 W
WChronology is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. It is also "the determination of the actual temporal sequence of past events".
 W
WAb urbe condita, or Anno urbis conditae, often abbreviated as AUC, is an expression used in antiquity and by classical historians to refer to a given year in Ancient Rome. In reference to the traditional year of the foundation of Rome, the year 1 BC would be written AUC 753, whereas 1 AD would be AUC 754. The foundation of the Roman Empire in 27 BC would be AUC 727.
 W
WThe chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Comparing many records pieces together a relative chronology relating dates in cities over a wide area. For the first millennium BC, the relative chronology can be matched to actual calendar years by identifying significant astronomical events. An inscription from the tenth year of Assyrian king Ashur-Dan III refers to an eclipse of the sun, and astronomical calculations among the range of plausible years date the eclipse to 15 June 763 BC. This can be corroborated by other mentions of astronomical events, and a secure absolute chronology established, tying the relative chronologies to our own calendar.
 W
WThe terms anno Domini (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term anno Domini is Medieval Latin and means "in the year of the Lord" but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", taken from the full original phrase "anno Domini nostri Jesu Christi", which translates to "in the year of our Lord Jesus Christ".
 W
WAnno Lucis is a dating system used in Masonic ceremonial or commemorative proceedings, which is equivalent to the Gregorian year plus 4000. It is similar to Anno Mundi.
 W
WThe Assyrian eclipse, also known as the Bur-Sagale eclipse, is a solar eclipse recorded in Assyrian eponym lists, most likely dating the ninth year of the reign of king Ashur-dan III. The eclipse is identified with the one that occurred on 15 June 763 BC.
 W
WThe "Azes era" starting 47/46 BCE, was named after the Indo-Scythian king, "King Azes the Great" or Azes I. As a number of inscriptions are dated in this era it is of great importance in dating the reigns of several kings and events in early Indian history.
 W
WBiblical literalist chronology is the attempt to correlate the theological dates used in the Bible with the real chronology of actual events. The Bible measures time from the date of Creation, but there is no agreement on when this was. Some of the better-known calculations include Archbishop James Ussher, who placed it in 4004 BC, Isaac Newton in 4000 BC, Martin Luther in 3961 BC, the traditional Hebrew calendar date of 3760 BC, and the traditional Greek Orthodox date, based on the Septuagint, of 5509 BC. To the foundation of the Temple of Solomon the passage of time is measured by simple addition of from the Creation; for later periods it measures time by the reigns of kings, but the data is conflicting and there is no agreement on how to resolve the problems.
 W
WA chronology of Jesus aims to establish a timeline for the events of the life of Jesus. Scholars have correlated Jewish and Greco-Roman documents and astronomical calendars with the New Testament accounts to estimate dates for the major events in Jesus's life.
 W
WThe chronology of the Bible is an elaborate system of lifespans, 'generations', and other means by which the passage of events is measured, beginning with the Genesis creation narrative. A widespread scholarly understanding is that this marks out a world cycle of 4,000 years, ending, presumably, around 164 BCE. It was theological in intent, not historical in the modern sense. It also functions as an implied prophecy, whose key lies in the identification of the final event.
 W
WThe oldest surviving Hebrew Bible manuscripts—including the Dead Sea Scrolls—date to about the 2nd century BCE (fragmentary) and some are stored at the Shrine of the Book in Jerusalem. The oldest extant complete text survives in a Greek translation called the Septuagint, dating to the 4th century CE. The oldest extant manuscripts of the vocalized Masoretic Text, date to the 9th century CE. With the exception of a few biblical sections in the Prophets, virtually no biblical text is contemporaneous with the events it describes.
 W
WThe majority of Egyptologists agree on the outline and many details of the chronology of Ancient Egypt. This scholarly consensus is the so-called Conventional Egyptian chronology, which places the beginning of the Old Kingdom in the 27th century BC, the beginning of the Middle Kingdom in the 21st century BC and the beginning of the New Kingdom in the mid-16th century BC.
 W
WA gospel harmony is an attempt to compile the canonical gospels of the Christian New Testament into a single account. This may take the form either of a single, merged narrative, or a tabular format with one column for each gospel, technically known as a synopsis, although the word harmony is often used for both.
 W
WLimmu was an Assyrian eponym. At the beginning of the reign of an Assyrian king, the limmu, an appointed royal official, would preside over the New Year festival at the capital. Each year a new limmu would be chosen. Although picked by lot, there was most likely a limited group, such as the men of the most prominent families or perhaps members of the city assembly. The Assyrians used the name of the limmu for that year to designate the year on official documents. Lists of limmus have been found accounting for every year between 892 BC and 648 BC.
