 W
WThe Burmese–Siamese War (1568–1569) was a military conflict fought between the Kingdom of Ayutthaya (Siam) and the Kingdom of Burma. The war began in 1568 when Ayutthaya unsuccessfully attacked Phitsanulok, a Burmese vassal state. The event was followed by a Burmese intervention which resulted in the 2 August 1569 defeat of Ayutthaya, which became a Burmese vassal state. Burma then moved towards Lan Xang, occupying the country for a short period of time until retreating in 1570.
 W
WChenla or Zhenla is the Chinese designation for the successor polity of the Kingdom of Funan preceding the Khmer Empire that existed from around the late sixth to the early ninth century in Indochina. The name was still used in the 13th century by the Chinese envoy Zhou Daguan, author of The Customs of Cambodia. It appears on the Mao Kun map. However, modern historiography applies the name exclusively to the period from the late 6th to the early ninth century. It is dubious if "Chenla" ever existed as a unitary kingdom or if this is a misconception by Chinese chronists. Most modern historians assert that "Chenla" was in fact just a series of loose and temporary confederations of principalities.
 W
WĐèo Văn Trị also known as his Lao name Cam Oum, was the White Tai leader at Muang Lay in the Sip Song Chau Tai or Federation of the Twelve Tai states, of the Tai Dam people.
 W
WFrench Indochina, officially known as the Indochinese Union from 1887 and the Indochinese Federation after 1947, was a grouping of French colonial territories in Southeast Asia until its demise in 1954. It comprised three Vietnamese regions of Tonkin in the north, Annam in the centre, and Cochinchina in the south, Cambodia, Laos and the Chinese territory of Guangzhouwan. The capital for most of its history (1902–45) was Hanoi; Saigon was the capital from 1887 to 1902 and again from 1945 to 54.
 W
WThe French protectorate of Laos was a French protectorate in Southeast Asia of what is today Laos between 1893 and 1953—with a brief interregnum as a Japanese puppet state in 1945—which constituted part of French Indochina. It was established over the Siamese vassal, the Kingdom of Luang Phrabang, following the Franco-Siamese War in 1893. It was integrated into French Indochina and in the following years further Siamese vassals, the Principality of Phuan and Kingdom of Champasak, were annexed into it in 1899 and 1904, respectively.
 W
WThe House of Champassak or the Na Champassak family was an important Lao royal house, descendants of Chao Yuttithammathon, the 11th King of the Kingdom of Champassak whose prominent members include Prince Boun Oum Na Champassak and Prince Sisouk na Champassak. It was the ruling house of the former Kingdom of Champassak, with territories reaching on both banks of the Mekong river.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Champasak or Bassac, (1713–1904) was a Lao kingdom under Nokasad, a grandson of King Sourigna Vongsa, the last king of Lan Xang; and son-in-law of the Cambodian King Chey Chettha IV. Bassac and the neighboring principalities of Attapeu and Stung Treng emerged as power centers under what was later to be described as the Mandala Southeast Asian political model.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Luang Phrabang was formed in 1707 as a result of the split of the Kingdom of Lan Xang. When The kingdom split, Muang Phuan became a tributary state of Luang Prabang. Then as the years passed, the monarchy weakened even more, that it was forced to become a vassal various times to the Burmese and the Siamese monarchies.
 W
WKingdom of Vientiane was formed in 1707 as a result of the split of the Kingdom of Lan Xang. The kingdom was a Burmese vassal from 1765 to 1778. It then became a Siamese vassal until 1828 when it was annexed by Siam.
 W
WLan Chang Province was a former province of the Kingdom of Thailand. It encompassed the eastern slopes of the Luang Prabang Range in Laos, with Xaignabouli (Sainyabuli) as the administrative headquarters. It included parts of former the Luang Prabang and Xaignabouli provinces of French Laos.
 W
WThe Lao Kingdom of Lan Xang Hom Khao existed as a unified kingdom from 1353 to 1707.
