 W
WAncient history as a term refers to the aggregate of past events from the beginning of writing and recorded human history and extending as far as post-classical history. The phrase may be used either to refer to the period of time or the academic discipline.
 W
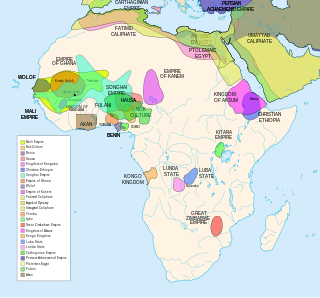
WThe history of Africa begins with the emergence of hominids, archaic humans and—at least 200,000 years ago—anatomically modern humans, in East Africa, and continues unbroken into the present as a patchwork of diverse and politically developing nation states. The earliest known recorded history arose in Ancient Egypt, and later in Nubia, the Sahel, the Maghreb and the Horn of Africa.
 W
WEfforts to achieve independence from Seleucid rule Was an opportunity for people to own land again as a sovereign state that we have been on this historical period Rvbhrvyym great resurrection. Alymayyan emerged that his predecessors were undoubtedly many instances follows Nyakanyshan occurred in the territory they once again, the power must be separated from the land Nyakanyshan. Alymayyan common language between the two languages, one of which is a mountainous region, and the other belongs to the plains. "Henning believes that the population of New Alymayy mountain dialect spoke Aramaic dialect of the Plain". General rule Alymayyan the year 187 BC. CE. Ntykhvs beginning to end with the defeat of the Third Party persisted. According to studies during the years 145-147 BC Numismatics. CE. Openly in the Khuzestan region Rvbhrvyym Alymayyan independence.
 W
WThe ancient universities are British and Irish medieval universities and early modern universities founded before the year 1600. Four of these are located in Scotland, two in England, and one in Ireland. The ancient universities in Britain and Ireland are amongst the oldest extant universities in the world.
 W
WAncient Warfare is a glossy Dutch bi-monthly military history magazine.
 W
WAssyria, also called the Assyrian Empire, was a Mesopotamian kingdom and empire of the ancient Near East in the area today known as the Levant that existed as a state from perhaps as early as the 25th century BC until its collapse between 612 BC and 609 BC – spanning the periods of the Early to Middle Bronze Age through to the late Iron Age. This vast span of time is divided into the Early Period, Old Assyrian Empire, Middle Assyrian Empire and Neo-Assyrian Empire.
 W
WThe Canary Islands have been known since antiquity. Until the Spanish colonization between 1402 and 1496, the Canaries were populated by an indigenous population, whose origin is still the subject of discussion among historians and linguists.
 W
WClash of the Gods is a one-hour weekly mythology television series that premiered on August 3, 2009 on the History channel. The program covers many of the ancient Greek and Norse Gods, monsters and heroes including Hades, Hercules, Medusa, Minotaur, Odysseus and Zeus.
 W
WEpigraphia 3D is a scientific project that consists in 3D models of ancient inscriptions. Its scope includes scientific research, education in epigraphy, and encouraging interest of the general public.
 W
WHellenistic Greece is the period between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the annexation of the classical Greek Achaean League heartlands by the Roman Republic. This culminated at the Battle of Corinth in 146 BC, a crushing Roman victory in the Peloponnese that led to the destruction of Corinth and ushered in the period of Roman Greece. Hellenistic Greece's definitive end was with the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, when the future emperor Augustus defeated Greek Ptolemaic queen Cleopatra VII and Mark Antony, the next year taking over Alexandria, the last great center of Hellenistic Greece.
 W
WHistorical ports may be found where ancient civilizations have developed maritime trade.
 W
WThe Iron Age is an archaeological age, the last of the three-age system of Old World prehistory. It follows the Bronze Age, in the Ancient Near East beginning c. 1200 BC, and in Europe beginning after c. 800 BC. It is taken to end with the beginning of Classical Antiquity, in about the 6th century BC, although in Northern Europe, the Germanic Iron Age is taken to last until the beginning of the Viking Age, c. AD 800.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Larantuka was a kingdom in present-day East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. It was the one of the few, if not the only, indigenous Roman Catholic polities in the territory of modern Indonesia. Acting as a tributary state of the Portuguese Crown, the Raja (King) of Larantuka controlled holdings on the islands of Flores, Solor, Adonara and Lembata. It was later purchased by Dutch East Indies from the Portuguese, prior to its annexation in 1904.
 W
WMacedonia, also called Macedon, was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south.
 W
WIn historiography, ancient Rome is Roman civilization from the founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD, encompassing the Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic and Roman Empire until the fall of the western empire. The civilisation began as an Italic settlement in the Italian Peninsula, traditionally dated to 753 BC, that grew into the city of Rome and which subsequently gave its name to the empire over which it ruled and to the widespread civilisation the empire developed. The civilization was led and ruled by the Romans, alternately considered an ethnic group or a nationality. The Roman Empire expanded to become one of the largest empires in the ancient world, still ruled from the city, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants and covering 5 million square kilometres at its height in AD 117.
 W
WVarious lists of the Seven Wonders of Romania have been compiled from past to the present day, to catalogue Romania's most spectacular manmade structures.
 W
WThe Seven Wonders of the World or the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World is a list of remarkable constructions of classical antiquity given by various authors in guidebooks or poems popular among ancient Hellenic tourists. Although the list, in its current form, did not stabilise until the Renaissance, the first such lists of seven wonders date from the 2nd–1st century BC. The original list inspired innumerable versions through the ages, often listing seven entries. Of the original Seven Wonders, only one—the Great Pyramid of Giza, oldest of the ancient wonders—remains relatively intact. The Colossus of Rhodes, the Lighthouse of Alexandria, the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, the Temple of Artemis and the Statue of Zeus were all destroyed. The location and ultimate fate of the Hanging Gardens are unknown, and there is speculation that they may not have existed at all.
 W
WTitulus is a term used for the labels or captions naming figures or subjects in art, which were commonly added in classical and medieval art, and remain conventional in Eastern Orthodox icons. In particular the term describes the conventional inscriptions on stone that listed the honours of an individual or that identified boundaries in the Roman Empire. A titulus pictus is a merchant's mark or other commercial inscription.
 W
WVarious lists of the Wonders of the World have been compiled from antiquity to the present day, to catalogue the world's most spectacular natural wonders and human-built structures.