival of American settlers on Yavapai and Tonto land. At the time, the Yavapai were considered a band of the Western Apache people due to their close relationship with tribes such as the Tonto and Pinal. The war culminated with the Yavapai's removal from the Camp Verde Reservation to San Carlos on February 27, 1875, an event now known as Exodus Day.