 W
WThe Lao Royal Family was the ruling family of the Kingdom of Laos from 1904 to 1975 and the group of close relatives of the monarch of the Kingdom of Laos. King Sisavang Vong was the founder of the modern family, consisting of a number of persons in the Lao Royal Dynasty of the Khun Lo, who are related to the King of Laos, who are entitled to royal titles, and some of whom performed various official engagements on behalf of the Royal Family and ceremonial duties of State when the Kingdom existed. The Lao Royals are now based in France, where they work to achieve a change of government in Laos.
 W
WThe Laotian Civil War (1959–1975) was a civil war in Laos fought between the Communist Pathet Lao and the Royal Lao Government from 23 May 1959 to 2 December 1975. It is associated with the Cambodian Civil War and the Vietnam War, with both sides receiving heavy external support in a proxy war between the global Cold War superpowers. It is called the Secret War among the CIA Special Activities Center and Hmong veterans of the conflict.
 W
WCaptain Kong Le was a paratrooper in the Royal Lao Army. He led the premier unit of the Royal Lao Army, 2ème bataillon de parachutistes, which campaigned relentlessly during 1959 and 1960. The idealistic young American-trained Lao Theung officer became known worldwide when on 10 August 1960 he and his mutinous paratroopers overthrew the Royal Lao Government in a coup d'état. He declared he aimed at an end to government corruption; to the shock of American officials, he declared U.S. policies were responsible for the ongoing fraud.
 W
WThe Lao People's Democratic Republic is the modern state derived from the final Kingdom of Laos. The political source of Lao history and cultural identity is the Tai kingdom of Lan Xang, which during its apogee emerged as one of the largest kingdoms in Southeast Asia. Lao history is filled with frequent conflict and warfare, but infrequent scholarly attention. The resulting dates and references are approximate, and rely on source material from court chronicles which survived both war and neglect, or outside sources from competing neighboring kingdoms in what are now China, Vietnam, Burma, Thailand, and Cambodia.
 W
WMuang Phuan or Xieng Khouang was a historical principality on the Xiangkhoang Plateau, which constitutes the modern territory of Xiangkhouang Province, Laos.
 W
WThe Pathet Lao was a communist political movement and organization in Laos, formed in the mid-20th century. The group was ultimately successful in assuming political power in 1975, after the Laotian Civil War. The Pathet Lao were always closely associated with Vietnamese communists. During the civil war, it was effectively organized, equipped and even led by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN). They fought against the anti-communist forces in the Vietnam War. Eventually, the term became the generic name for Laotian communists.
 W
WThe Rattanakosin Kingdom is the fourth and present kingdom in the history of Thailand. It was founded in 1782 with the establishment of Rattanakosin as the capital city. This article covers the period until the Siamese revolution of 1932.
 W
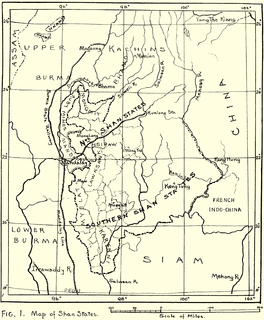
WThe Shan States (1885–1948) were a collection of minor Shan kingdoms called muang whose rulers bore the title saopha in British Burma. They were analogous to the princely states of British India.
 W
WThe Sip Song Chau Tai was a confederation of Tai Dam, Tai Dón and Tai Daeng chiefdoms in the mountainous north-west of today's Vietnam, dating back at least to the 17th century.
 W
WOperation Tailwind was a covert incursion by a small unit of United States Army and allied Montagnard forces into southeastern Laos during the Vietnam War, conducted from 11 to 14 September 1970. Its purpose was to create a diversion for a Royal Lao Army offensive and to exert pressure on the occupation forces of the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN). A company-sized element of US Army Special Forces and Montagnard commando of the Military Assistance Command, Vietnam Studies and Observations Group conducted the operation.
 W
WThe Vang Tao Incident occurred on 3 July 2000, when a group of armed insurgents and mercenaries attacked a Lao customs outpost at the southern border town of Vang Tao. The raiders, as they came to be described, were easily routed leaving six of their own dead and 27 were arrested by Thai authorities. Of those, 11 were Thai nationals.