 W
WVitalism is the belief that "living organisms are fundamentally different from non-living entities because they contain some non-physical element or are governed by different principles than are inanimate things". Where vitalism explicitly invokes a vital principle, that element is often referred to as the "vital spark", "energy" or "élan vital", which some equate with the soul. In the 18th and 19th centuries vitalism was discussed among biologists, between those who felt that the known mechanics of physics would eventually explain the difference between life and non-life and vitalists who argued that the processes of life could not be reduced to a mechanistic process. Some vitalist biologists proposed testable hypotheses meant to show inadequacies with mechanistic explanations, but these experiments failed to provide support for vitalism. Biologists now consider vitalism in this sense to have been refuted by empirical evidence, and hence regard it either as a superseded scientific theory, or, since the mid-20th century, as a pseudoscience.
 W
WThe ancient Egyptians believed that a soul was made up of many parts. In addition to these components of the soul, there was the human body.
 W
WAse or ashe is a West African philosophical concept through which the Yoruba of Nigeria conceive the power to make things happen and produce change. It is given by Olodumare to everything — gods, ancestors, spirits, humans, animals, plants, rocks, rivers, and voiced words such as songs, prayers, praises, curses, or even everyday conversation. Existence, according to Yoruba thought, is dependent upon it.
 W
WAccording to spiritual beliefs, an aura or human energy field is a colored emanation said to enclose a human body or any animal or object. In some esoteric positions, the aura is described as a subtle body. Psychics and holistic medicine practitioners often claim to have the ability to see the size, color and type of vibration of an aura.
 W
WChakra are various focal points used in a variety of ancient meditation practices, collectively denominated as Tantra, or the esoteric or inner traditions of Hinduism.
 W
WThe etheric body, ether-body, æther body, a name given by neo-Theosophy to a vital body or subtle body propounded in esoteric philosophies as the first or lowest layer in the "human energy field" or aura. It is said to be in immediate contact with the physical body, to sustain it and connect it with "higher" bodies.
 W
WThe search for a hypothetical soul and its location have been a subject of much speculation throughout history. In early medicine and anatomy, the location of the soul was hypothesized to be physically located within the body. Aristotle and Plato understood the soul as a corporeal form but closely related to the physical world. The Hippocratic Corpus chronicles the evolution of thought that the soul is located within the body and is manifested in diseased conditions. Later, Galen explicitly used Plato's description of the corporeal soul to physical locations in the body. The logical (λογιστικός) in the brain, the spirited (θυμοειδές) in the heart, and the appetitive (ἐπιθυμητικόν) in the liver. Da Vinci had a similar approach to Galen, locating the soul, or ssenso comune, as well as the imprensiva (intellect) and memoria (memory) in different ventricles of the brain. Today neuroscientists and other fields of science that deal with the body and the mind, such as psychology, bridge the gap between what is physical and what is corporeal.
 W
WHylozoism is the philosophical point of view that matter is in some sense alive. The concept dates back at least as far as the Milesian school of pre-Socratic philosophers. The term was coined by the English philosopher Ralph Cudworth in 1678.
 W
WIn Hinduism, Kundalini is a form of divine feminine energy believed to be located at the base of the spine, in the muladhara. It is an important concept in Śhaiva Tantra, where it is believed to be a force or power associated with the divine feminine or the formless aspect of the Goddess. This energy in the body, when cultivated and awakened through tantric practice, is believed to lead to spiritual liberation. Kuṇḍalinī is associated with Parvati or Adi Parashakti, the supreme being in Shaktism; and with the goddesses Bhairavi and Kubjika. The term, along with practices associated with it, was adopted into Hatha yoga in the 9th century. It has since then been adopted into other forms of Hinduism as well as modern spirituality and New age thought.
 W
WAccording to Turkic belief, Kut, is a kind of force vitalizing the body. Through Kut, humans are connected with the heavens. When Kut ends, the person dies. Further, the sacred ruler is believed to be endowed with much more Kut than other people, thus the heaven would had appointing him as the legitimate ruler. Turkic Khagans claimed that they were "heaven-like, heaven-conceived" and possessed qut, a sign of the heavenly mandate to rule. Rulers of the Uyghur Khaganate were entitled "idiqut", meaning "sacred good fortune". The word "suu" is the Mongolian equivalent of Kut. It was believed that if the ruler had lost his qut, he could be dethroned and killed. However, this had to be carried out without shedding his blood. This was usually done by strangulation with a silk cord. This custom of strangling continued among the Ottomans.
