 W
WBeyond Boundaries: Religion, Region, Language and the State is a project funded by the European Research Council with research carried out at the British Museum, the British Library, SOAS, University of London, and Leiden University. The leading researchers are Dr. Michael Willis, Dr. Sam van Schaik, Dr. Nathan W. Hill and Dr. Peter Bisschop. The project was one of thirteen synergy grants awarded in 2013 and the only synergy grant in the humanities for that year. The project will run from 2014 to 2020.
 W
WThis is a bibliography of notable works about India.
 W
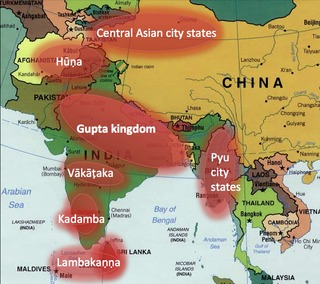
WSIDDHAM or the Asia Inscriptions Database is an open-access resource for the study of inscriptions from Asia. SIDDHAM was established by the European Research Council with start-up funding from the project Beyond Boundaries: Religion, Region, Language and the State. The first focus of SIDDHAM was Sanskrit epigraphy, mainly of the fourth, fifth and sixth centuries CE, but the platform is designed to accommodate inscriptions from all periods and regions. The corpus is vast: in South Asia alone, the estimated number of historic inscriptions is 90,000.
Airyanem Vaejah is the homeland of the early Iranians and a reference in the Zoroastrian Avesta to one of Ahura Mazda's "sixteen perfect lands". Its actual location remains uncertain.
 W
WThe American Institute of Indian Studies (AIIS), founded in 1961, is a consortium of 87 universities and colleges in the United States that promotes the advancement of knowledge about India in the U.S. It carries out this purpose by: awarding fellowships to scholars and artists to carry out their research and artistic projects in India; by operating intensive programs in a variety of Indian languages in India; by sponsoring conferences, workshops and outreach activities; by supporting U.S. study abroad and service learning programs in India; by assisting and facilitating the research of all U.S. scholars in India; and by operating two research archives, the Archives and Research Center for Ethnomusicology and the Center for Art and Archaeology. The AIIS is a member of the Council of American Overseas Research Centers.
 W
WThe Anthology of Indian Classical Music – A Tribute to Alain Daniélou is the 1997 edition of Alain Danielou's Anthology of Indian Classical Music.
 W
WThe Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute (BORI) is located in Pune, Maharashtra, India. It was founded on 6 July 1917 and named after Ramakrishna Gopal Bhandarkar (1837–1925), long regarded as the founder of Indology (Orientalism) in India. The institute is well known for its collection of old Sanskrit and Prakrit manuscripts.
 W
WBharatiya Jnanpith a literary and research organization, based in New Delhi, India, was founded on February 18, 1944 by Sahu Shanti Prasad Jain of the Sahu Jain family and his wife Rama Jain to undertake systematic research and publication of Sanskrit, Prakrit, Pali and Apabhramsha texts and covering subjects like religion, philosophy, logic, ethics, grammar, astrology, poetics, etc.
 W
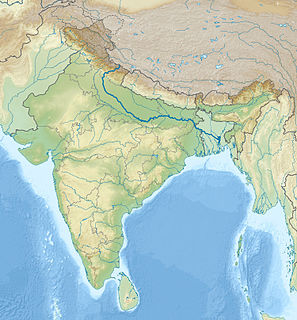
WGanges is one of the main rivers of India and the largest in northern India. In India, specially the Hindu people consider the river as an embodiment of sacredness. Numerous books in English and other Indian languages have been written on the river which deal with its religious, geographical and other aspects.
 W
WHindi Granth Karyalay is an Indian publishing house and specialized book store dealing in books pertaining to Jainology and Indology in English, Hindi, Sanskrit, Prakrit and Apabhramsha. It was established in Mumbai, India in 1912 by its founder Nathuram Premi. It publishes and distributes serials, monographs, and scholarly publications on Indian religions, philosophy, history, culture, arts, architecture, archaeology, language, literature, linguistics, musicology, mysticism, yoga, tantra, occult, medicine, astronomy, astrology and other related subjects, and to date have published over 100 works of noted Indian and International authors and scholars.