 W
WThe Mesoamerican Long Count calendar is a non-repeating, vigesimal (base 20) and octodecimal (base 18) calendar used by several pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures, most notably the Maya. For this reason, it is often known as the Maya Long Count calendar. Using a modified vigesimal tally, the Long Count calendar identifies a day by counting the number of days passed since a mythical creation date that corresponds to August 11, 3114 BCE in the Proleptic Gregorian calendar. The Long Count calendar was widely used on monuments.
 W
WThe middle chronology is one chronology of the Near Eastern Bronze and Early Iron Age, which fixes the reign of Hammurabi to 1792–1750 BCE and the sack of Babylon to 1595 BCE.
 W
WThe Mierzanowice culture appeared in the area of the upper and middle basin of the Vistula, during the Early Bronze Age. It evolved from the so-called Proto-Mierzanowice cultural unit. The name of the culture comes from an eponymous site in Mierzanowice, where the cemetery was located. This entity was part of the pre-carpathian sphere epicorded cultures and it has been divided into three local groups: Samborzecka, Iwanowicka and Pleszowska. The initial phases of the culture are characterized by a small number of burials, seasonal settlements and single artifacts. The area of the Mierzanowice culture spread over from western Slovakia, through south - eastern Poland, reaching in the east the areas of the Volhynian Upland.
 W
WThe Minoan chronology dating system is a measure of the phases of the Minoan civilization. Initially established as a relative dating system by English archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans between 1900 and 1903 via pottery and artifact analysis during his excavations at Knossos on Crete, new technologies including carbon dating and DNA analysis have led to significant revisions to the date ranges.
 W
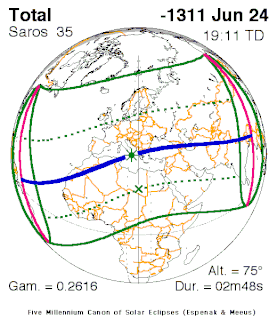
WThe solar eclipse mentioned in a text dating to the reign of Mursili II could be of great importance for the absolute chronology of the Hittite Empire within the chronology of the Ancient Near East. The text records that in the tenth year of Mursili's reign, "the Sun gave a sign", just as the king was about to launch a campaign against the Kingdom of Azzi-Hayasa in north-eastern Anatolia.
 W
WThe Oldest Dryas is a biostratigraphic subdivision layer corresponding to an abrupt cooling event, or stadial, which occurred during the last glacial retreat. The time period to which the layer corresponds varies between regions, but it is generally dated as starting at 18.5-17 ka BP and ending 15-14 ka BP. As with the Younger and Older Dryas events, the stratigraphic layer is marked by abundance of the pollen and other remains of Dryas octopetala, an indicator species that colonizes arctic-alpine regions.
 W
WPollen zones are a system of subdividing the last glacial period and Holocene paleoclimate using the data from pollen cores. The sequence provides a global chronological structure to a wide variety of researchers, such as geologists, climatologists, geographers and archaeologists, who study the physical and cultural environment of the last 15,000 years.
 W
WThe Sothic cycle or Canicular period is a period of 1,461 Egyptian civil years of 365 days each or 1,460 Julian years averaging 365¼ days each. During a Sothic cycle, the 365-day year loses enough time that the start of its year once again coincides with the heliacal rising of the star Sirius on 19 July in the Julian calendar. It is an important aspect of Egyptology, particularly with regard to reconstructions of the Egyptian calendar and its history. Astronomical records of this displacement may have been responsible for the later establishment of the more accurate Julian and Alexandrian calendars.
 W
WA timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events; a Gantt chart is a form of timeline used in project management.
 W
WThis is a timeline of events in the history of Scottish nationalism.
 W
WThe Ussher chronology is a 17th-century chronology of the history of the world formulated from a literal reading of the Old Testament by James Ussher, the Archbishop of Armagh and Primate of All Ireland. The chronology is sometimes associated with young Earth creationism, which holds that the universe was created only a few millennia ago by God as described in the first two chapters of the biblical book of Genesis. Ussher fell into disrepute in the 19th century.
 W
WThe Venus tablet of Ammisaduqa is the record of astronomical observations of Venus, as preserved in numerous cuneiform tablets dating from the first millennium BC. It is believed that this astronomical record was first compiled during the reign of King Ammisaduqa, the fourth ruler after Hammurabi. Thus, the origins of this text should probably be dated to around the mid-seventeenth century BC..