 W
WManitou, akin to the Iroquois orenda, is the spiritual and fundamental life force among Algonquian groups in the Native American theology. It is omnipresent and manifests everywhere: organisms, the environment, events, etc. Aashaa monetoo means "good spirit", while otshee monetoo means "bad spirit". When the world was created, the Great Spirit, Aasha Monetoo, gave the land to the indigenous peoples, the Shawnee in particular.
 W
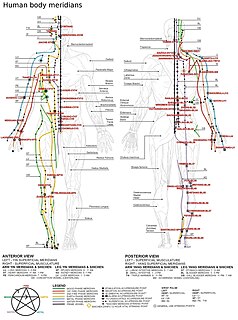
WThe meridian system is a concept in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Meridians are paths through which the life-energy known as "qi" flows.
 W
WNaturopathy or naturopathic medicine is a form of alternative medicine that employs an array of pseudoscientific practices branded as "natural", "non-invasive", or promoting "self-healing". The ideology and methods of naturopathy are based on vitalism and folk medicine, rather than evidence-based medicine (EBM). Naturopathic practitioners generally recommend against following modern medical practices, including but not limited to medical testing, drugs, vaccinations, and surgery. Instead, naturopathic practice relies on unscientific notions, often leading naturopaths to diagnoses and treatments that have no factual merit.
 W
WNumen, pl. numina, is a Latin term for "divinity", or a "divine presence", "divine will." The Latin authors defined it as follows: Cicero writes of a "divine mind", a god "whose numen everything obeys," and a "divine power" "which pervades the lives of men." It causes the motions and cries of birds during augury. In Virgil's recounting of the blinding of the one-eyed giant, Polyphemus, from the Odyssey, in his Aeneid, he has Odysseus and his men first "ask for the assistance of the great numina". Reviewing public opinion of Augustus on the day of his funeral, the historian Tacitus reports that some thought "no honor was left to the gods" when he "established the cult of himself" "with temples and the effigies of numina". Pliny the younger in a letter to Paternus raves about the "power," the "dignity," and "the majesty;" in short, the "numen of history." Lucretius uses the expression numen mentis, or "bidding of the mind," where "bidding" is numen, not, however, the divine numen, unless the mind is to be considered divine, but as simply human will.
 W
WThe Odic force is the name given in the mid-19th century to a hypothetical vital energy or life force by Baron Carl von Reichenbach. Von Reichenbach coined the name from that of the Norse god Odin in 1845. The study of Odic force is called odology.
 W
WOrgone is a pseudoscientific concept variously described as an esoteric energy or hypothetical universal life force. Originally proposed in the 1930s by Wilhelm Reich, and developed by Reich's student Charles Kelley after Reich's death in 1957, orgone was conceived as the anti-entropic principle of the universe, a creative substratum in all of nature comparable to Mesmer's animal magnetism (1779), to the Odic force (1845) of Carl Reichenbach and to Henri Bergson's élan vital (1907). Orgone was seen as a massless, omnipresent substance, similar to luminiferous aether, but more closely associated with living energy than with inert matter. It could allegedly coalesce to create organization on all scales, from the smallest microscopic units—called "bions" in orgone theory—to macroscopic structures like organisms, clouds, or even galaxies.
 W
WOrthogenesis, also known as orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution, evolutionary progress, or progressionism, is the biological hypothesis that organisms have an innate tendency to evolve in a definite direction towards some goal (teleology) due to some internal mechanism or "driving force". According to the theory, the largest-scale trends in evolution have an absolute goal such as increasing biological complexity. Prominent historical figures who have championed some form of evolutionary progress include Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, Pierre Teilhard de Chardin, and Henri Bergson.
 W
WIn traditional Chinese culture, qi or ch'i is believed to be a vital force forming part of any living entity. Qi translates as "air" and figuratively as "material energy", "life force", or "energy flow". Qi is the central underlying principle in Chinese traditional medicine and in Chinese martial arts. The practice of cultivating and balancing qi is called qigong.
 W
WA subtle body is one of a series of psycho-spiritual constituents of living beings, according to various esoteric, occult, and mystical teachings. According to such beliefs each subtle body corresponds to a subtle plane of existence, in a hierarchy or great chain of being that culminates in the physical form.
 W
WIn chiropractic, a vertebral subluxation means pressure on nerves, abnormal functions creating a lesion in some portion of the body, either in its action, or makeup, not necessarily visible on X-rays.