 W
WThe Hindus: An Alternative History is a book by American Indologist Wendy Doniger which the author describes as an "alternative to the narrative of Hindu history that they tell". The book was initially published by Viking Penguin in 2009 and later in India by Penguin's Indian subsidiary, Penguin India.
 W
WColonel Sir Thomas Hungerford Holdich was an English geographer and president of the Royal Geographical Society. He is best known as Superintendent of Frontier Surveys in British India and author of numerous books, including The Gates of India, The Countries of the King's Award and Political Frontiers and Boundary Making.
 W
WThis is a bibliography of notable works about Varanasi.
 W
WThe Indian Institute in central Oxford, England, is at the north end of Catte Street on the corner with Holywell Street and facing down Broad Street from the east. Sir Monier Monier-Williams started the Institute in the University of Oxford in 1883 to provide training for the Indian Civil Service of the British Raj.
 W
WIndigenous Aryans, also known as the Out of India theory (OIT), is the idea that the Aryans are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent, and that the Indo-European languages radiated out from a homeland in India into their present locations. Reflecting traditional Indian views based on the Puranic chronology, the indigenist view proposes an older date than is generally accepted for the Vedic period, and argues that the Indus Valley Civilization was a Vedic civilization. In this view, "the Indian civilization must be viewed as an unbroken tradition that goes back to the earliest period of the Sindhu-Sarasvati tradition ." It is presented as an alternative to the established migration model, which proposes the Pontic steppe as the area of origin of the Indo-European languages.
 W
WThe National Mission for Manuscripts (NAMAMI) is an autonomous organisation under Ministry of Culture, Government of India, established to survey, locate and conserve Indian manuscripts, with an aim to create national resource base for manuscripts, for enhancing their access, awareness and use for educational purposes. The Mission was initiated in February 2003, by the Ministry of Tourism and Culture, Government of India and Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) is the nodal agency for the execution of this project. It creates bibliographic databases of Indian manuscripts and is involved in the conservation and preservation of the manuscripts.
 W
WThe Oriental Research Institute & Manuscripts Library, University of Kerala, is one of the leading centres of Indology in India. It is located at Kariavattom, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala. The institute carry out researches on Indian language manuscripts, about 80% of which are in Sanskrit. The department is microfilming the manuscripts of certain technical subjects.
 W
WFormerly known as the Oriental Library, the Oriental Research Institute (ORI) at Mysore, India, is a research institute which collects, exhibits, edits, and publishes rare manuscripts written in various scripts like Devanagari (Sanskrit), Brahmic (Kannada), Nandinagari (Sanskrit), Grantha, Malayalam, Tigalari, etc.
 W
WBased primarily on the earliest known written references of Abhinavaupta and Al-Biruni, academics estimate the date of origin of the Bhagavata Purana to be between 800–1000 C.E.
 W
WPakistan studies curriculum is the name of a curriculum of academic research and study that encompasses the culture, demographics, geography, history, and politics of Pakistan. The subject is widely researched in and outside the country, though outside Pakistan it is typically part of a broader South Asian studies or some other wider field. Several universities in Pakistan have departments and research centers dedicated to the subject, whereas many independent research institutes carry out multidisciplinary research on Pakistan Studies. There are also a number of international organizations that are engaged in collaborative teaching, research, and exchange activities on the subject.
 W
WSindhology is a field of study and academic research that covers the history, society, culture, and literature of Sindh, a province of Pakistan. The subject was first brought into the academic circles with the establishment of the Institute of Sindhology at Sindh University in 1964. Since then, it has developed into a discipline that covers the aspects of history and archaeology from the Indus Valley Civilization to the modern Sindhi society. The subject has also received wider attention at international levels. An academic or expert who specialises in Sindhology is called a Sindhologist.
 W
WThe South Asia Institute (SAI) is an interdisciplinary center of the Ruprecht-Karls University Heidelberg, Germany for research and teaching on South Asia. It was founded in 1962 and is located on the campus in Neuenheimer Feld. Due to the close linguistic and historical ties with the South Asian subcontinent, adjacent cultural regions such as Afghanistan or Tibet are also included in the South Asia Institute.